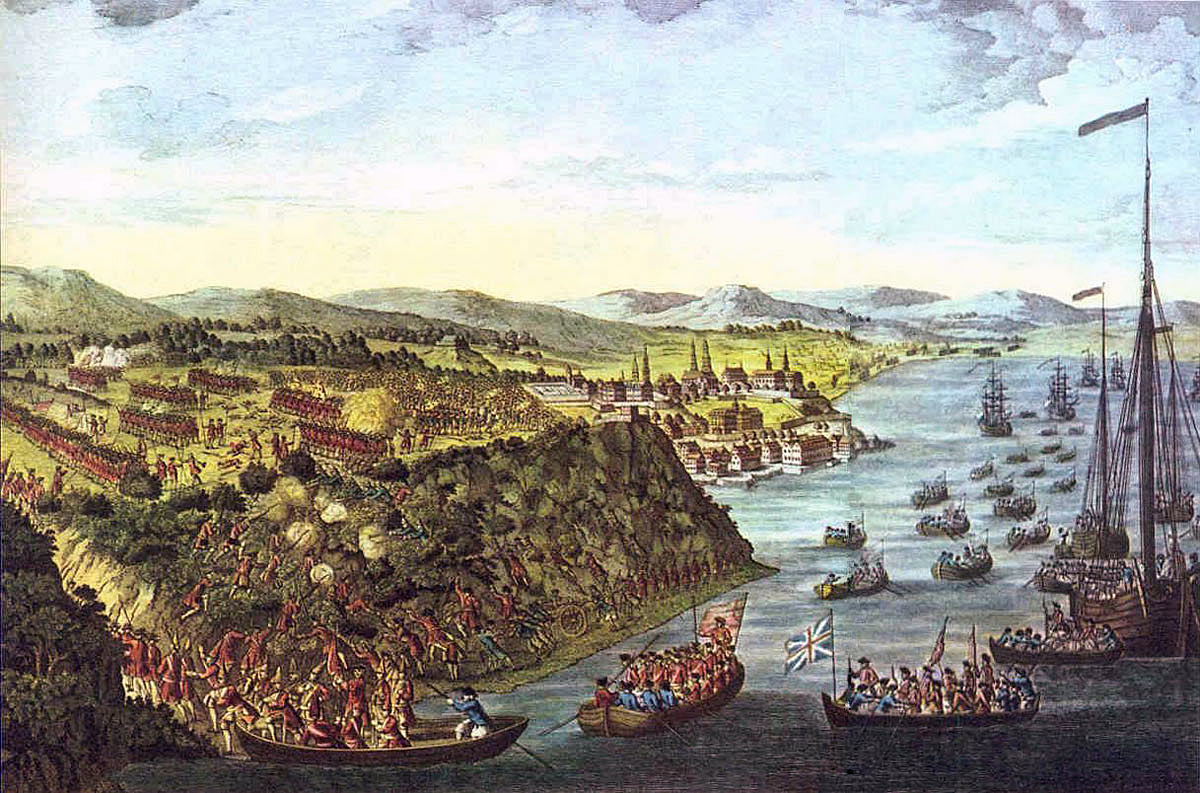
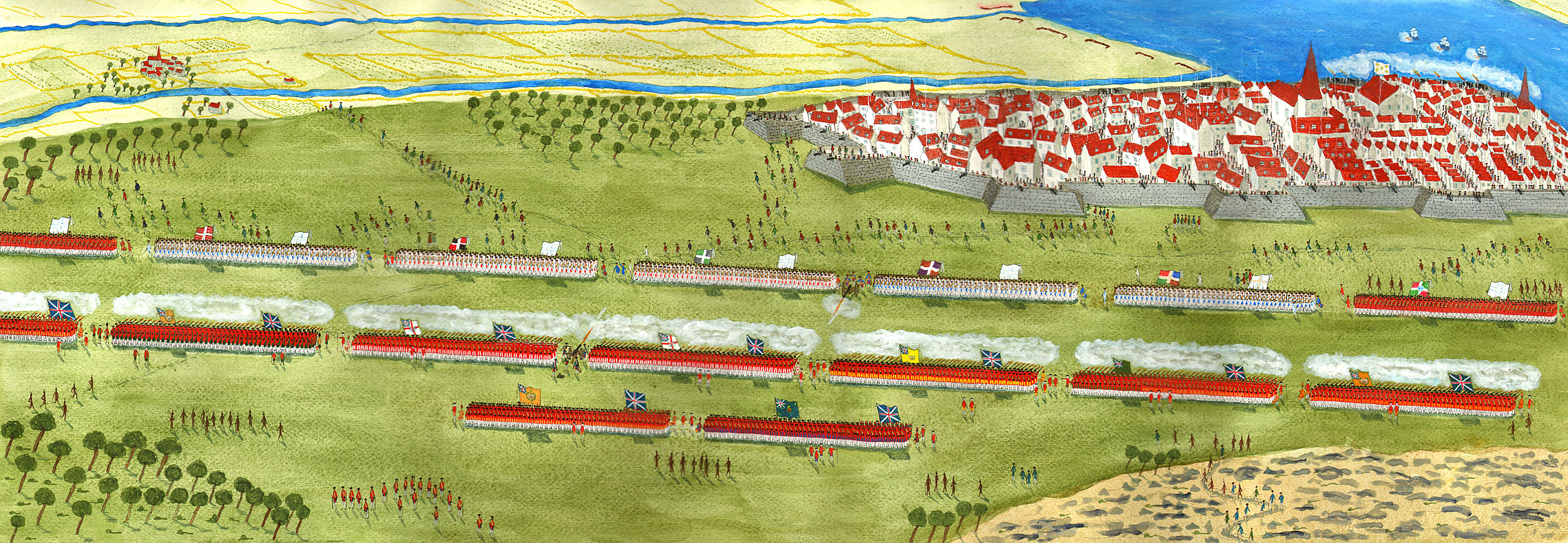
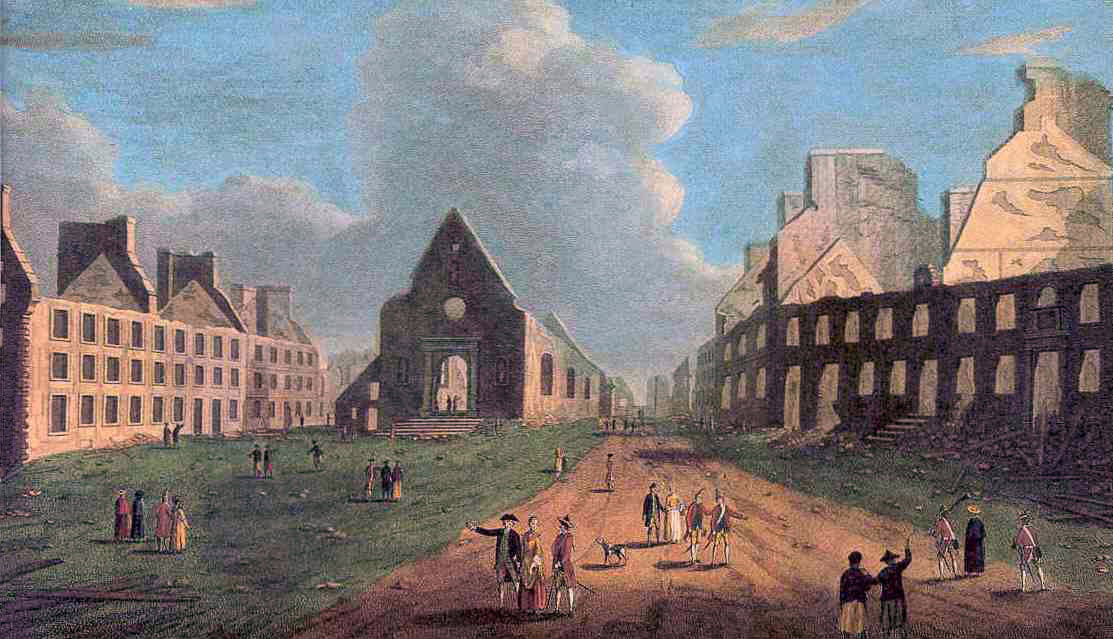General Wolfe’s decisive defeat of the French army under the Marquis de Montcalm at Quebec on 13th September 1759, that led to the British capture of Canada, with the deaths of both generals at the moment of victory
The previous battle of the French and Indian War is the Capture of Louisburg
The next battle in the British Battles sequence is the Battle of Lexington and Concorde
To the French and Indian War index

Major-General James Wolfe: Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War
Battle: Quebec
War: The French and Indian War also known as the Seven Year War (1757 – 1762)
Date of the Battle of Quebec: 13th September 1759
Place of the Battle of Quebec: Quebec in Canada
Combatants at the Battle of Quebec: British and Americans against the French and Canadians
Commanders at the Battle of Quebec: Major General James Wolfe against the Marquis de Montcalm
Size of the Armies at the Battle of Quebec: The British Army besieging Quebec was around 8,000 troops. The force Major General Wolfe took onto the Plains of Abraham for the battle was around 4,500 men and 1 gun. The Marquis de Montcalm brought to the battle a force of around 5,000 men and 3 guns.

