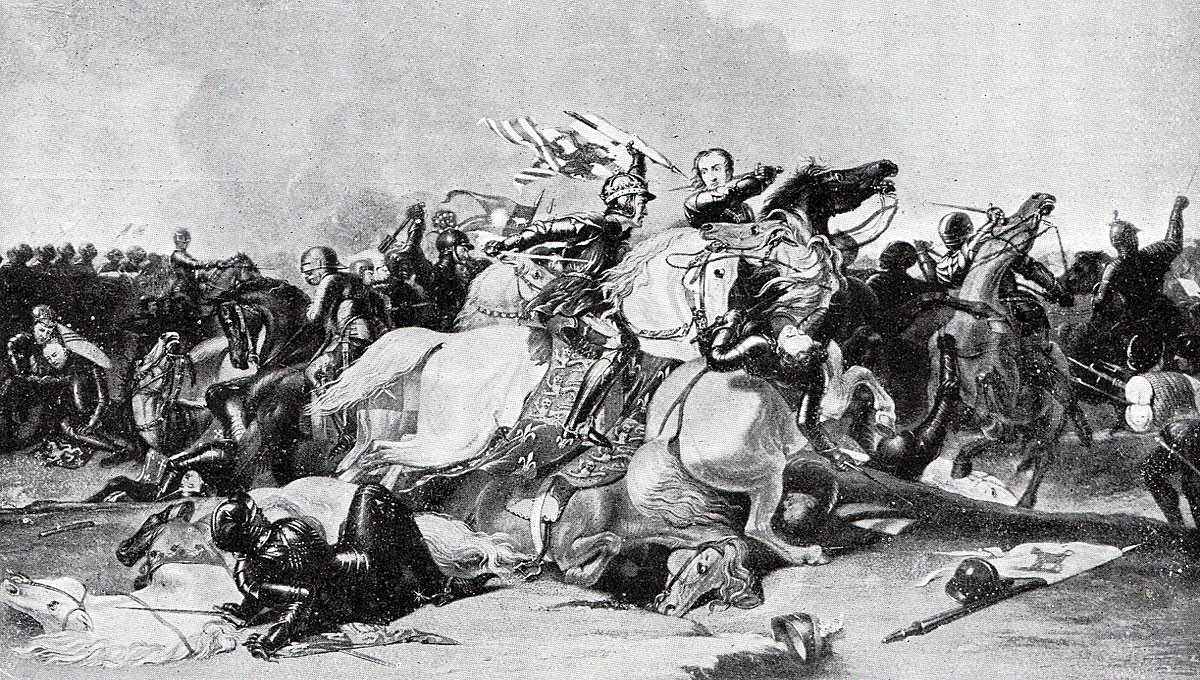
Henry Tudor’s historic victory over King Richard III on 22nd August 1485, with the death of Richard and the establishment of the Tudor Dynasty as Kings and Queens of England
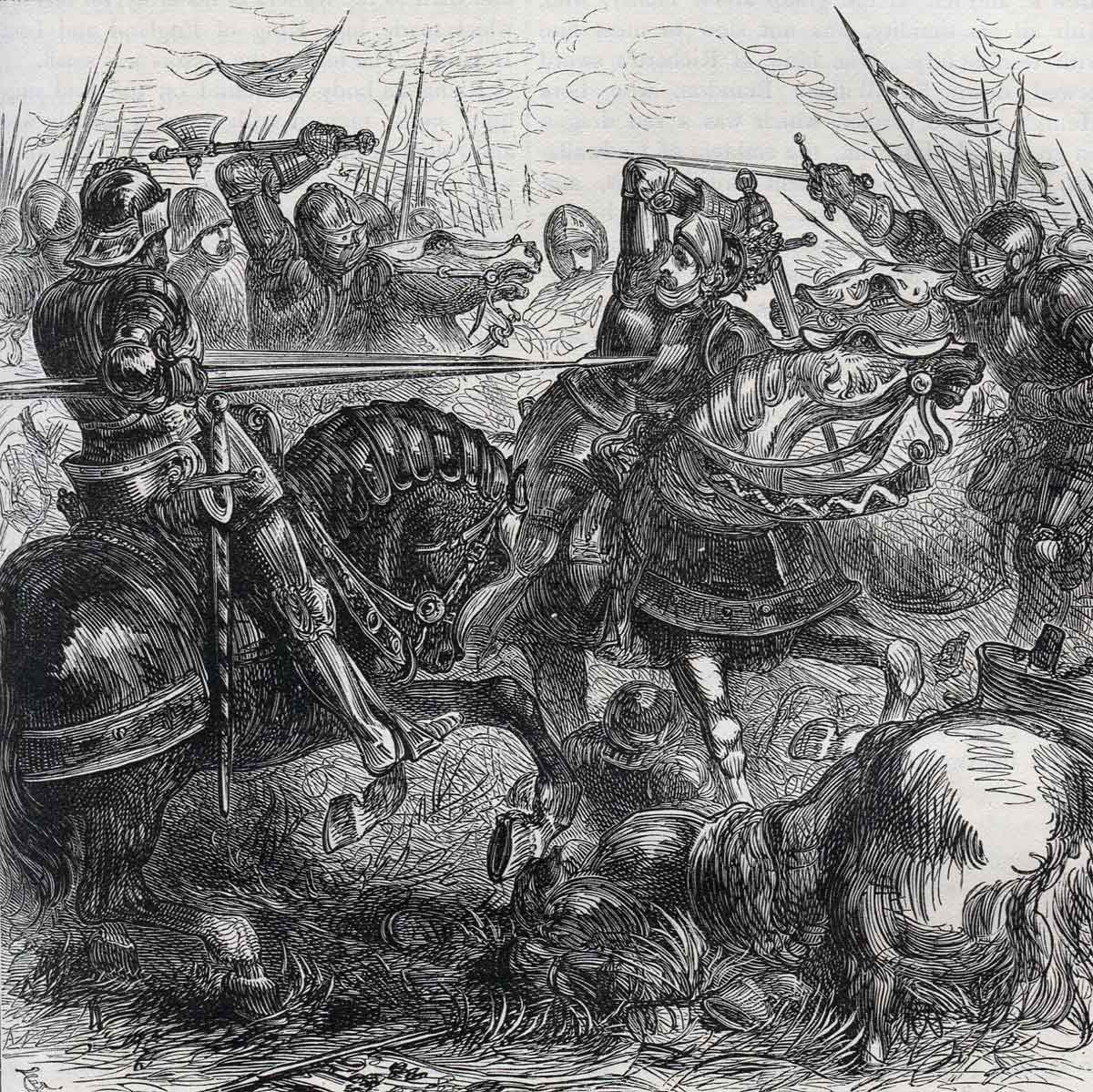

Death of King Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses
The previous battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Tewkesbury
The next battle in the British Battles sequence is the Battle of Flodden
to the Wars of the Roses Index
Battle: Bosworth Field
War: Wars of the Roses
Date of the Battle of Bosworth Field: 22nd August 1485
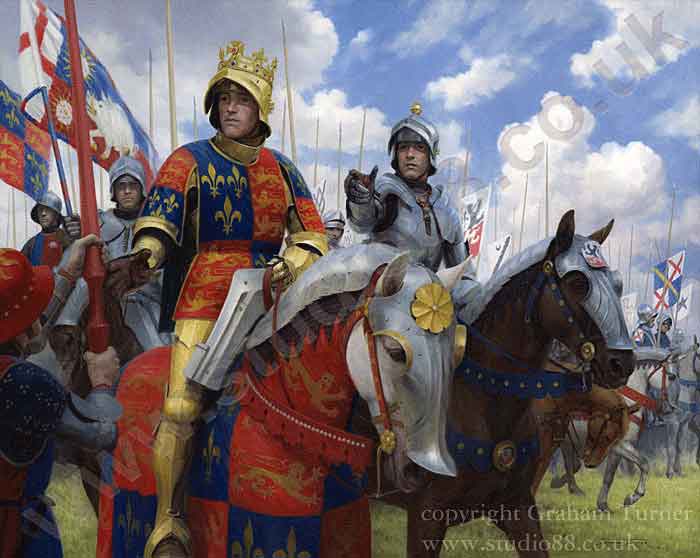

