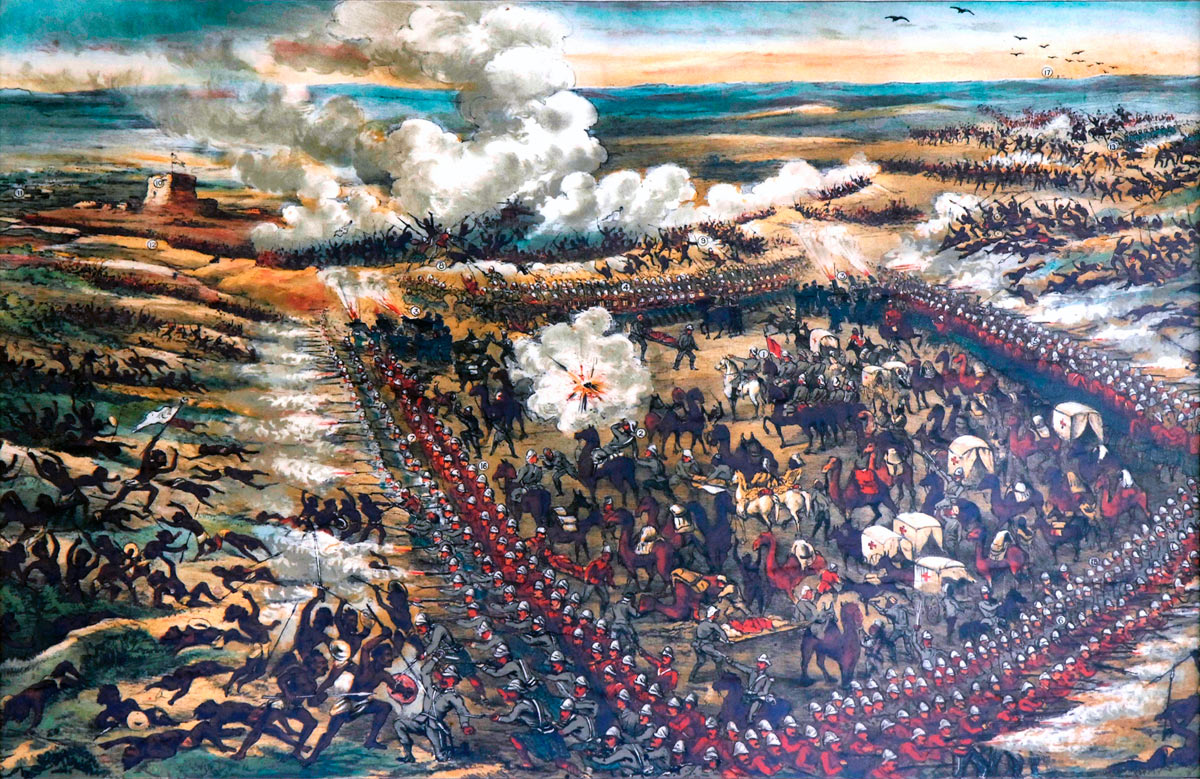
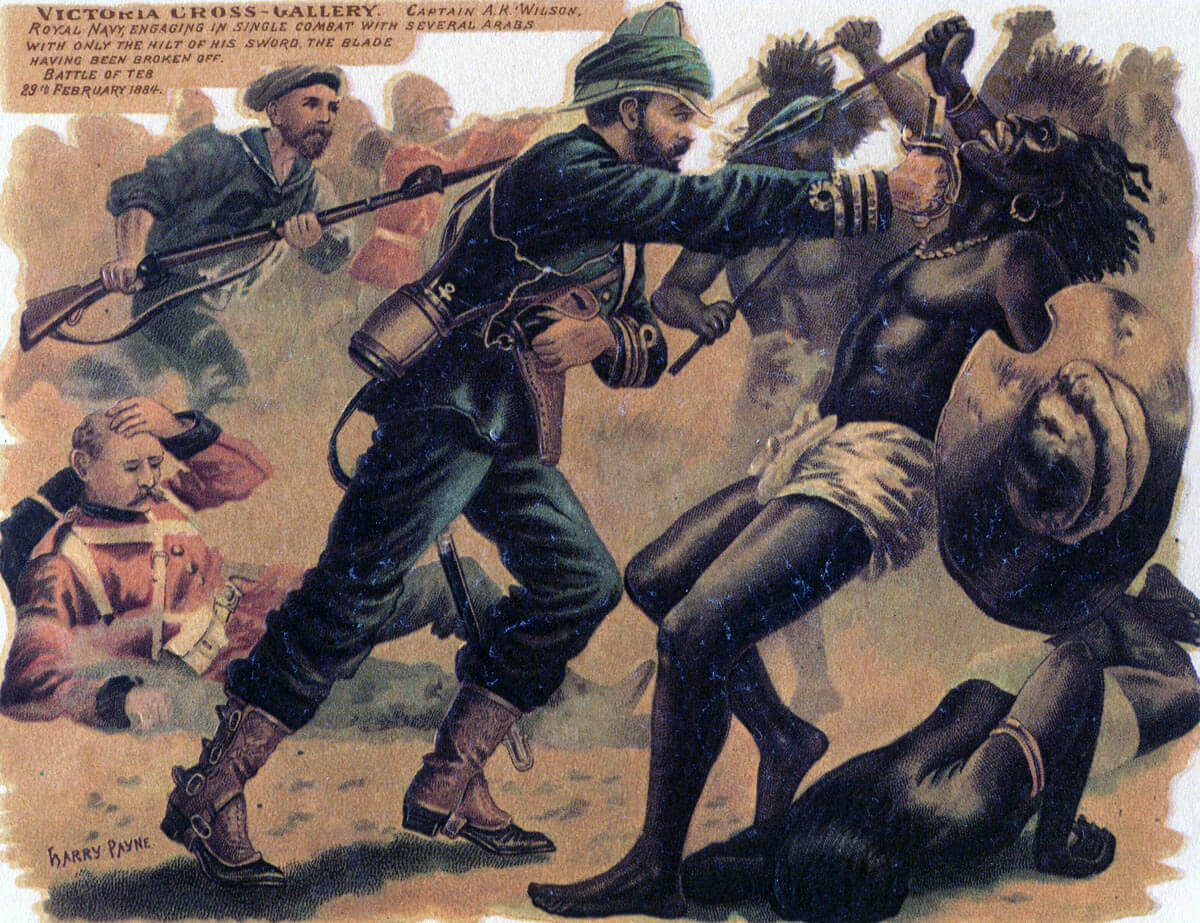
The first battle of the British army’s involvement in the Sudan, fought on 29th February 1884, using modern firearms against Islamist tribesmen armed largely with spears and swords
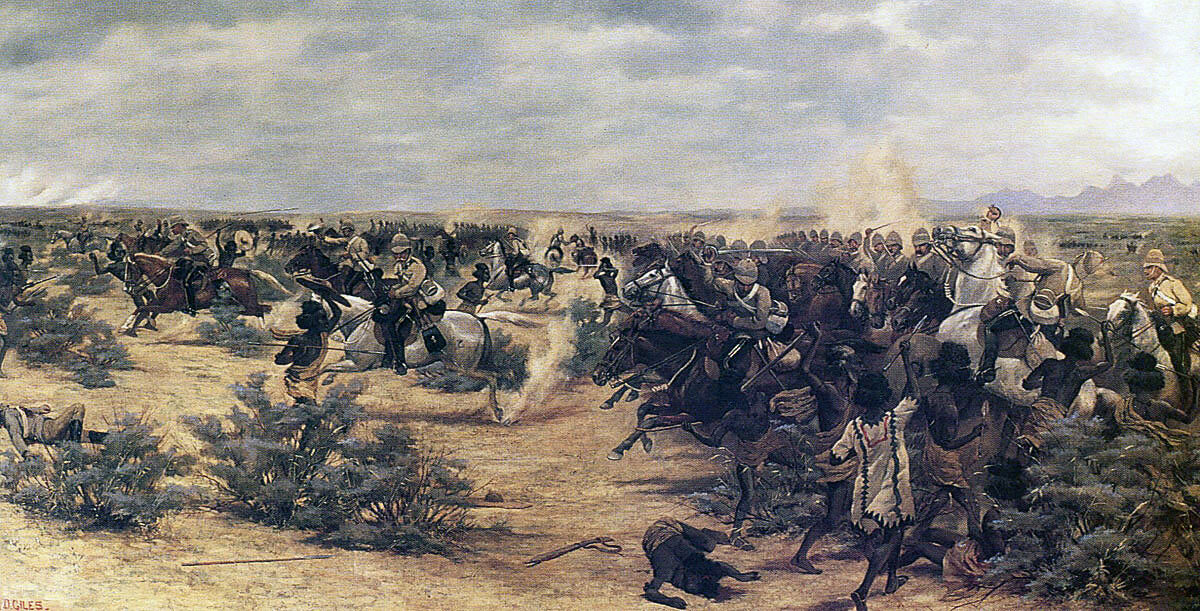

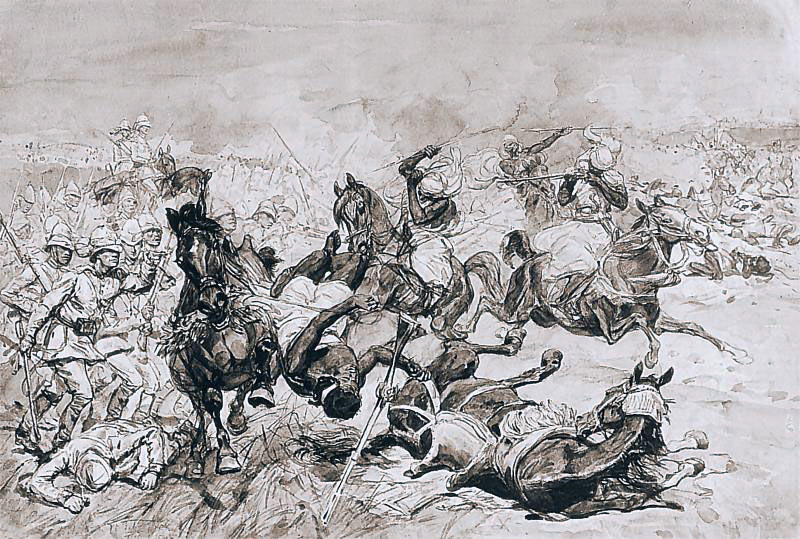
10th Hussars charging at the Battle of El Teb on 29th February 1884 in the Sudanese War: picture by Major GD Giles

Osman Digna commander of the Mahdists at the Battle of El Teb on 29th February 1884 in the Sudanese War
The previous battle of the War in Egypt and the Sudan is the Battle of Tel-el-Kebir
The next battle of the War in Egypt and the Sudan is the Battle of Tamai
To the War in Egypt and the Sudan index
Battle: El Teb
War: Sudan Campaign.
Date of the Battle of El Teb: 29th February 1884.
Place of the Battle of El Teb: The East of the Sudan near the Red Sea coast.
Combatants at the Battle of El Teb: A British Army against the Sudanese Jihadist Arabs in revolt against the Khedive of Egypt.
Commanders at the Battle of El Teb: Major General Graham commanded the British troops against the Mahdi’s lieutenant, Osman Digna.

Major General Gerald Graham VC, British Commander at the Battle of El Teb on 29th February 1884 in the Sudanese War
Size of the armies at the Battle of El Teb: British: 3,342 infantry, gunners and sappers, 864 cavalry and 28 guns. The size of the Mahdist army is unknown, but was probably in the region of 15,000 tribesmen and defected Egyptian troops.
Uniforms, arms and equipment at the Battle of El Teb: The British infantry were armed with the Martini Henry single shot breech loading rifle and bayonet. The English infantry wore khaki drill. The Highlanders wore grey jackets and kilts. All wore pith helmets. The cavalry were armed with sword and carbine.