Marquis de Montcalm French commander at the Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War: picture by Richard Caton Woodville
British Regiments at the Battle of Quebec:
15th Foot later the East Yorkshire Regiment and now the Yorkshire Regiment *
22nd Foot later the Cheshire Regiment (only the grenadier and light companies) and now the Mercian Regiment
28th Foot later the Gloucestershire Regiment and now the Rifles *
35th Foot later the Royal Sussex Regiment and now the Princess of Wales’s Royal Regiment *
40th Foot later the South Lancashire Regiment and now the Duke of Lancaster’s Regiment (only the grenadier and light companies)
43rd Foot later the Oxfordshire and Buckinghamshire Light Infantry and now the Rifles *
45th Foot later the Sherwood Foresters and now the Mercian Regiment
47th Foot later the North Lancashire Regiment and now the Duke of Lancaster’s Regiment *
48th Foot later the Northamptonshire Regiment and now the Royal Anglian Regiment *
58th Foot later the Northamptonshire Regiment and now the Royal Anglian Regiment *
60th Foot later the King’s Royal Rifle Corps and now the Rifles *
Fraser’s Highlanders, disbanded at the end of the war.
The Louisburg Grenadiers, the Light Infantry and 6 companies of American rangers.
* These regiments have Quebec as a battle honour.

General Wolfe and his troops climbing the Heights of Abraham at the Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War: picture by Richard Caton Woodville
Uniforms, arms and equipment at the Battle of Quebec:
The British Foot wore red coats falling to the knee with the skirts, lapels and cuffs turned back to reveal a wide expanse of the lining of the regiment’s colour. The coat was embroidered with the regiment’s distinctive lace pattern. The lining colour was part of a regiment’s character so that the 3rd Foot was known as the “Buffs” and the 19th Foot as “the Green Howard’s” from their lining colours. The main headwear for the foot was the black tricorne hat, a wide brimmed hat with the brim turned up and fastened to form three angles.
The grenadiers wore a mitre cap with an embroidered front of the regimental facing colour. This was the standard form of uniform. However on arrival in America the soldiers quickly adapted their dress. Coats were cut back or abandoned. Many took to wearing hunting shirts and leggings. Hats were adapted and mutilated. It is unlikely that the grenadiers retained their inconvenient mitres for long. The new light companies in particular adopted local dress.
Each soldier carried a musket, 24 rounds of ammunition carried in a pouch slung from a shoulder belt, a short sword and a bayonet that he fixed to the muzzle of his musket. In America the sword was quickly abandoned as useless.
The city of Quebec lies on the north bank of the St Lawrence to the West of the St Charles river. Montcalm established his army along the north shore of the St Lawrence between the St Charles and Montmorency rivers building fortifications along the St Lawrence bank. The city was strongly fortified and ships added to the defences.