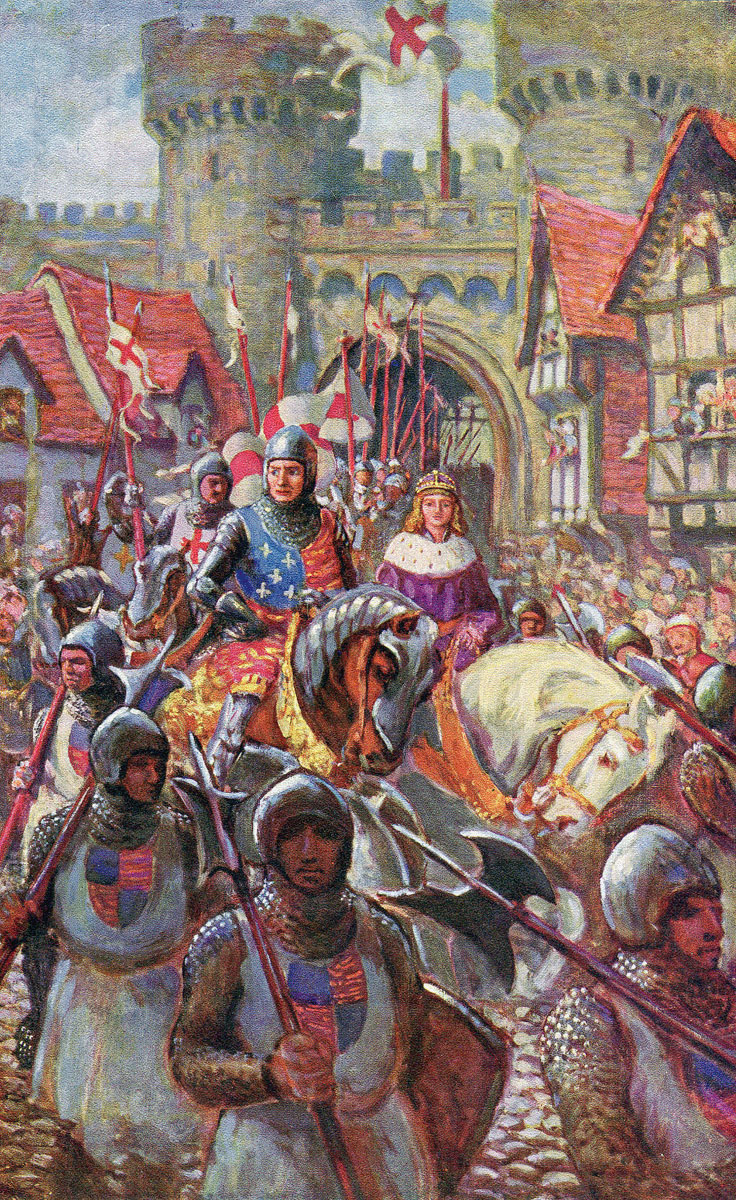
King Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Graham Turner
Place of the Battle of Bosworth Field: In Warwickshire to the south-west of the small town of Sutton Cheney.
Combatants at the Battle of Bosworth Field: The Yorkist army of King Richard III against the army of Henry Tudor and the forces of Lord Stanley and Sir William Stanley.
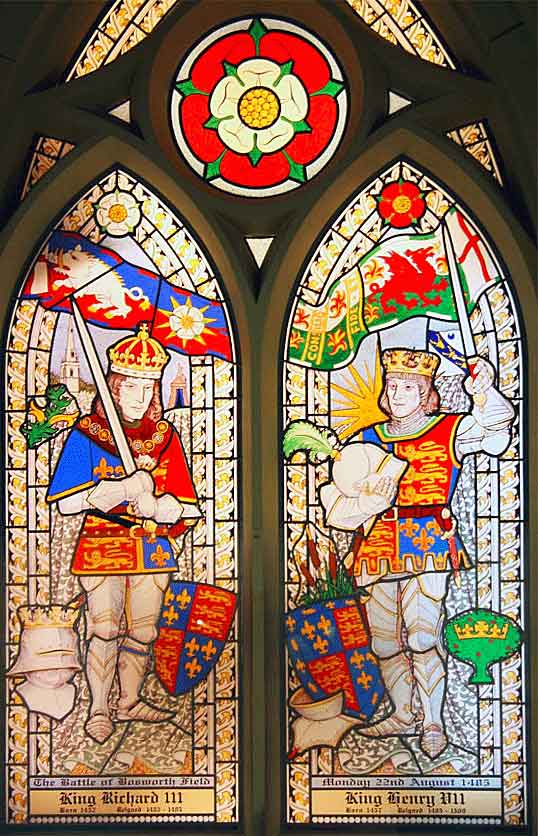

Stained glass window in Sutton Cheney Church showing King Richard III and King Henry VII: Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses
Commanders at the Battle of Bosworth Field:
King Richard III led the Yorkist army.
