Queen Margaret of Anjou’s crushing defeat of the Yorkists on 30th December 1460, with the death of the Yorkist leader, Richard, Duke of York and his young son, the Earl of Rutland
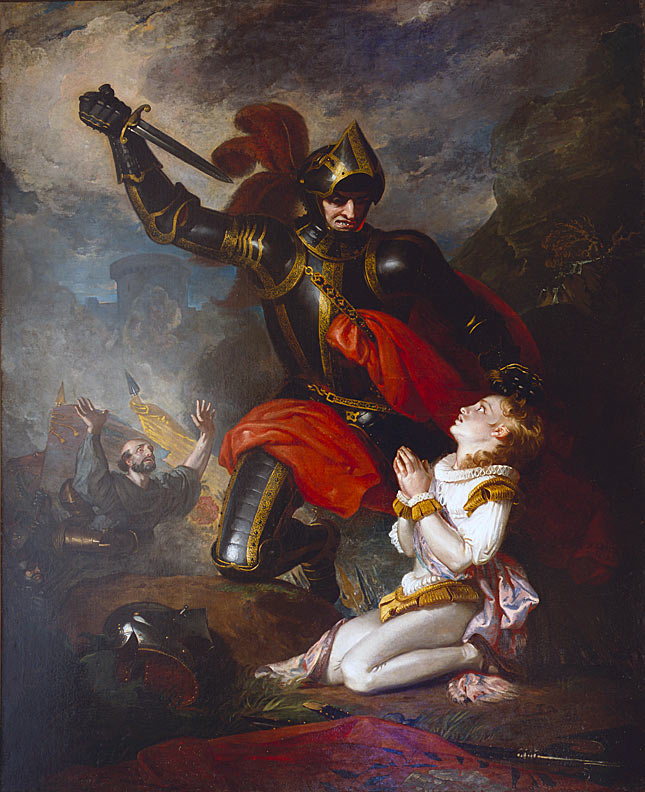

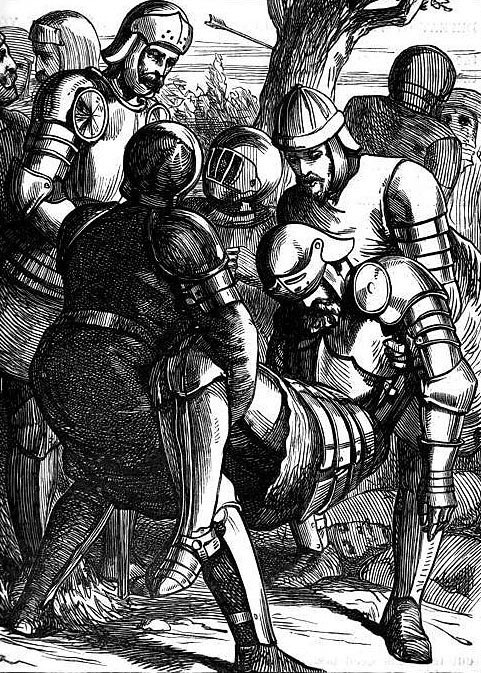
Murder of the Earl of Rutland by Lord Clifford, at the Battle of Wakefield on 30th December 1460 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Charles Robert Leslie
The previous battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Northampton
The next battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Mortimer’s Cross
Battle: Wakefield
War: Wars of the Roses
Date of the Battle of Wakefield: 30th December1460
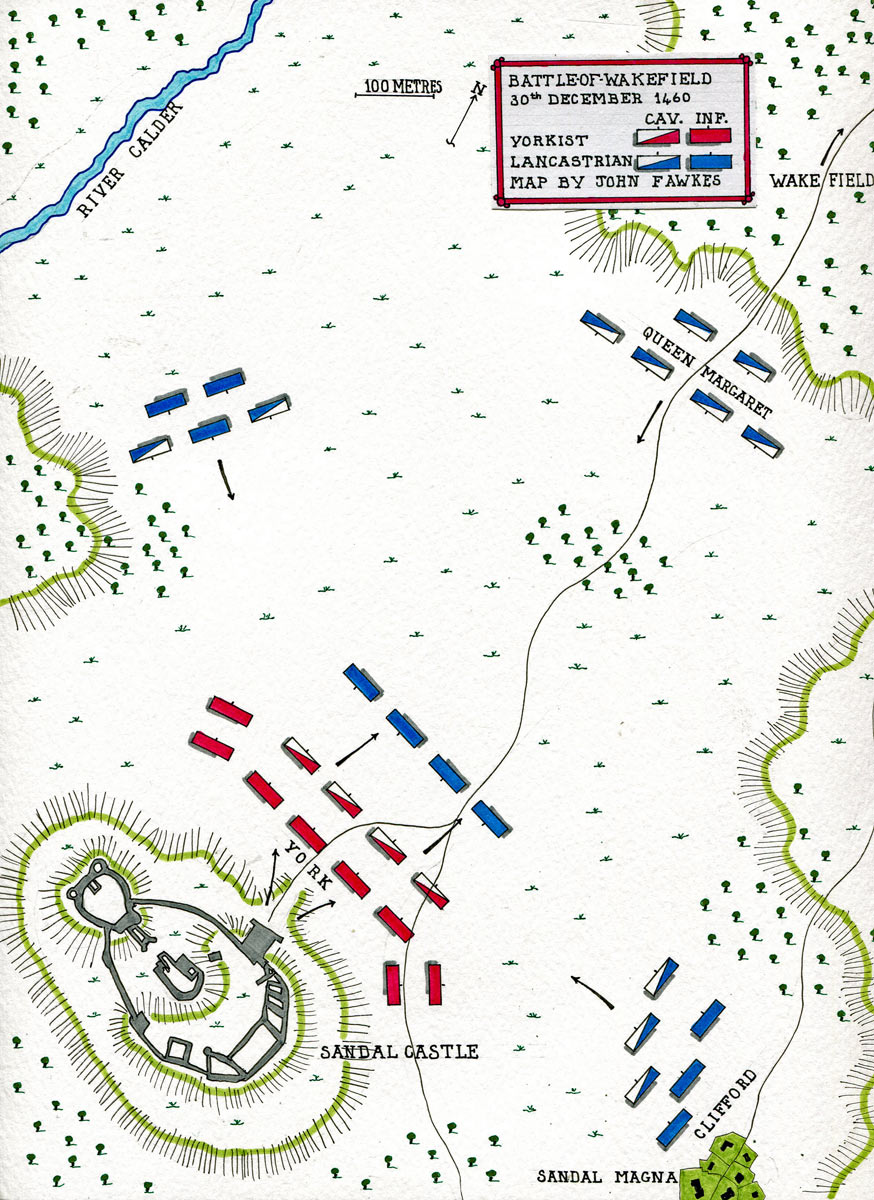
Place of the Battle of Wakefield: At Sandal Castle, across the River Calder from Wakefield, in Southern Yorkshire
Combatants at the Battle of Northampton: Lancastrians against the Yorkists
Commanders at the Battle of Wakefield: Queen Margaret of Anjou, wife of King Henry VI, commanded the Lancastrian army, with the Earl of Clifford.
Richard, Duke of York, commanded the Yorkist army.
Size of the armies at the Battle of Wakefield: The Lancastrian army probably comprised some 15,000 men, the Yorkist army some 4,000 men.
Winner of the Battle of Wakefield: Queen Margaret and her Lancastrian army resoundingly defeated the Yorkists, killing the Duke of York and many of his senior subordinates.
Uniforms, arms and equipment at the Battle of Wakefield: The male commanders and their noble supporters and knights rode to battle on horseback, in armour, with sword, lance and shield.
Their immediate entourage comprised mounted men-at-arms, in armour and armed with sword, lance and shield, although often fighting on foot.
Both armies relied upon strong forces of longbowmen.
Handheld Firearms were beginning to appear on the battlefield but were still unreliable and dangerous to discharge.
Artillery, although widely used in warfare, was heavy, cumbersome and difficult to move and fire.
There is no indication that artillery was used at the Battle of Wakefield.
The end of the Hundred Years War caused numbers of English and Welsh men-at-arms and archers to return to their home countries from France. The wealthier English and Welsh nobles were able to recruit companies of disciplined armed retainers from these veterans, forming the backbone of their field armies.

Queen Margaret of Anjou and Edward, Prince of Wales: Battle of Wakefield on 30th December 1460 in the Wars of the Roses
Background to the Battle of Wakefield: Following the Battle of Northampton on 10th July 1460, the Duke of York returned from Ireland and attempted to persuade the English Parliament to accept his claim to the throne of England, in place of King Henry VI, in thrall to the Yorkists following his capture at the Battle of Northampton.