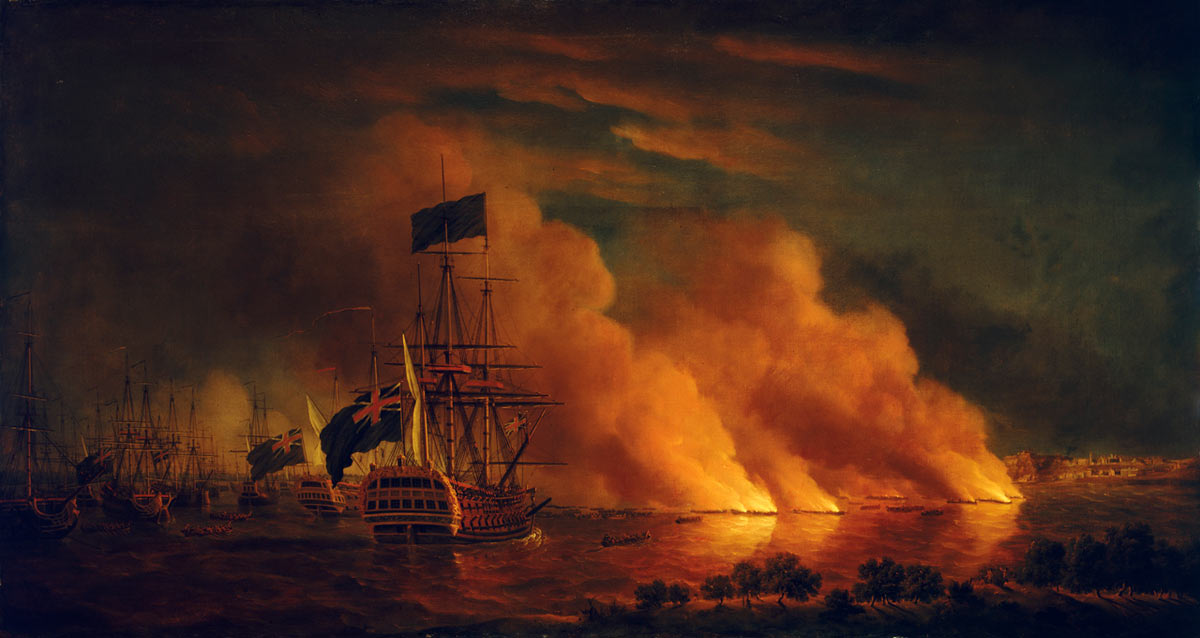

French fire ships off Quebec: Battle of Quebec September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War
The British and American force arrived and established itself on the Isle of Orleans downstream from Quebec in late June 1759. Monckton’s brigade took post on the southern bank of the river opposite the city and began to bombard it. The other two brigades occupied the banks of the Montmorency.

Major-General James Wolfe: Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War
The musket of the period was a cumbersome and inaccurate weapon. Each round of ammunition comprised a charge of gunpowder and a lead ball wrapped in “cartridge paper”. When ordered to load the soldier took a cartridge and ripped it open, often with his teeth. He poured sufficient powder into the pan of the firing mechanism to fill it. He poured the main portion of powder down the barrel, folded the paper and pushed it into the barrel and dropped the ball on top. He used the ramrod carried under the barrel of the musket to push the whole charge to the bottom of the barrel next to the hole leading to the firing pan.
He then cocked the firing mechanism which comprised a hammer holding a wedge of flint and the weapon was ready to fire. Pulling the trigger caused the flint held by the hammer to strike against the pan lid, flicking it open as it did so. The spark from the flint ignited the powder in the pan which fired the charge in the barrel. With a significant number of shots the musket would fail to fire, particularly in wet weather.
If the musket did fire it gave out a gout of flame and smoke with the discharged ball and if the target was large and within 50 yards it might be hit. An experienced user of the musket might be able to load and fire three or four times in a minute.
After ten rounds or so the musket began to foul from the powder residue and loading became slower and more difficult. The soldier would use a “picker” to keep the hole from the pan through the barrel clear. After each shot he would blow down the barrel. Sparks from each shot might fly into his eye or onto his hair. His face and hands would become blackened with soot.
Officers carried short pikes and swords. In America they too quickly adapted their equipment and dress to local usage. Pikes were abandoned and many officers carried muskets and pistols.
The French foot wore similar uniforms to the British but of white. They also quickly adapted their dress to local conditions. The French musket fired a smaller ball than the English.
The Rangers and Militia wore whatever they chose. In addition to their muskets these troops being largely hunters carried tomahawks, knives and other implements.