Henry Tudor’s army was commanded by the Earl of Oxford.
Lord Stanley and Sir William Stanley commanded their own forces.
Size of the armies at the Battle of Bosworth Field: King Richard III’s army comprised around 8,000 men.
Henry Tudor’s army comprised around 6,000 men, of whom 2,000 were French.
Lord Stanley’s force was around 3,000 and Sir William Stanley commanded some 1,000 men.
Winner of the Battle of Bosworth Field: Henry Tudor, who assumed the Crown of England as King Henry VII, through the timely intervention of Lord Stanley and Sir William Stanley.
Uniforms, arms and equipment at the Battle of Bosworth Field: The commanders and their noble supporters and knights rode to battle on horseback, in armour, with sword, lance and shield.
Their immediate entourage comprised mounted men-at-arms, in armour and armed with sword, lance and shield, although often fighting on foot.
Both armies relied upon strong forces of longbowmen.
Handheld firearms were beginning to appear on the battlefield but were still unreliable and dangerous to discharge.
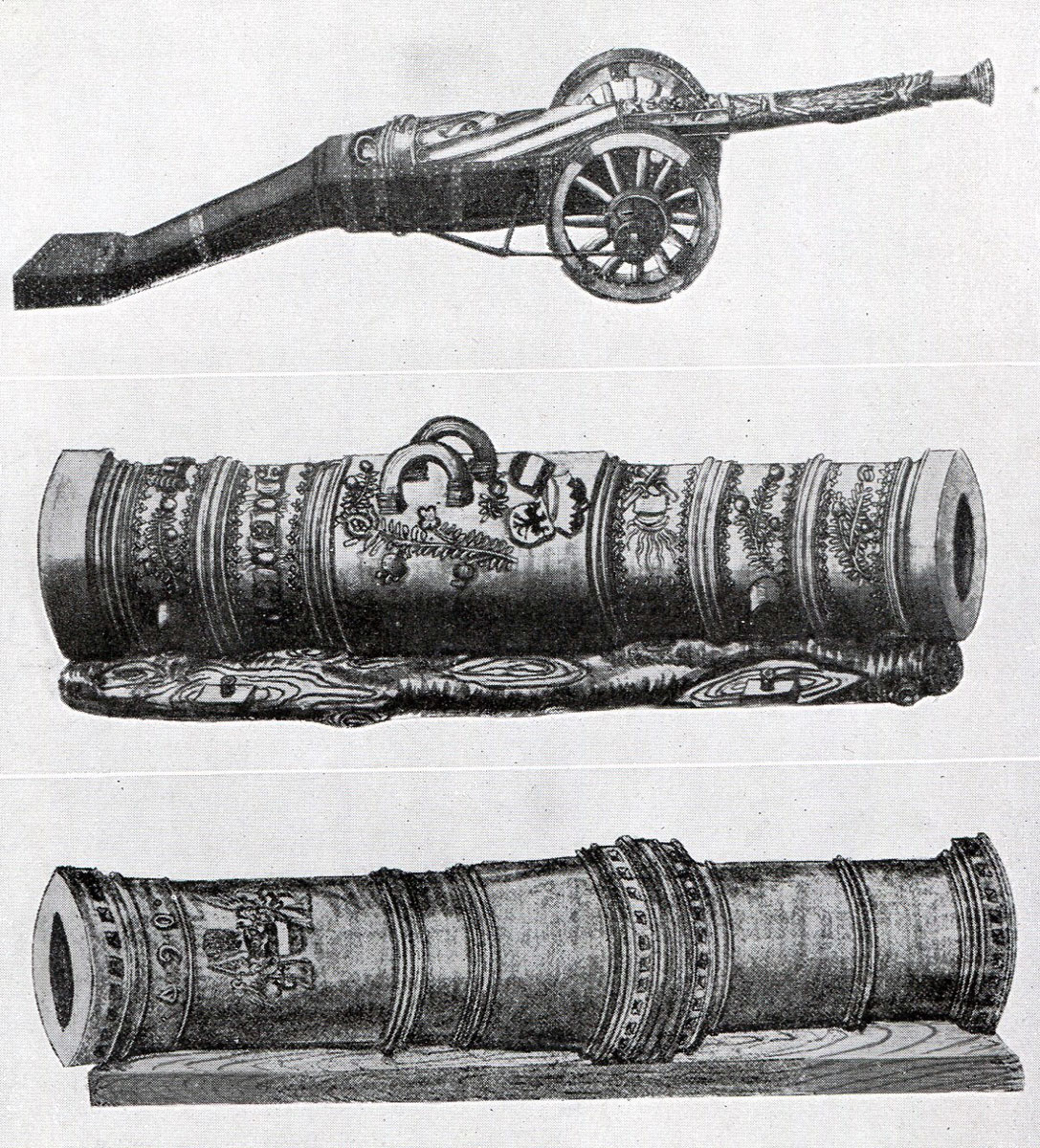
Artillery, although widely used in warfare, was heavy, cumbersome and difficult to move and fire.
Cannon appears to have been used extensively by both sides at the Battle of Bosworth Field. The present position of the battlefield is based on the discovery in a field by Fenn Lane Farm of a large quantity of battle relics including many cannon balls.
The end of the Hundred Years War caused numbers of English and Welsh men-at-arms and archers to return to their home countries from France. The wealthier English and Welsh nobles were able to recruit companies of disciplined armed retainers from these veterans, forming the backbone of their field armies.