The Mahdists fought with their traditional weapons of the sword, spear and dagger. They wore white robes patched with black cloth and fought under their characteristic black flags. There was no Mahdist cavalry.
The Mahdists also carried rifles, taken from the various Egyptian detachments they had overwhelmed. They also deployed the Khedive’s Krupp guns captured in the same way, keeping the Egyptian gunners alive to man the guns.
Winner of the Battle of El Teb: The British force.
British Regiments at the Battle of El Teb:
10th Hussars
19th Hussars
Mounted Infantry
Royal Artillery with six 7 pounders, ten mountain guns and four 9 centimetre Krupp guns.
Naval Brigade; 162 men with two 9 pounders, six Gatling and Gardiner guns.
1st Battalion Black Watch
3rd Battalion King’s Royal Rifle Corps
1st Battalion Gordon Highlanders
2nd Battalion Royal Irish Fusiliers
1st Battalion York and Lancaster Regiment
Royal Marine Light Infantry
Royal Engineers
Account of the Battle of El Teb:
Sudan, lying to the South of Egypt and bordering Abyssinia, in the 19th Century lay under the rule of the Khedive of Egypt, within the Ottoman Turkish Empire. The Muslim Arab population lived mainly along the banks of the Nile and in the eastern areas up to the shore of the Persian Gulf. To the South and West were the regions of Darfour and Kordofan, with largely African populations. Egyptian garrisons, scattered across the country, occupied the towns. The Muslim religion predominated.
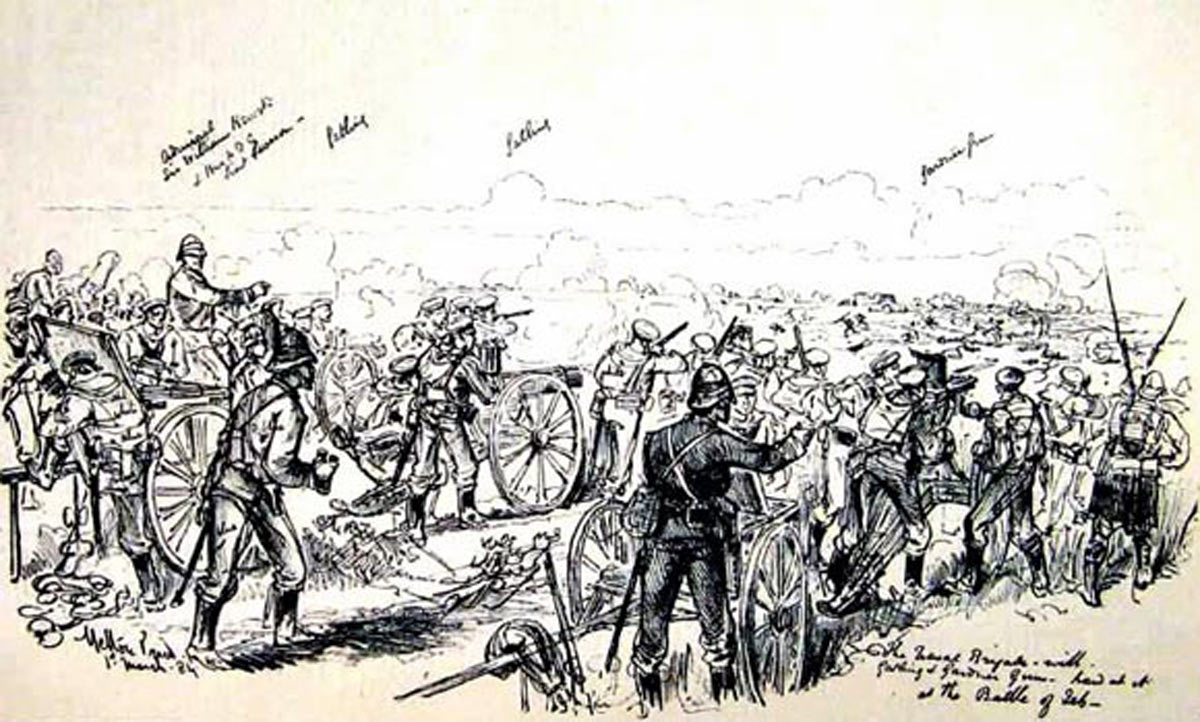

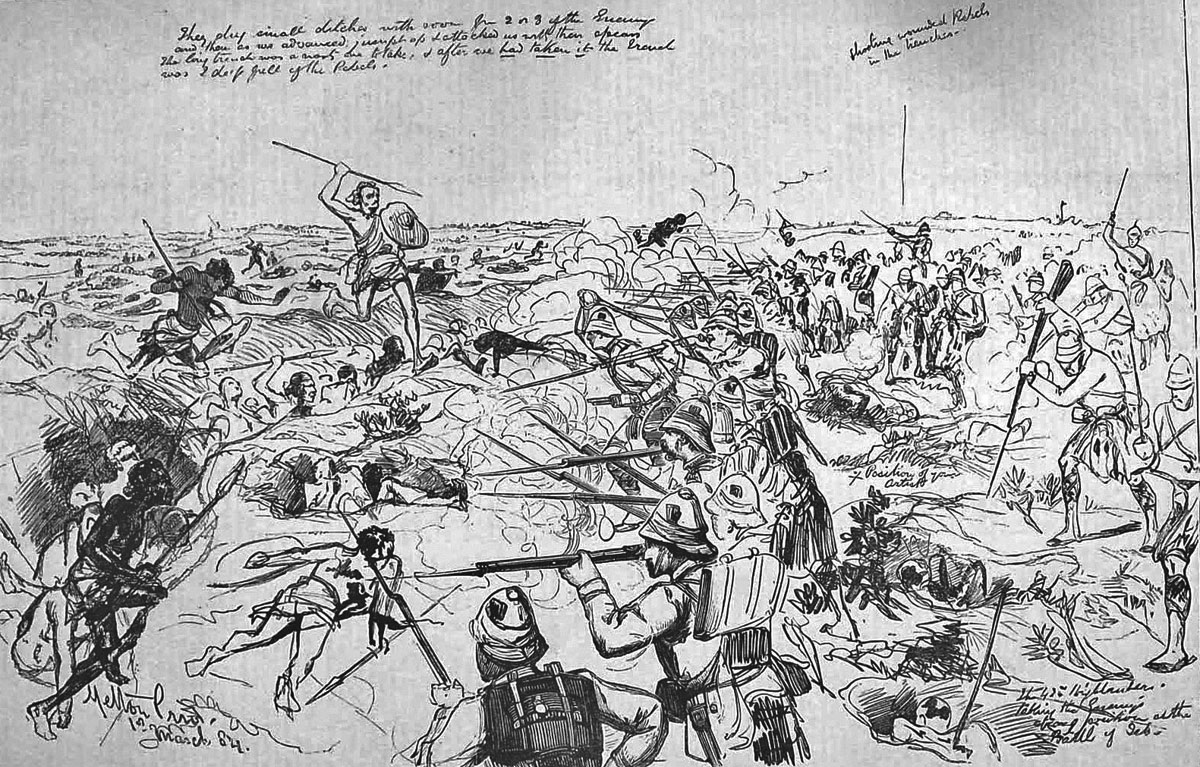
Royal Navy at the Battle of El Teb on 29th February 1884 in the Sudanese War: drawing by Melton Pryor
In 1881, a young Muslim boat builder’s apprentice, named Mohammed Ahmed, raised the standard of Jihadist revolt in the Sudan against the Khedive, proclaiming himself the ‘Mahdi’ or saviour. The revolt in the East of the Sudan was led by the Mahdi’s lieutenant, Osman Digna.