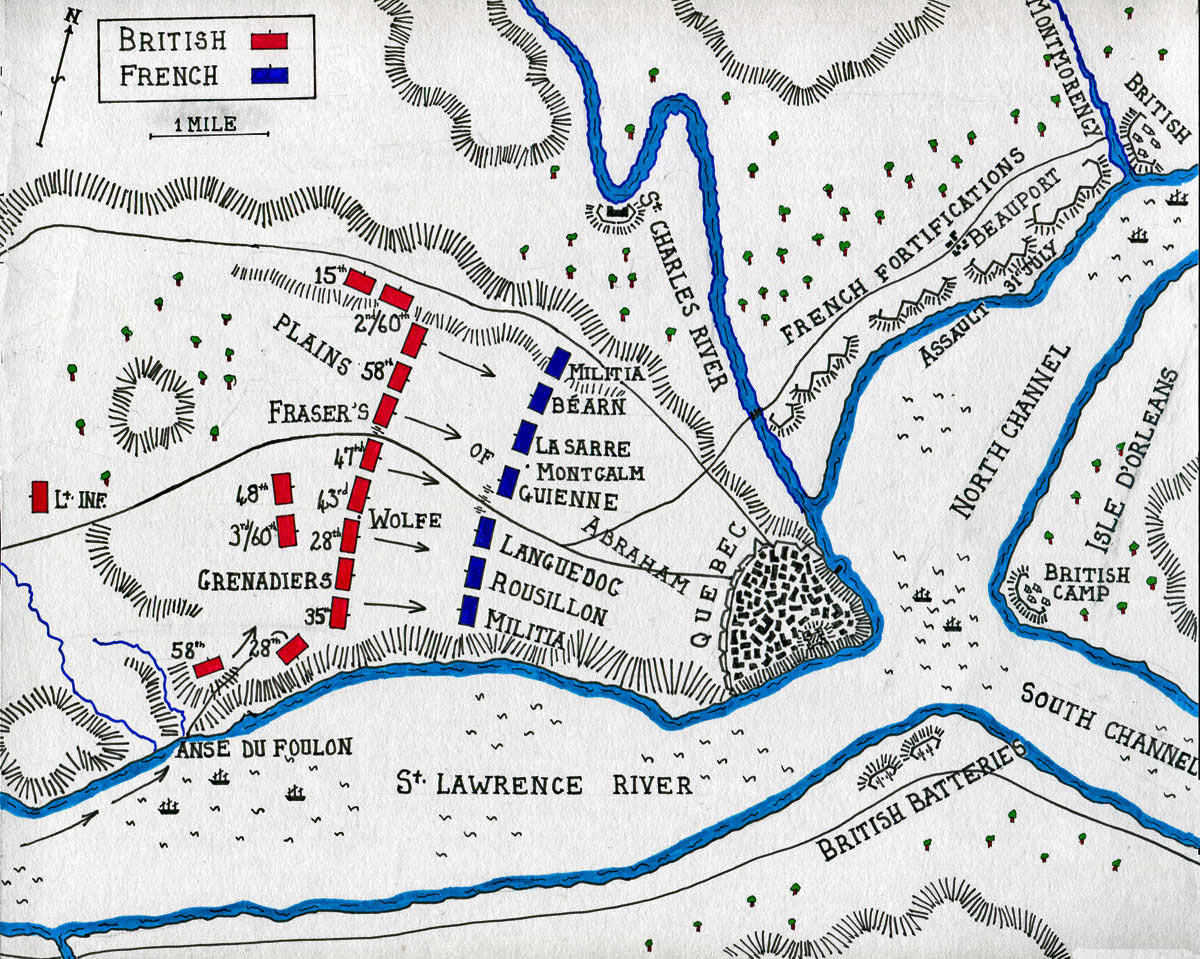
Map of the Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War: map by John Fawkes
Account of the Battle of Quebec:
Following the capture of Louisburg in 1758, Wolfe took sick leave in England. In February 1759 he returned to America to command the attack on the St Lawrence and Quebec. The British force assembled at Louisburg as three brigades under Monckton, Townsend and Murray. The grenadier companies were formed into one battalion and other picked men into a battalion of Light Infantry.

British landing barge: Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War
In the first week of June 1759 the force set sail for the St Lawrence. The French had been expecting attacks from Lake Ontario in the West and Lake Champlain in the South and the descent on the St Lawrence took them by surprise. Montcalm assembled five regular French battalions, militia and a thousand Indians to Quebec.
On 31st July 1759 Wolfe attempted an attack on Montcalm’s riverside fortifications. The disorganised assault was repulsed with heavy loss. The grenadiers and 60th losing around 500 casualties.
Over the following weeks British ships managed to pass the batteries into the area of the river above the city. This move prevented supplies from reaching the French garrison and population. On his recovery Wolfe determined to attempt a landing on the steep northern bank of the St Lawrence to the West of the city.
On the night of 4th September 1759 the troops encamped on the Montmorency were disembarked. On 12th September Wolfe was informed that French supply ships were expected to venture down the St Lawrence that night. A feint attack was made on Montcalm’s fortifications east of the city to draw French troops away from the proposed landing site.