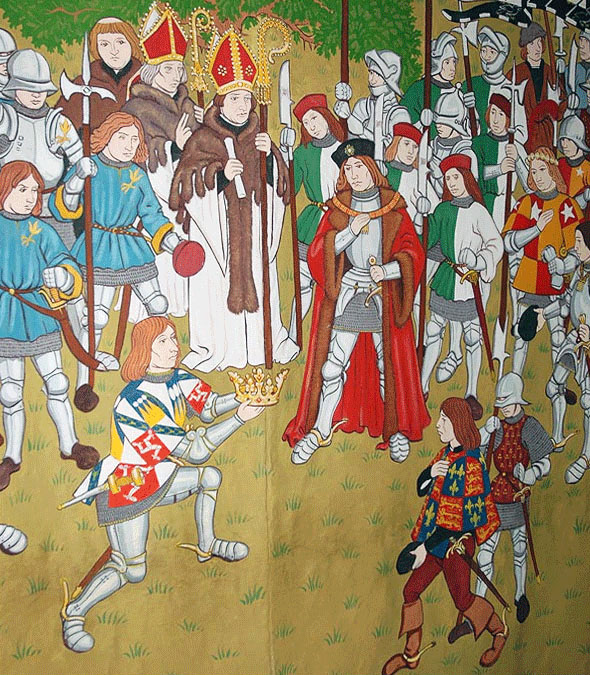

Lord Stanley presents King Richard III’s crown to Henry Tudor after the Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses: 15th century tapestry
Background to the Battle of Bosworth Field: The Yorkist King Edward IV died on 9th April 1483, following a prolonged period of ill-health, leaving his eldest son, the twelve-year-old Edward, Prince of Wales, as the heir to the English throne.
By one of his last important provisions, King Edward IV appointed his brother, Richard, Duke of Gloucester, Protector, or Regent, during his son’s minority.
On 26th June 1483, the Duke of Gloucester assumed the throne, becoming King Richard III of England.
Prince Edward, the Prince of Wales, was imprisoned with his brother in the Tower of London, where both were murdered. Blame for the murders is laid at the door of Richard III.
Within two years of his coronation, King Richard III was facing a revolt by the Duke of Buckingham, allied to the Woodvilles and the exiled Henry Tudor, Earl of Richmond.

Richard, Duke of Gloucester, accompanies the Prince of Wales to London: Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses
The revolt was unsuccessful and the Duke of Buckingham executed.
Henry Tudor resolved to repeat the enterprise with his own bid for the throne of England.
Henry Tudor arrived from Harfleur in Normandy, on 7th August 1485, at the West Wales port of Milford Haven with a force of 2,000 French mercenaries.
As a Welshman, Tudor expected support from the Welsh nobles and gentry.
Henry Tudor was accompanied by his uncle Jasper Tudor, the Earl of Oxford and other Lancastrian and Yorkist knights.
Henry Tudor anticipated that he would be supported by the powerful Stanleys, particularly as Lord Stanley was married to Tudor’s mother, Margaret Beaufort.
King Richard III, warned that Tudor proposed to mount a challenge for the throne from France, was at Nottingham, awaiting news as to where the invading force would land, before moving to confront it.
Once news of Henry’s landing at Milford Haven was received, Richard III gathered his army from across England.
Two commanders represented the King’s interest in Wales, Sir Rice ap Thomas and Sir Walter Herbert.
Thomas went over to Tudor and assisted in raising troops in Wales for his army. Herbert did little to oppose Tudor’s progress.
Henry Tudor advanced through Wales making for Shrewsbury, gathering supporters and their troops on the way.
It would seem that many of the noblemen King Richard III was relying upon dallied in bringing their troops to his army, possibly through lack of commitment to him and through a concern to see who was likely to win before committing themselves.
This would seem to have been so with the powerful Stanley family.
Earlier in the summer of 1485, Richard permitted Lord Stanley to leave his army and return to Lancashire, but retained his son, Lord Strange, as a hostage to ensure Stanley’s continued support.
Lord Stanley did not return to the Royal Army and Lord Strange made an unsuccessful attempt to escape from Nottingham Castle.
Henry Tudor advanced from Shrewsbury to Stafford, where he met Sir William Stanley and then turned south-east, marching through Staffordshire down Watling Street towards London.
During this progress, Henry acquired a number of cannon to form his artillery train.
Meanwhile, Lord Stanley and Sir William Stanley were in the field with their retainers, but were marching in parallel with Henry Tudor’s army. They were thereby able to give Tudor the impression that they might well support him, while at the same time leading King Richard to believe that they were in some way attempting to counter Henry’s advance.
Lord Stanley’s problem was that the King still held his son, Lord Strange, as hostage for Stanley’s loyalty.
On 19th August 1485, on receiving the news that Henry Tudor was at Litchfield, King Richard III left Nottingham with his army, incomplete as it was, to intercept Tudor before he could march on London.
On 20th August 1485, Henry Tudor met with the Stanleys at Atherstone, a small Warwickshire town on Watling Street.
On 21st August 1485, Henry Tudor marched east from Atherstone and King Richard III advanced from Leicester. Both sides encamped in the area of the battlefield.
There were consequently four camps: Henry Tudor’s, Richard III’s and one for each of the Stanleys.
The next morning, 22nd August 1485, battle lines were drawn up in the undulating, open, marshy countryside to the south-west of the Warwickshire town of Sutton Cheney.
———————————-
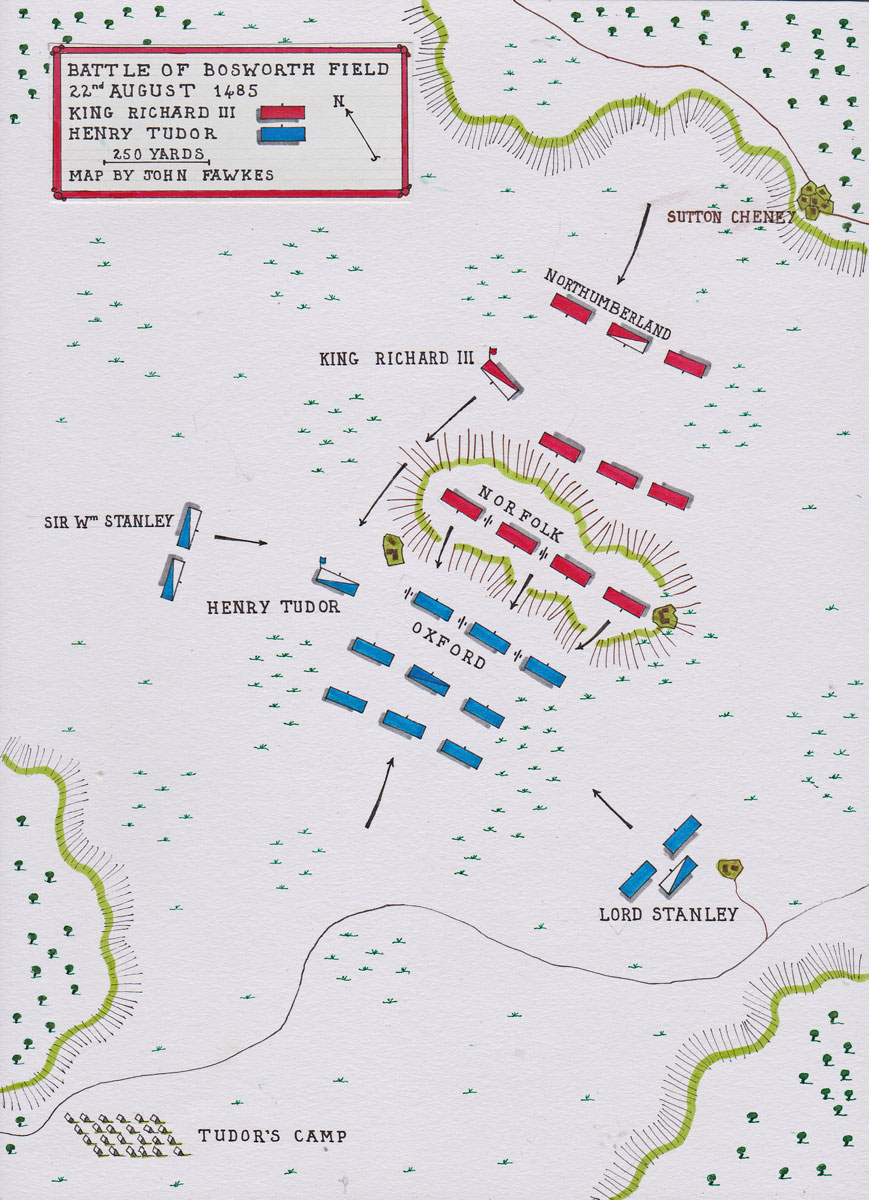
Map of the Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses: map by John Fawkes
Account of the Battle of Bosworth Field:
The place now accepted as the battlefield for the Battle of Bosworth Field is at Fenn Lane Farm.