On 29th April 1883, the Mahdi’s army annihilated an Egyptian force, commanded by a retired Bombay Army officer, Colonel Hicks, at Kashgate. The remaining Egyptian garrisons, scattered across the Sudan, lay at the mercy of the Mahdi and his tribesmen.
In January 1884, a British officer, Baker Pasha, took an Egyptian force to Suakin, on the coast of the Persian Gulf, to provide cover for a withdrawal of the Egyptian garrisons in the East of the Sudan. This force was annihilated by the Mahdists at the First Battle of El Teb, a few miles inland from a port called Trinkitat. The Mahdists moved on to besiege the other garrison towns in the area held by the Egyptians. Baker survived the loss of his force.
In January 1884, at the urging of the British Government, the Khedive appointed General Charles Gordon to oversee the evacuation of the Egyptian forces from the Sudan. General Gordon had acted as Governor of the Sudan in the 1870s with considerable effect. Gordon travelled from London to Khartoum, the capital of the Sudan, arriving on 18th February 1884.
In the meanwhile, a British army, commanded by Major General Graham, was dispatched from Egypt by ship down the Persian Gulf to land at Suakin and relieve the Egyptian garrison at Tokar, 50 miles to the South of Suakin.
General Graham’s force began to arrive at Suakin on 20th February 1884, the first regiment being the 10th Hussars. Other Royal Navy ships arrived with the remaining regiments. Once assembled, the force moved down the coast by ship to the lagoon of Trinkitat, for the march to the relief of Tokar.
On 22nd February 1884, General Graham received information from a group of Egyptian soldiers that the governor of Tokar had surrendered to the Mahdi’s forces, his troops joining the rebels to avoid being massacred.
The British force moved inland, between two patches of salt marsh, to occupy a position called Fort Baker, the scene of Baker Pasha’s disaster the previous month: Colonel Baker was accompanying the British force.
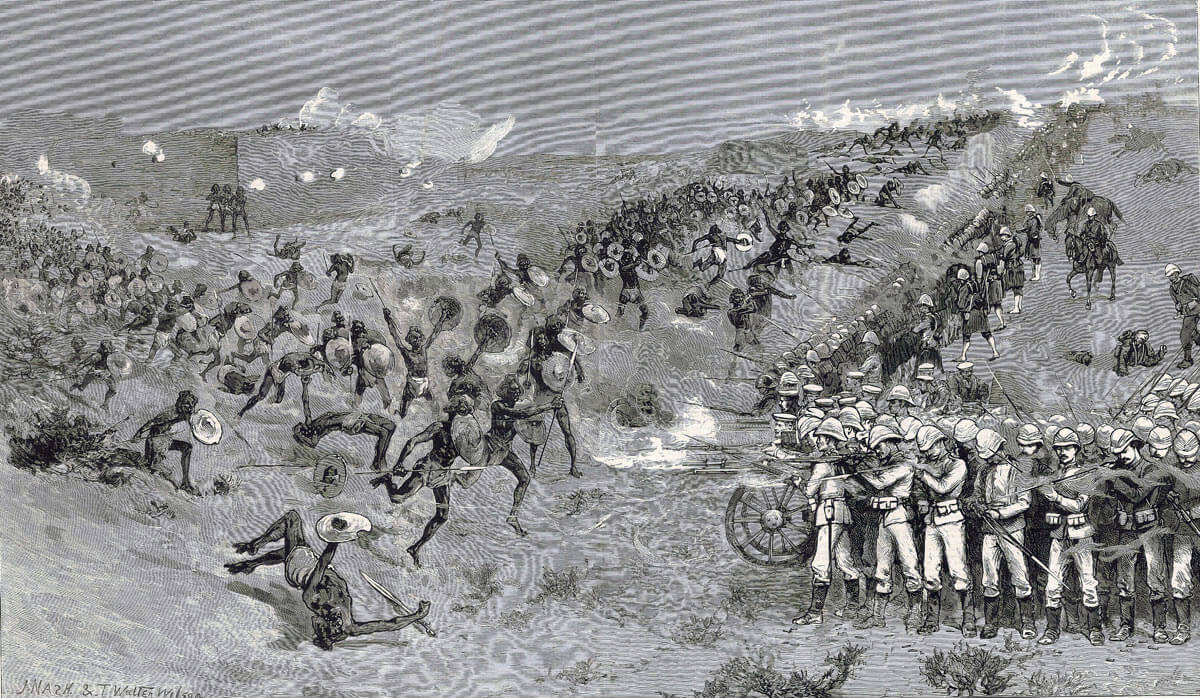

British Square at the Battle of El Teb on 29th February 1884 in the Sudanese War: drawing by A. Nash and T. Walter Wilson
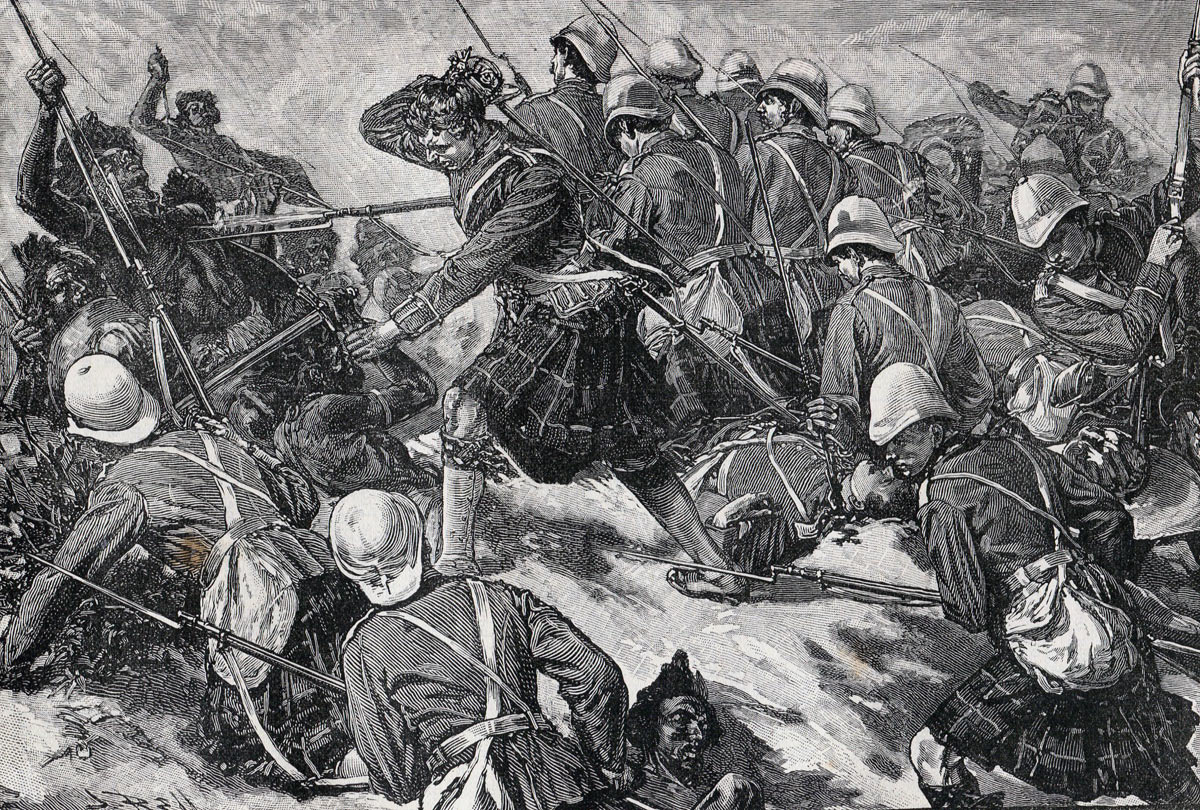
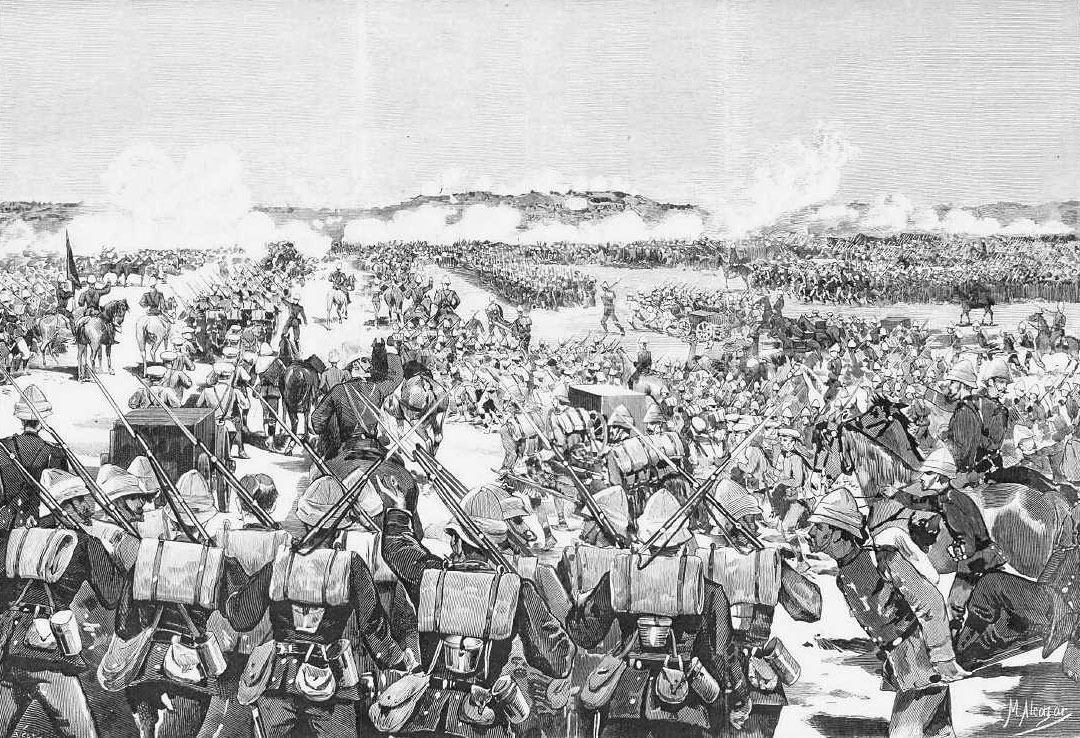
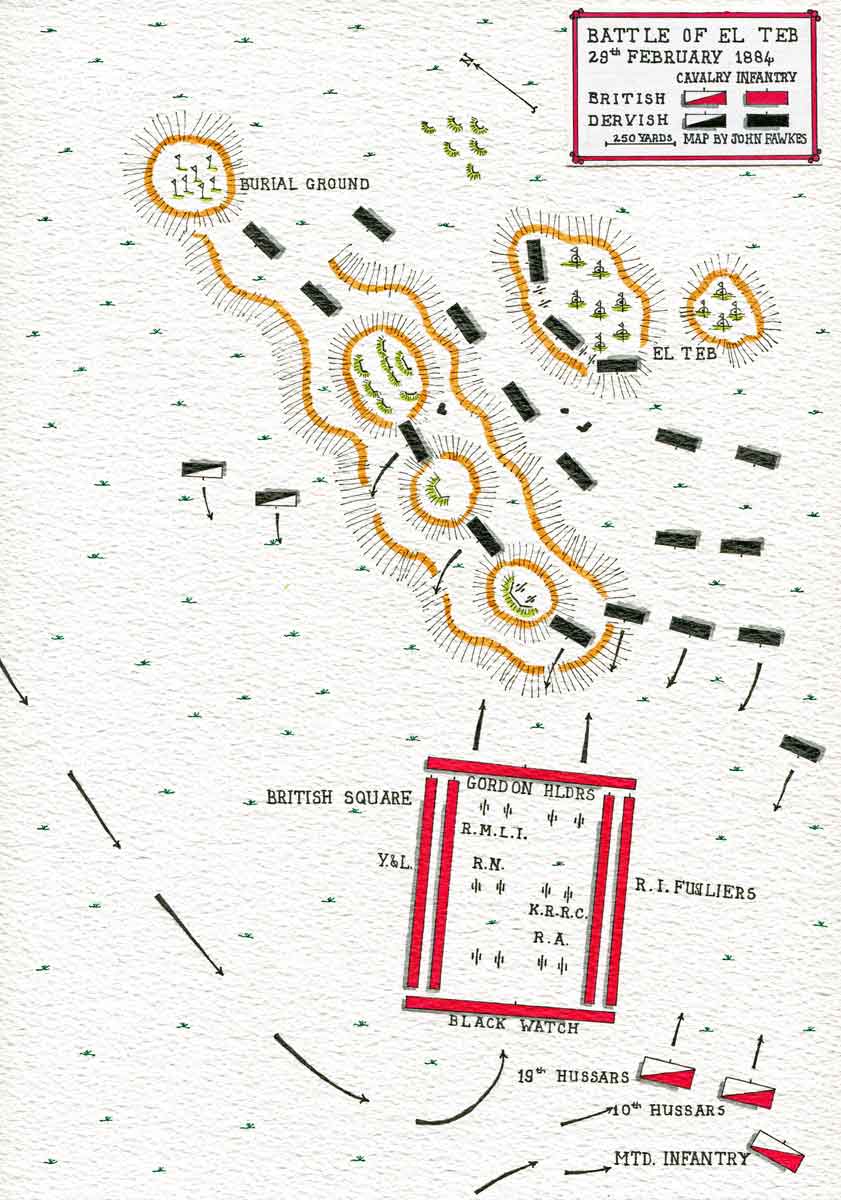
On 29th February 1884, the British infantry brigade formed a square and began the advance to the hamlet of El Teb, some 2 ½ miles inland along the track to Tokar, where Osman Digna’s Mahdists lay dug into entrenched positions.

Colonel Buller observing the Mahdists before the Battle of El Teb on 29th February 1884 in the Sudanese War
The front of the square was formed by the Gordon Highlanders and the rear by the Black Watch, both in company columns of fours at company intervals. The right flank was formed by the 2nd Royal Irish Fusiliers and 3rd King’s Royal Rifle Corps, the left flank by the 1st York and Lancaster Regiment and the detachment of Royal Marine Light Infantry, all in open column of companies. The angles of the square were filled by guns manned by Royal Artillery and Royal Navy personnel.
Colonel Buller, who won his Victoria Cross on Mount Hlobane in the Zulu War (see the Battle of Khambula), commanded the infantry brigade. The only baggage animals taken with the force carried spare ammunition. The cavalry, 10th and 19th Hussars and Mounted Infantry commanded by Colonel Stewart, followed the infantry square at a distance.
At 11.20am, the Mahdists opened rifle and artillery fire, using the small arms and Krupp guns captured from the Egyptian forces they had annihilated in the course of the revolt.