The Duke of York’s move to take the throne was rejected by Parliament, but an enactment was passed whereby York would become king on the death of King Henry VI.
King Henry VI’s wife, Queen Margaret of Anjou, reacted angrily to this dispossessing of her son, the Prince of Wales and began assembling a Lancastrian army in the North of England.
In this process, the Lancastrians harried the estates of the Duke of York and other prominent Yorkists in the north of England.
In the autumn of 1460, the Duke of York hurried north from London, with his closest supporters and a small army of some 5,000 men.
York reached his manor of Sandal, on the south side of the River Calder from the Yorkshire City of Wakefield, on 21st December 1460 and spent Christmas in Sandal Castle, his army billeted in the neighbouring villages.
York’s son, Edward, Earl of March, was on the move from his estates on the Welsh Borders to support his father with an army.
Queen Margaret of Anjou, with her Lancastrian army, spent Christmas at Pontefract Castle, some 12 miles from Wakefield.
Immediately after Christmas Day, Queen Margaret marched to Wakefield to confront the Duke of York.
———————————-
Account of the Battle of Wakefield:
The question posed in relation to the 1460 Battle of Wakefield is ‘Why did the Duke of York leave Sandal Castle to fight a more numerous Lancastrian army?’
Any day, York’s son Edward, Earl of March, would arrive at Sandal with substantial reinforcements and Queen Margaret did not have the train to mount a regular siege of Sandal Castle.
York had only to sit tight in Sandal Castle, to force the Lancastrians into a humiliating withdrawal or face probable defeat on March’s arrival.
It is said that Queen Margaret sent the Duke of York a number of insulting messages, saying that he was too cowardly to come out of his castle and give battle to an army led by a woman.
Part of the Lancastrian army was immediately outside the castle. The rest were positioned out of sight of the battlements, among the surrounding hills, leading York to underestimate the numbers he faced and to believe that he would win a battle.
On the approach of the Lancastrian army, the Yorkist troops billeted in the neighbouring villages were forced into Sandal Castle, leading to a severe shortage of rations in the castle.
Whatever the reasons he considered most important, the Duke of York was determined to leave Sandal Castle and attack Queen Margaret’s army.
York held a Council of War on 29th December 1460. At the Council, the Duke of York’s senior subordinates, the Earl of Salisbury, Sir Thomas Nevill, Sir David Hall, Sir John Parr, Sir John Mortimer, Sir Hugh Mortimer and several other experienced soldiers urged him to remain within Sandal Castle and await his son March with the reinforcements he was bringing.
In spite of this advice, the Duke of York was determined to sally out and attack the Lancastrian army.
On the morning of 30th December 1460, the gates of Sandal Castle were thrown open. The Yorkist army marched out and attacked the Lancastrian troops in the immediate vicinity of the castle.
The Lancastrians were taken by surprise by the attack. The Duke of York inspired his men to fight with great ferocity and initially the Lancastrians were driven back in disorder.
But the Lancastrians were in greater numbers than the Yorkists and more of Queen Margaret’s army appeared from the woods and hills around Sandal Castle.
The critical moment came when the Earl of Clifford brought the main body of Lancastrian troops up from Sandal Common, where they were encamped and attacked the Yorkists.
From then on, the Yorkists were facing defeat.
The Duke of York was wounded several times and lost control of his army. Panic spread through the Yorkist ranks, leading to a final collapse.
Clifford’s troops surrounded the dwindling Yorkist army and captured the survivors, including the wounded Duke of York.
The Lancastrians occupied Sandal Castle, left by the emerging Yorkists without a garrison.
The few Yorkist troops not taken by the Lancastrians fled into the countryside and the battle was over.
Casualties at the Battle of Wakefield: 2,900 Yorkist soldiers were killed and most of the rest of the Duke of York’s army taken prisoner.
Among the prominent Yorkists killed in the Battle of Wakefield were Sir Thomas Harrington, Sir David Hall, Sir Hugh Hastings, Sir Thomas Nevil, Sir John Mortimer and Sir Hugh Mortimer.
Among the captured Yorkists was the Earl of Salisbury.
Lancastrian casualties are not known but were probably significant.