The nature of the area in 1485 was open, uncultivated, undulating, boggy moorland.
King Richard III put 8,000 men into the field. The Duke of Norfolk and his son, Lord Surrey, commanded the van, with 1,500 archers and 500 men at arms and knights.
The Earl of Northumberland commanded the rear of 1,500 billmen and 1,000 mounted men at arms and knights.
In the centre, King Richard III stood with the main guard of 1,500 billmen and 2,000 pikemen and his own retainers.
Henry Tudor’s army marched forward to engage the Royal army.
The Stanley’s forces stood by and watched the initial engagement.
Seymour surmises that Sir William Stanley watched the opening of the battle from a position to the north, while Lord Stanley took up a position to the south of Tudor’s army.
Seymour estimates the force available to the Stanleys at not more than 4,000 men.
King Richard III sent a message to Lord Stanley, ordering him to join the Royal army or his son, Lord Strange, would die.
It is said that Stanley replied that he had other sons.
Henry Tudor also sent a message to Lord Stanley, who replied that he would join Tudor at the appropriate time.
It may well be that Stanley had in mind to join the battle on Tudor’s side, at a point where his intervention would be decisive in winning the battle for Tudor and at a time when it would be too late for King Richard III to implement his threat to execute Stanley’s son, Lord Strange.
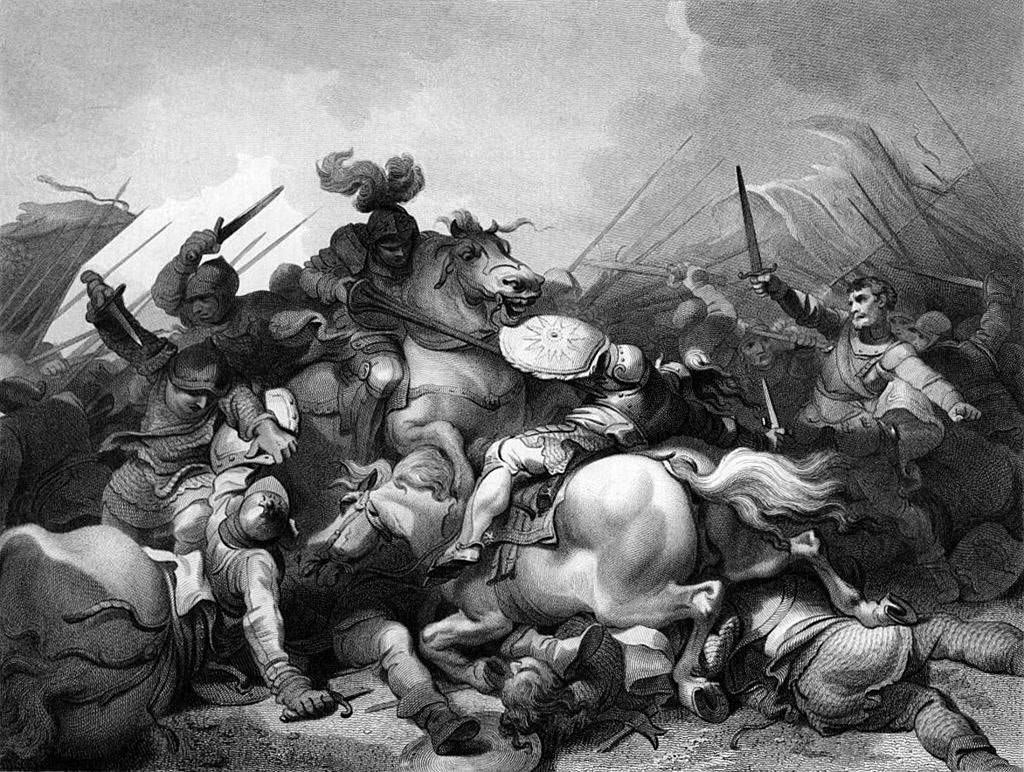

Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Philip James de Loutherbourg
Seymour considers that the Royal army probably fought in column with the van leading, the King’s division in the middle followed by Northumberland’s rear division.
The King’s army halted and awaited the arrival of their opponents. A boggy area to the army’s left restricted deployment in that direction.
Henry Tudor’s army approached, negotiating several areas of boggy ground, a manoeuvre that slowed up the advance.
The Earl of Oxford lead the van and, after deploying the artillery and several lines of archers, opened up a cannonade and arrow storm, to give the rest of Tudor’s army the opportunity to come up.
Other subordinate commanders in Tudor’s army were Sir Gilbert Talbot, Sir John Savage and Henry’s uncle, Jasper Tudor.
The French troops, referred to as ‘the broken companies’, were commanded by Bernard, a Scottish mercenary.
