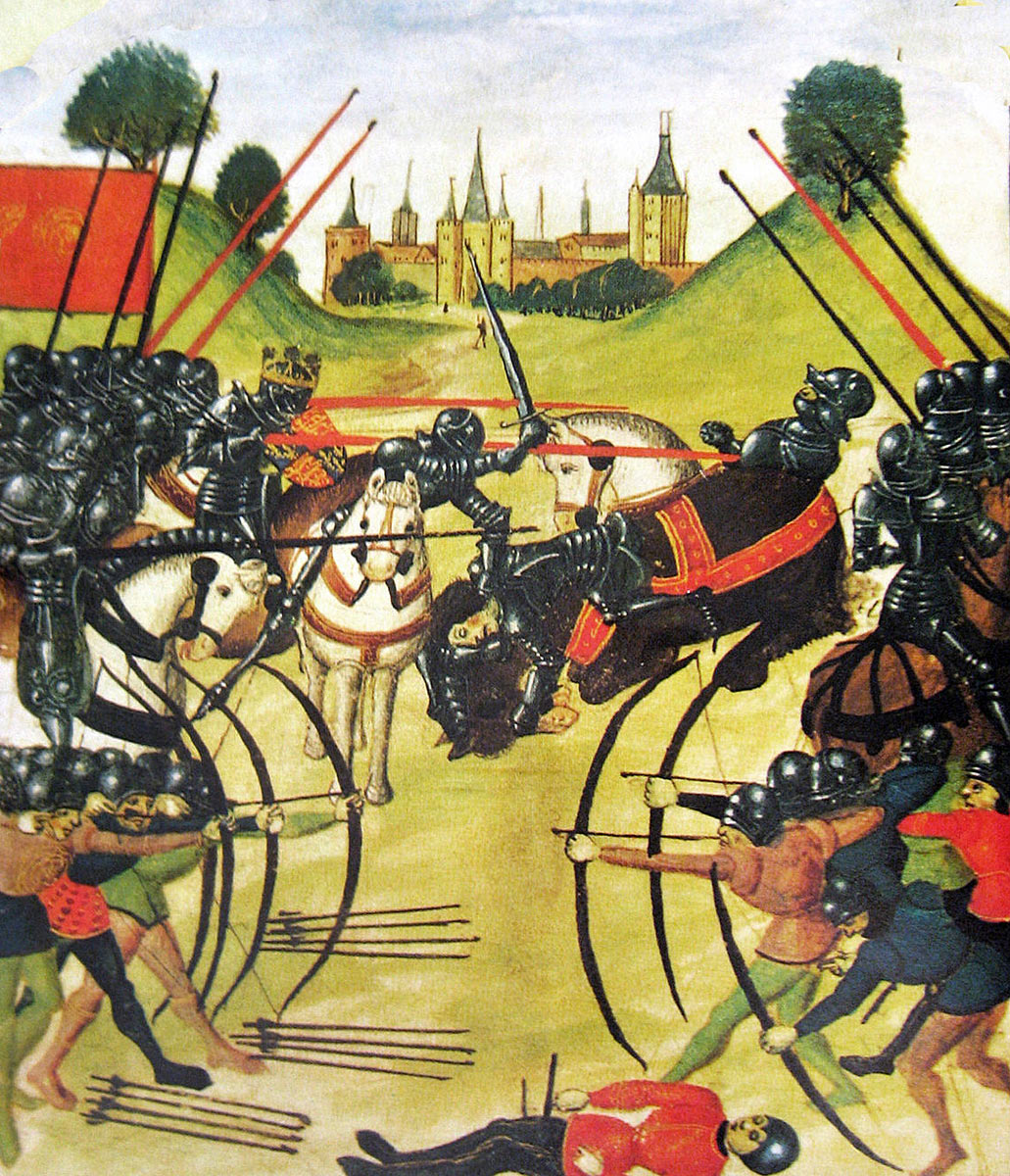
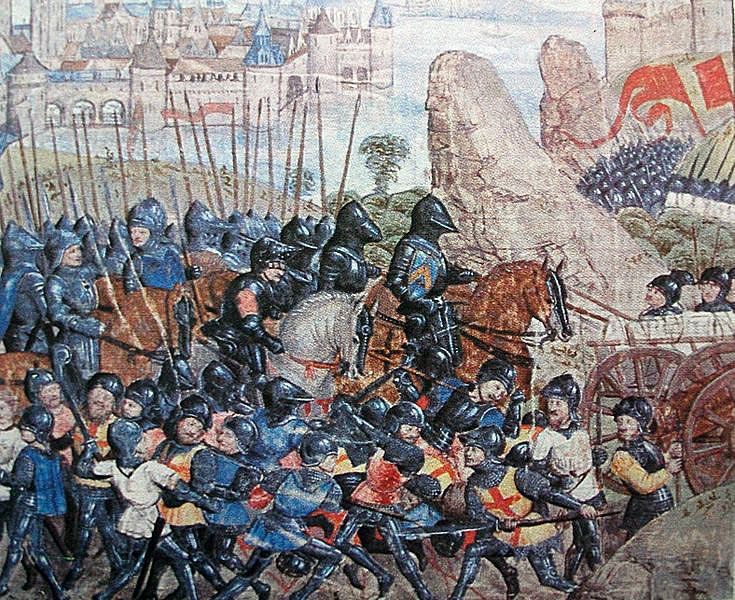
Final defeat of the Lancastrians on 4th May 1471, with the death of Edward Prince of Wales and the murder in the Tower of King Henry VI, leaving the Yorkist King Edward IV free to continue his reign unopposed
The previous battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Barnet
The next battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Bosworth Field
Battle: Tewkesbury
War: Wars of the Roses