Follow-up to the Battle of Wakefield: The most notable casualties of the battle were the Duke of York, the leader of the Yorkist cause and a pressing aspirant to the Throne of England and his young son, Edmund, Earl of Rutland.
The Battle of Wakefield is particularly remembered for the incident in which the Earl of Rutland, was killed by the Earl of Clifford, purportedly in revenge for the death of Clifford’s father at the First Battle of St Albans.
As the Yorkist army burst out of Sandal Castle and attacked the Lancastrians assembled outside, the Earl of Rutland, aged seventeen years, was taken by his tutor towards Wakefield in an attempt to escape.
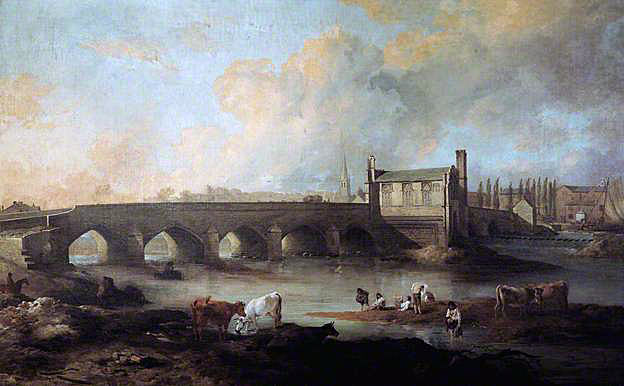
Wakefield Bridge and Chantry Chapel: Battle of Wakefield on 30th December 1460 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Philip Reinagle
Clifford caught Rutland and his tutor about to cross the bridge into Wakefield and killed Rutland.

Duke of York in the mock coronation before being executed after the Battle of Wakefield on 30th December 1460 in the Wars of the Roses
Some accounts of the battle have the Duke of York killed in the fighting. Others, including Shakespeare, have York captured and subject to a mocking coronation by Queen Margaret and Clifford, a paper crown placed on York’s head, before having him executed. Clifford’s last act was to present York with a handkerchief soaked in his son, Rutland’s, blood.
The captured Earl of Salisbury was taken to Pontefract Castle by the Lancastrians and executed.
The Duke of York’s head was taken to York and displayed on the Micklegate, as Shakespeare commented, ‘that York might overlook York.’ The Earl of Rutland’s and the Earl of Salisbury’s heads were also displayed.
The Duke of York’s eldest surviving son, Edward, Earl of March (subsequently King Edward IV), took up the Yorkist cause and advanced on York, fighting the Battle of Towton on Palm Sunday, 29th March 1461.

Coat of Arms of the Duke of York: Battle of Wakefield on 30th December 1460 in the Wars of the Roses
Emblems of the Battle of Wakefield: The Duke of York’s emblem was a Falcon Volant Argent with a Fetterlock Or. The falcon in the emblem was shown attempting to force a lock, being symbolic of York’s attempts to acquire the English Crown. The emblem is not the same as his coat of arms.
Anecdotes and traditions from the Battle of Wakefield:
- The Battle of Wakefield has been given prominence through the death of the Yorkist leader, Richard, Duke of York and the murder of his young son, the Earl of Rutland. Shakespeare portrays the death of the Earl of Rutland in ‘King Henry VI’ Act I, Scene 3. The murder has been the subject of several paintings.
- Sandal Castle was held for King Charles I in the English Civil War by Colonel Bonivant. The castle was besieged by General Poyntz and bombarded into submission in October 1645. With the end of the war, Sandal Castle was dismantled on the orders of Parliament and little of the castle now remains.
- It is said that one, Anthony Trollope, joined the Sandal Castle garrison and persuaded the Yorkists to march out, Trollope having secretly changed sides to the Lancastrians.
- Many of the fleeing Yorkists were killed in Bridge Street, Wakefield, leading to the road being nicknamed ‘Fall Ings’.
- King Edward IV endowed the Chantry Chapel, at the end of Wakefield Bridge, in memory of his father, the Duke of York, and his brother, the Earl of Rutland, both killed at the Battle of Wakefield.
References for the Battle of Wakefield:
Battle of Wakefield 1460 by Philip Haigh
Battlefield Walks in Yorkshire by David Clark
Battles in Britain by William Seymour
Wars of the Roses by Michael Hicks
Chronicles of the Wars of the Roses
British Battles by Grant
The previous battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Northampton
The next battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Mortimer’s Cross