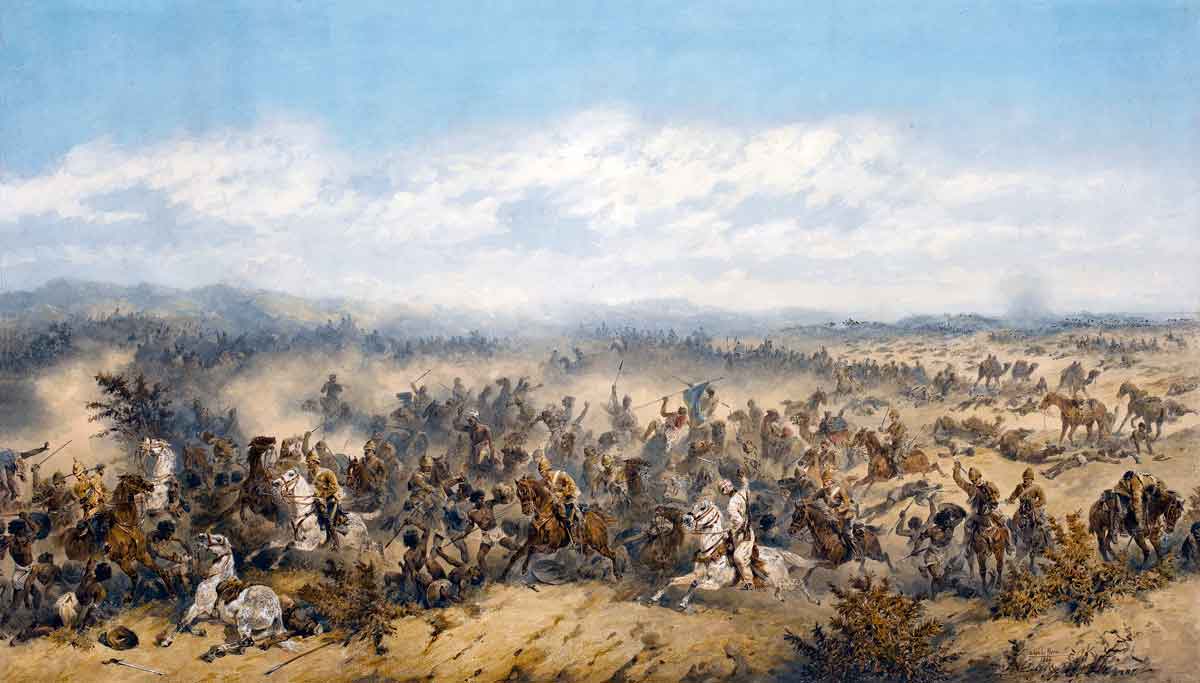

Charge of the 10th Hussars at the Battle of El Teb on 29th February 1884 in the Sudanese War: picture by Orlando Norie
The British square halted and the infantry were ordered to lie down, while the guns and machine guns fired on the Mahdists. The effect of this bombardment was to silence the Krupps. The square stood up and continued its advance under rifle fire. The British began to take casualties.
When the British square was within two hundred yards of the earthworks, the Mahdist tribesmen abandoned their firearms and charged with spears and swords. Large numbers of the tribesmen were shot down by the rifle fire of the British infantry and by the Gatling and Gardiner guns of the Naval Brigade. None broke into the British square.
Following this assault, the Mahdist tribesmen fell back and the square reformed and resumed its advance.
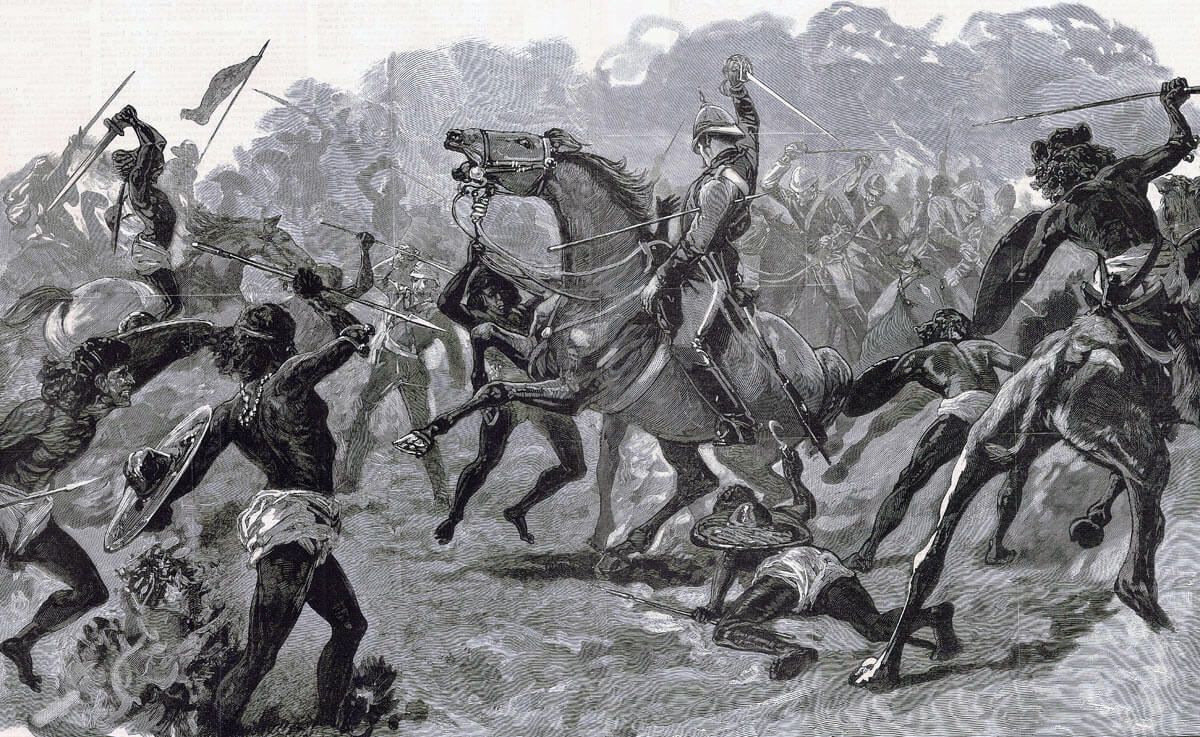

Lieutenant Colonel Barrow of the 19th Hussars wounded at the Battle of El Teb on 29th February 1884 in the Sudanese War
At this point, Colonel Stewart’s Cavalry Brigade advanced past the right flank of the square and charged the massed Mahdist tribesmen, leading to a confused struggle in the broken thorn bush covered country. The cavalry suffered heavy casualties in this scrimmage.
As the British infantry reached the Mahdist earthworks, the battalions formed lines and stormed the tribesmen’s positions at the point of the bayonet.
At around 1pm, General Graham’s troops took the hamlet of El Teb and the Mahdists began to stream away into the surrounding countryside.
Casualties at the Battle of El Teb: The British casualties were 5 officers and 24 non-commissioned ranks killed and 17 officers and 142 non-commissioned ranks wounded. The Mahdists suffered around 2,500 killed and an unknown number of wounded.