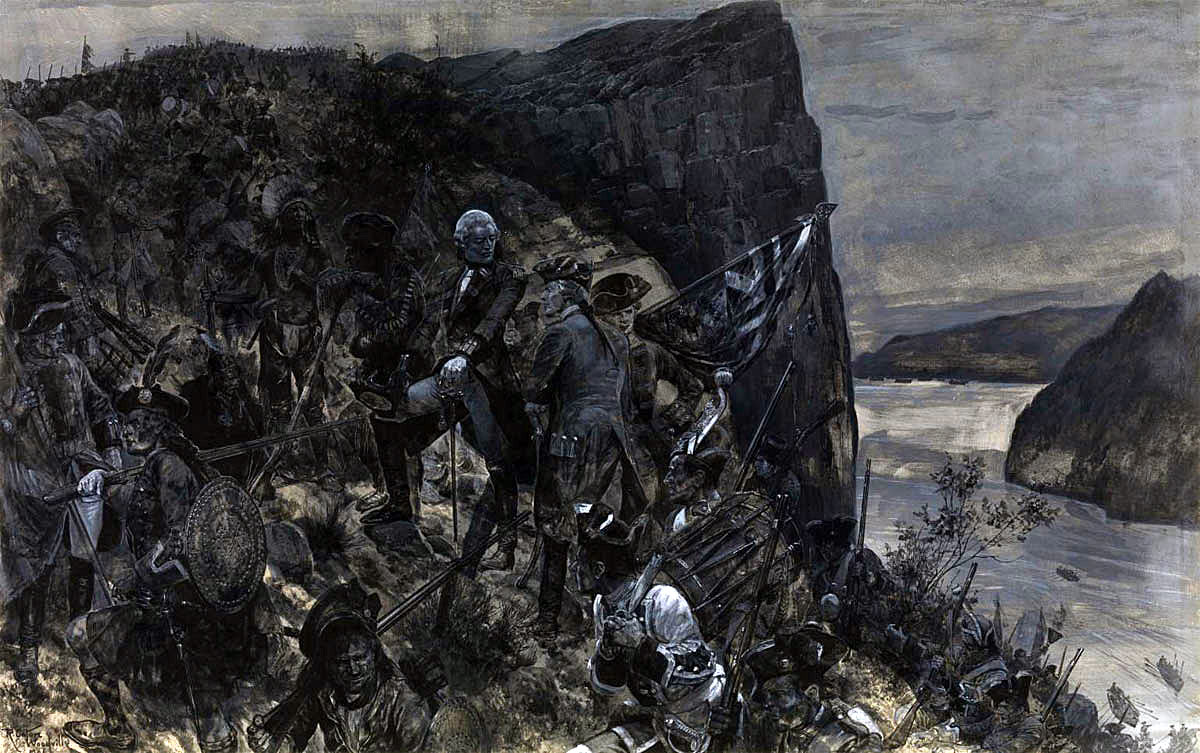

General Wolfe and his troops climbing the Heights of Abraham at the Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War: picture by Richard Caton Woodville
That night Wolfe’s flotilla rowed from the West down the river to the Anse du Foulon, the point Wolfe had chosen for the landing on the north bank. A French sentry challenged the boats but was answered by a highland officer in French. The force landed and scaled the cliff. By dawn 4,500 British and American troops were assembled on the cliff top.
The situation of this British force was precarious as Bougainville and a French force lay to the West in their rear. About a mile to their front was the area of wide open country called the Plains of Abraham extending to the walls of the city.
Wolfe formed his army on the plains in a single line of battalions, the right resting on the edge of the heights above the St Lawrence. From the right his regiments were: the 35th Foot, the grenadier companies of the 22nd, 40th and the 45th Foot, the 28th, 43rd, 47th Foot, Fraser’s Highlanders and the 58th Foot. One light gun had been dragged up the cliff and stood between the 47th and the Highlanders. The 15th Foot was formed at a right angel to the line on the left to protect the flank. Two battalions formed a reserve, the 3rd/60th and the 48th Foot. Two companies of the 58th guarded the access up the cliff and 3rd/60th guarded the rear against any incursion by Bougainville.

General Wolfe and his troops: Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War: picture by Richard Caton Woodville
Of the brigadiers, Monckton and Murray commanded the line and Townsend the reserves. Wolfe positioned himself with the 28th on the right of the line.
Montcalm did not become aware of the British incursion until the morning, when he saw the line formed outside Quebec. French, Canadian and Indians streamed through the city towards the Plains of Abraham. Montcalm applied to the governor of the city for some of the guns from the ramparts, but the governor agreed to release only three. Nevertheless Montcalm decided to attack the British line.
Montcalm formed his army; from the right a battalion of Canadian militia, then the regiments of Bearn, La Sarre, Guienne, Languedoc, Rousillon and another battalion of militia. Skirmishing Canadians and Indians formed on the flanks.