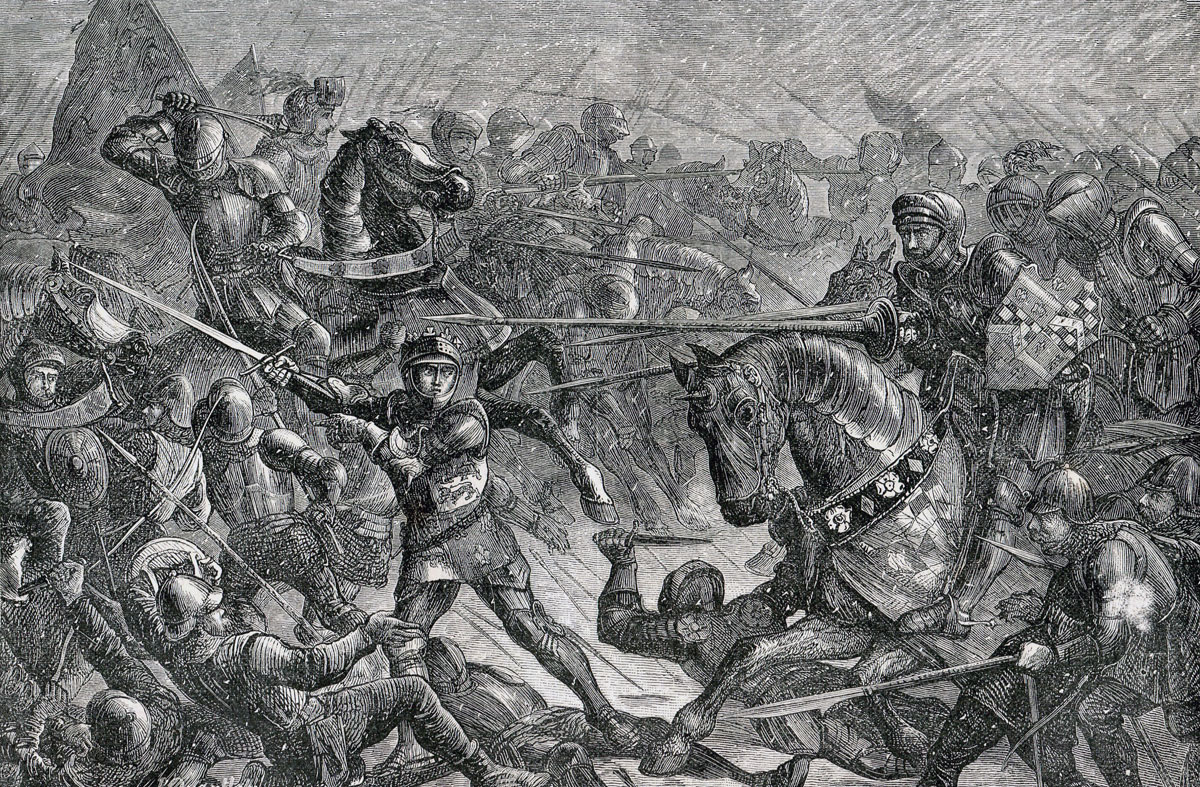
There was then a pause, after which the two armies advanced on each other and the hand-to-hand fighting began, to last some two hours.
An early casualty was Richard III’s senior commander, the Earl of Norfolk, rumoured to have been killed by the Earl of Oxford.
Both leaders waited for the Stanleys to commit themselves to the battle.
Before this happened, King Richard III was informed that the Earl of Northumberland was holding back with the royal rearguard and that its sorely needed support would not be provided. Northumberland was clearly changing sides.
King Richard III was now in desperate straits. The Stanleys were moving forward to join the battle in support of Henry Tudor.
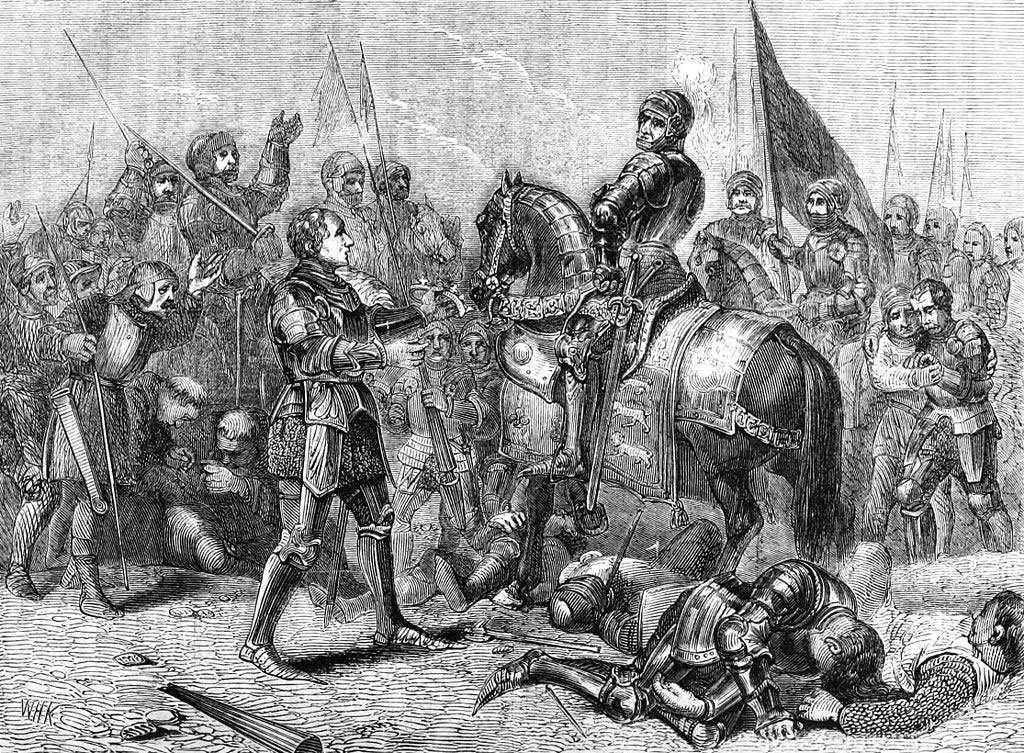

Lord Stanley presents King Richard III’s crown to Henry Tudor after the Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses
It was in the last desperate phase of the battle that King Richard III was killed.
One authority has it that Richard was struck down in an assault on Lord Stanley.