Date of the Battle of Tewkesbury: 4th May 1461
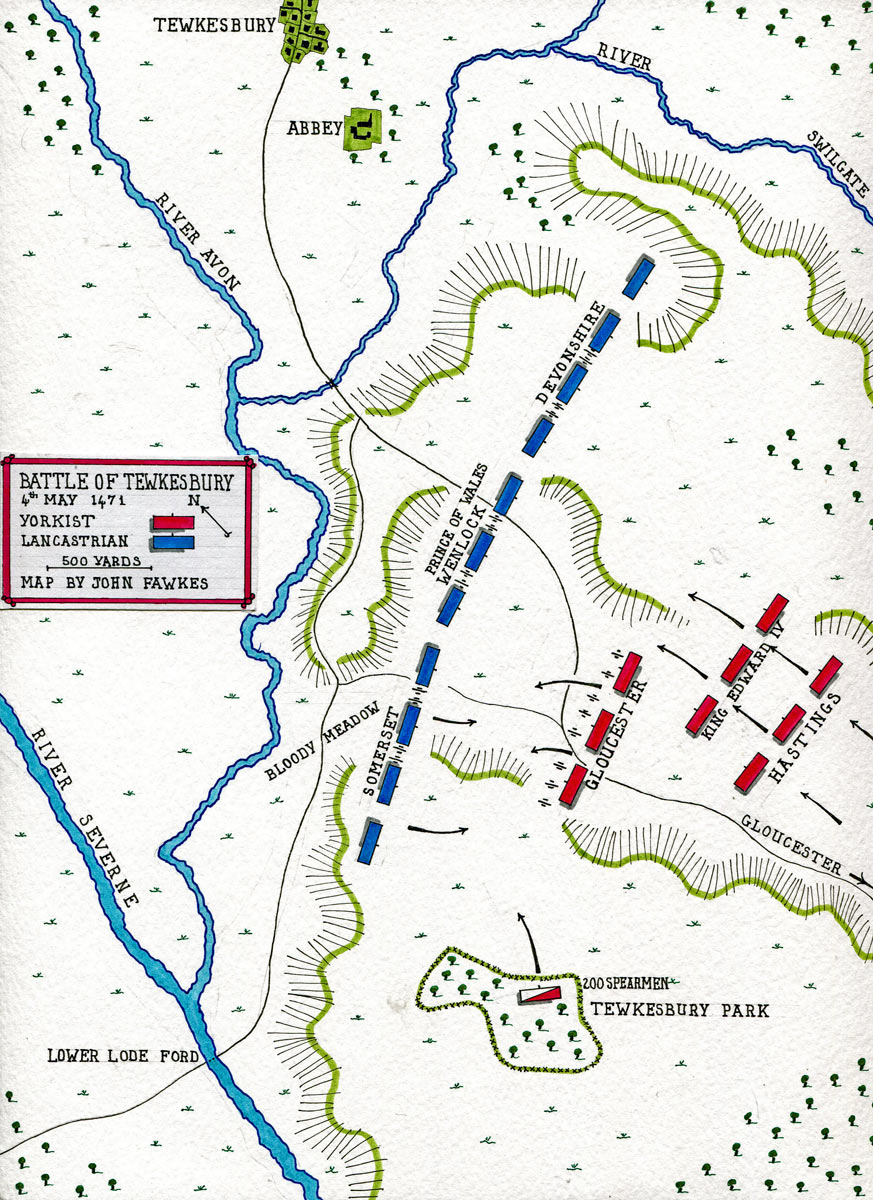
Place of the Battle of Tewkesbury: At Tewkesbury in Gloucestershire on the River Severn, near to the border of England and Wales
Combatants at the Battle of Tewkesbury: Lancastrians against the Yorkists
Commanders at the Battle of Tewkesbury:
The Duke of Somerset, Lord Wenlock and the Earl of Devonshire commanded the Lancastrian army, under the nominal leadership of Edward, Prince of Wales, son of the Lancastrian King Henry VI.