A savage fight developed on Wolfe’s left between the skirmishers and the British Light Infantry and the reserve regiments under Townsend. The three French guns and the single British gun fired at the opposing lines. The French regular battalions advanced to the attack and the British regiments, who had been lying down to avoid the fire, rose up. The French fired ineffectually at too great a distance and came on. The British foot withheld its fire until the range was 35 yards, it is said. Two volleys were sufficient to destroy the French line. The British infantry then advanced and drove the French from the field.

Death of General Wolfe at the Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War
Wolfe, who had been wounded in the hand, advanced with the 28th Foot until he was shot in the groin and then in the chest. A group of soldiers carried him to the rear.
Canadian skirmishers continued to fire on the British until they were driven back. The French army retreated into the city in confusion. Montcalm, who had been shot, was carried with the retreating throng until he was taken from his horse iinto a house nearby, where he died.
Wolfe rejected medical attention and was laid on the ground. Someone called “See them run”. Wolfe said “Who?” He was answered, “The French.” Wolfe directed the 28th to march to the bridge across the St Charles River to cut off the retreat and then died.
In addition to the two generals, Montcalm’s deputy was killed and Brigadier Monckton wounded. Townsend took command and immediately had to fight off an attack from Bougainville to his rear.
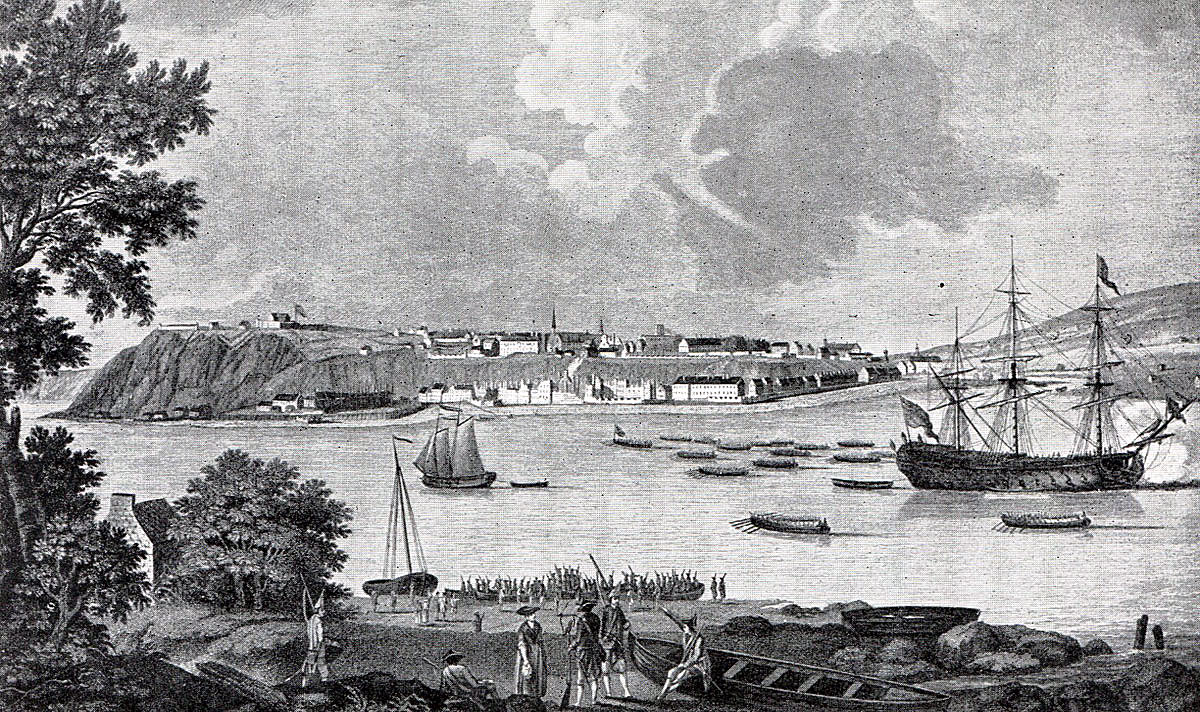
City of Quebec during the battle: Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War
Casualties (killed and wounded) at the Battle of Quebec:
Staff: 5
Royal Artillery: 15
15th Foot: 132
28th Foot: 126
35th Foot: 111
40th Foot: 38
43rd Foot: 48
47th Foot: 69
48th Foot: 65
58th Foot: 155
3rd/60th: 215
4th/60th: 32
Fraser’s Highlanders: 187
Grenadiers: 133
Roger’s Rangers: 51
Royal Marines: 30
Total: 1,412
The French casualties are unknown.