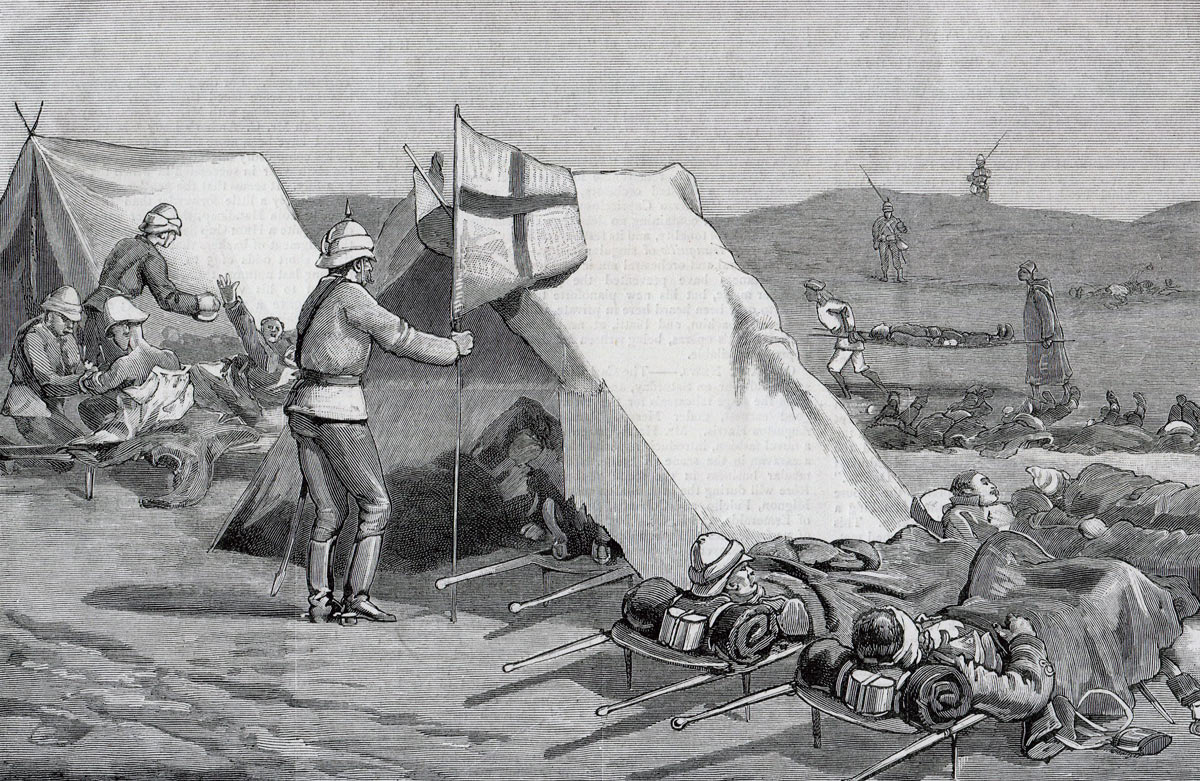

General Graham visits British casualties in the Field Hospital after the Battle of El Teb on 29th February 1884 in the Sudanese War
Follow-up to the Battle of El Teb: Following the battle, General Graham continued his advance on Tokar. He fought one further major engagement, the Battle of Tamai, before being ordered back to Egypt, leaving General Charles Gordon to manage the crisis in Sudan with Egyptian resources.
Anecdotes and traditions from the Battle of El Teb:
- The battles between the British and the Sudanese Jihadist tribesmen were of considerable ferocity. The Mahdi’s dictat was that all non-Muslims in the Sudan faced death, although the Muslim Egyptian and Turkish personnel in the Sudan fared little better at his hands. No British wounded in the battle survived unless immediately recovered. All the cavalrymen who fell from their horses during the charge were killed by the tribesmen, unless promptly rescued. Equally the British troops took few prisoners.
- The battle was fought over the same area in which Baker Pasha’s Egyptian force had been annihilated the previous month. After the battle, the Black Watch were given the task of gathering the corpses of the European officers killed in the earlier battle and burying them.
- Two Victoria Crosses were won at El Teb: One by Captain Arthur Wilson, Royal Navy, for holding off a Mahdist attack while his ratings brought their Gardiner gun into action; the other by Sergeant Marshall of the 19th Hussars for rescuing his wounded commanding officer, Colonel Barrow, whose horse had been killed during the final cavalry charge.
- The Mahdist artillery comprised Krupp guns captured with their Egyptian gun crews. If Egyptian gunners miss aimed or miss fired their gun they were flogged or killed by the Mahdists.
- It is said that Osman Digna and his commanders concealed from the rank and file of the Mahdist army that they were fighting British troops, maintaining that the enemy were Egyptians and Turks.
- Colonel Baker, Baker Pasha, had been a highly regarded commanding officer of the 10th Prince of Wales’ Hussars until convicted of an indecent assault and forced to leave the army in disgrace and take service with the Khedive of Egypt.
- Colonel Redvers Buller VC, commanding the infantry brigade, was wounded at El Teb. He went on to command the Natal Field Force in the Great Boer War, with a singular lack of success. None of the panache that inspired his campaigns as a junior officer survived his promotion to a senior commander.
- Colonel Fred Burnaby acted as intelligence officer for General Graham and was wounded in the arm at El Teb.

Campaign Medals for the Battle of El Teb:
For the Sudan campaign the British troops received the Egypt medal that had been issued for the Tel-El-Kebir campaign in 1882, but without the date. Where troops already had the Egypt 1882 medal they received an additional clasp ‘El Teb’ for that medal. In the same way, the Khedive Star was issued to those ranks that did not already have it.
References for the Battle of El Teb:
War on the Nile by Michael Barthorp.
British Battles by Grant.
History of British Cavalry Volume 3: 1872-1898 by the Marquess of Anglesey
The previous battle of the War in Egypt and the Sudan is the Battle of Tel-el-Kebir
The next battle of the War in Egypt and the Sudan is the Battle of Tamai
To the War in Egypt and the Sudan index