Another, more widely publicized account, has it that King Richard III saw Henry Tudor in an exposed position on the left flank of his army and rode to attack him with his personnel retainers, only to be overwhelmed by the arrival in the battle of Sir William Stanley’s men.
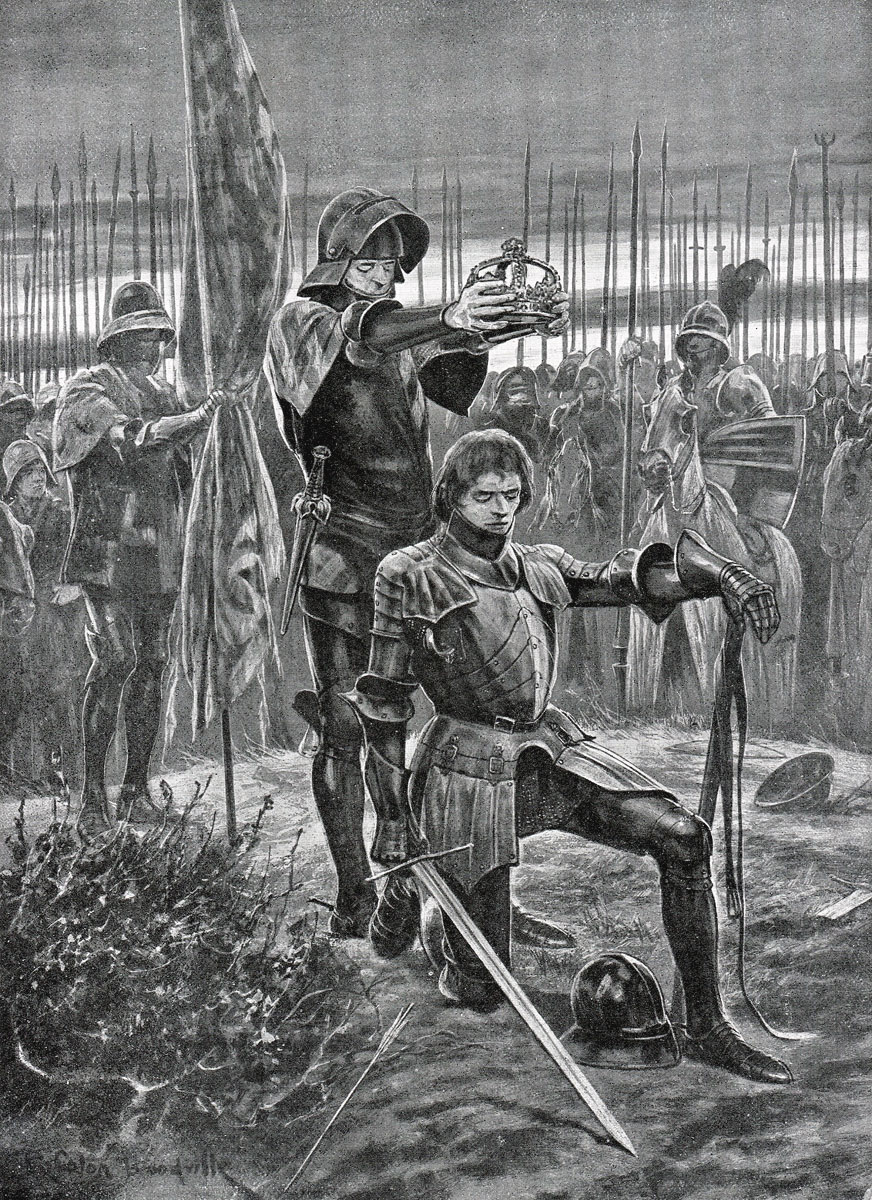

King Henry VII crowned after the Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Richard Caton Woodville
Either way, King Richard III was cut down and killed, fighting hard to the end.
With Richard’s death, his army broke and fled the field.

Body of King Richard III loaded onto a horse to be taken into Leicester after the Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses
Casualties at the Battle of Bosworth Field:
Estimates put the casualties at 1,000 for the Royal army and 200 for Henry Tudor’s army.
The senior members of King Richard III’s army killed in the battles were the Duke of Norfolk, Lord Ferrers of Chartley, Sir Robert Brackenbury, Sir Robert Percy and Sir Richard Radcliffe.
Lord Surrey, son of the Duke of Norfolk, was captured and imprisoned in the Tower of London.
Sir William Catesby was executed (one of King Richard III’s hated advisers: ‘the Cat, the Rat and Lovell our dog rule all England under the Hog’: as the contemporary rhyme had it)
In the army of Henry Tudor, Sir William Brandon was killed.
Follow-up to the Battle of Bosworth Field: Tradition has it that Lord Stanley found King Richard III’s crown hanging on a bush and delivered it to Henry Tudor, announcing him King Henry VII, thereby initiating the reign of the House of Tudor and ending the Plantagenet dynasty.
Marrying the Yorkist princess, Elizabeth Woodville, King Henry VII moved quickly to unite the two warring factions of the Yorkists and the Lancastrians and bring the feuds of the Wars of the Roses to an end.
King Henry VII back dated his sovereignty to the day before the Battle of Bosworth Field, enabling him to condemn as traitors all who fought for King Richard III.