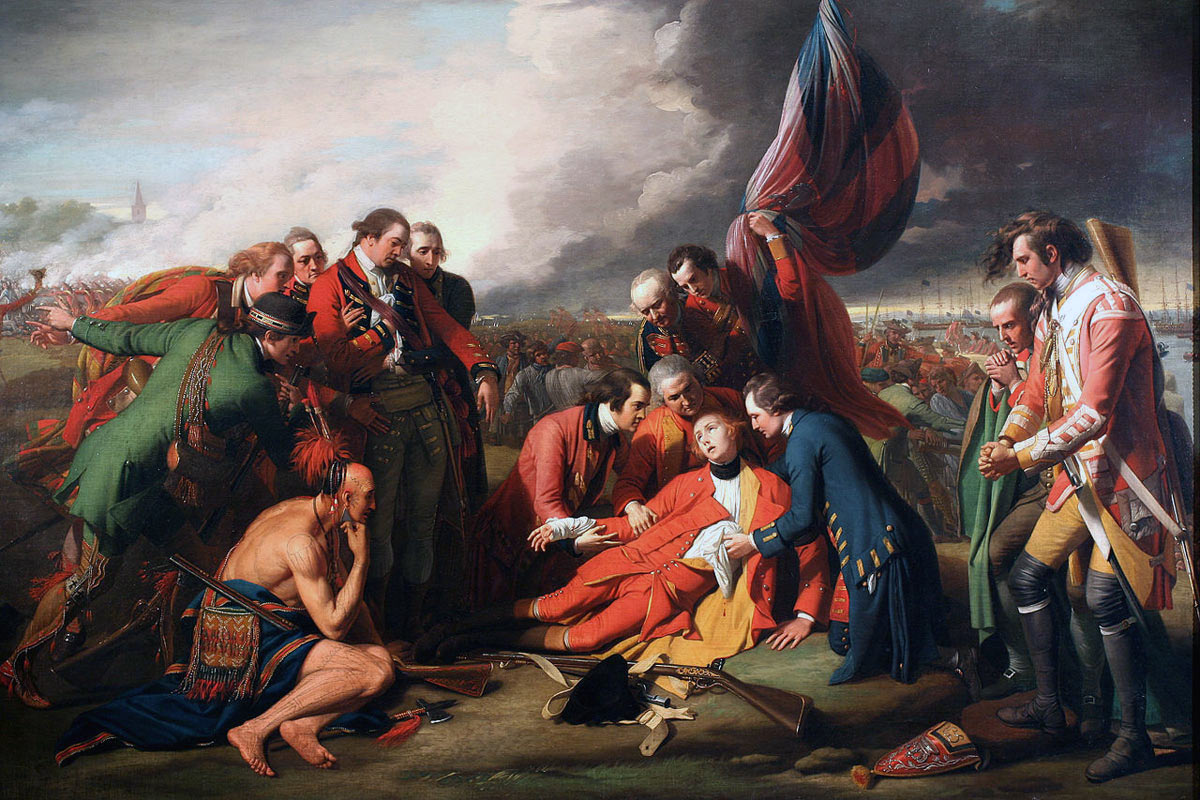

Death of General Wolfe at the Battle of Quebec 13th September 1759 in the French and Indian War or the Seven Years War: picture by Benjamin West
Follow-up to the Battle of Quebec:
After the battle the French civil governor of Canada, M. Vaudreuil left Quebec taking the majority of his surviving force and on 18th September 1759 the governor of Quebec surrendered the city to Townsend. The taking of Quebec was the beginning of the end of French rule in Canada although the British troops had to endure a severe winter in the ruined city.
Anecdotes and traditions from the Battle of Quebec:
- The 47th Foot took to wearing a black line in their lace to commemorate the death of Wolfe.
- The 35th Foot took the plumes from the hats of the Rousillon Regiment and adopted them as the regimental badge. The Rousillon Regiment held the same number in the French line of 35th.
References for the Battle of Quebec:
- History of the British Army by Fortescue
- Montcalm and Wolfe by Parkman
- Wolfe of Quebec by Robin Reilly
The previous battle of the French and Indian War is the Capture of Louisburg
The next battle in the British Battles sequence is the Battle of Lexington and Concorde
To the French and Indian War index