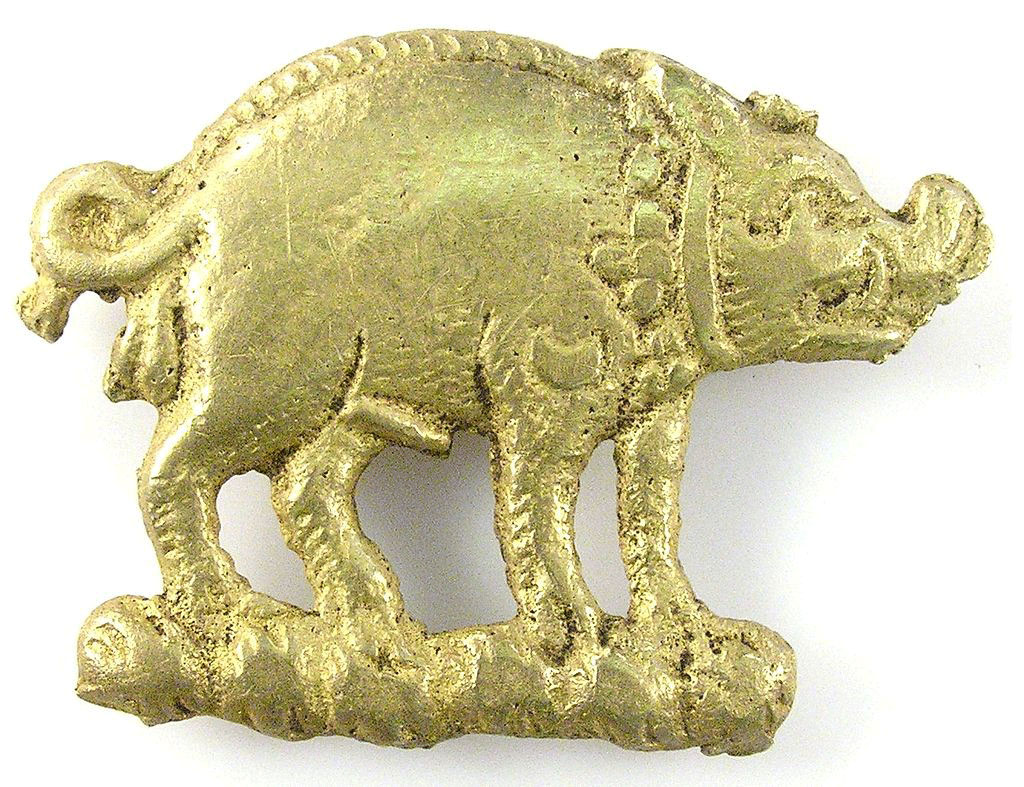

Boar badge found on the battlefield of the Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses
Emblems of the Battle of Bosworth Field: King Richard III’s emblem of the Boar was found on the battlefield in the form of a small badge, that will have been worn by a knight of King Richard III’s immediate household and who will have died with the King.
The fate of King Richard III after the Battle of Bosworth Field:
After the Battle of Bosworth Field, King Richard III’s body was found on the battlefield, stripped naked and carried on a horse led by Blanche Sanglier, a pursuivant-at-arms, to Leicester where it was displayed in public, before being buried in the Greyfriars Church.
King Richard III’s body was discovered in 2012 in a car park built on the site of the Greyfriars Church.
On 26 March 2015 King Richard III was re-buried in Leicester Cathedral.
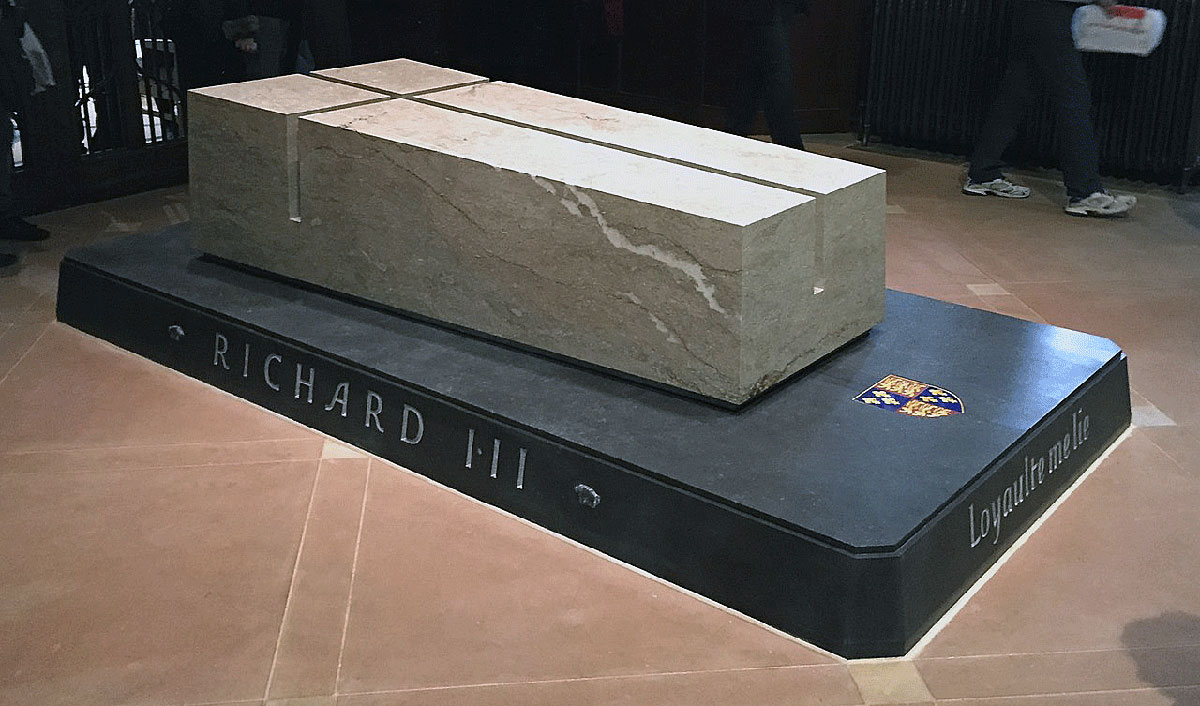

King Richard III’s tomb in Leicester Cathedral: Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses

Arms of John de Vere, Earl of Oxford: Battle of Bosworth Field on 22nd August 1485 in the Wars of the Roses
Anecdotes and traditions from the Battle of Bosworth Field:
- King Richard III’s message to Lord Stanley before the Battle of Bosworth Field was delivered by Sir Robert Brakenbury: ‘My Lord, the King salutes you. He commands your immediately attendance, with all your forces, or your son, Lord Strange, dies instantly.’ Lord Stanley is said to have replied: ‘Should the King stain his honour with my son’s blood, tell him I have more. I shall come at my convenience.’
- On hearing of Lord Stanley’s retort, King Richard III declared ‘Tis a false pretence. He is a traitor and the boy dies.’ Catesby was ordered to arrange Lord Strange’s execution, but on the intervention of Lord Ferrars, it was deferred. The onset of the battle then intervened, perhaps as Lord Stanley expected and counted on. Perhaps Ferrars pointed out that once Lord Strange was executed, the Stanleys were certainly lost to the King, while, so long as Strange remained alive and a hostage, a hold of some sort was maintained over the Stanleys.
References for the Battle of Bosworth Field:
Battles in Britain by William Seymour
Wars of the Roses by Michael Hicks
Chronicles of the Wars of the Roses
British Battles by Grant
Battle of Bosworth Field: Charles River Editors
The previous battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Tewkesbury
The next battle in the British Battles sequence is the Battle of Flodden
to the Wars of the Roses Index