King Edward IV, with his brother, Richard, Duke of Gloucester (later King Richard III) and Lord Hastings, commanded the Yorkist army.
Size of the armies at the Battle of Tewkesbury: The Lancastrian army probably comprised some 6,000 men; the Yorkist army some 5,000 men.
Winner of the Battle of Tewkesbury: The Yorkists, decisively.
Uniforms, arms and equipment at the Battle of Tewkesbury: The commanders and their noble supporters and knights rode to battle on horseback, in armour, with sword, lance and shield.
Their immediate entourage comprised mounted men-at-arms, in armour and armed with sword, lance and shield, although often fighting on foot.
Both armies relied upon strong forces of longbowmen.
Handheld firearms were beginning to appear on the battlefield but were still unreliable and dangerous to discharge.
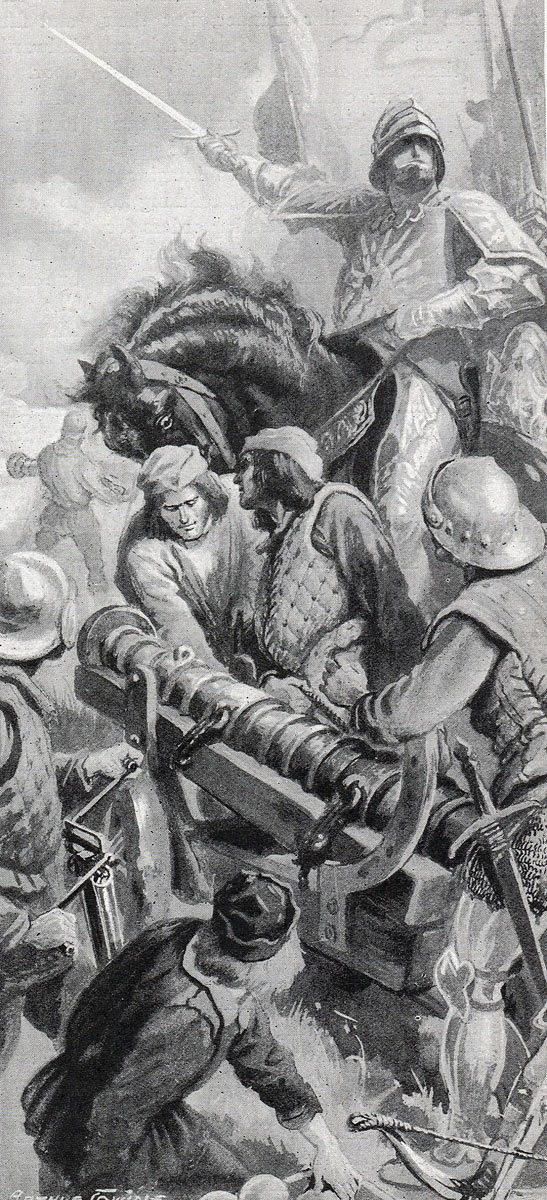
Artillery, although widely used in warfare, was heavy, cumbersome and difficult to move and fire.
Both sides possessed artillery. Some of the Lancastrian cannon were taken by a raiding party from the Gloucester garrison.
The Yorkist artillery was the larger and the better served.
The end of the Hundred Years War caused numbers of English and Welsh men-at-arms and archers to return to their home countries from France. The wealthier English and Welsh nobles were able to recruit companies of disciplined armed retainers from these veterans, forming the backbone of their field armies.
Background to the Battle of Tewkesbury: On the day of the Battle of Barnet, 14th April 1471, Queen Margaret of Anjou, wife of the Lancastrian King Henry VI, landed at Weymouth to join the Earl of Warwick in his attempt to repel the return of the Yorkist King Edward IV.
Queen Margaret was filled with despair at the news of Barnet and Warwick’s death and would have returned to France, were it not for the determination of her eighteen-year-old son, Edward, Prince of Wales, to continue the campaign against King Edward IV, supported as he was by the influential Duke of Somerset.
Any attempt to capture London was out of the question after the defeat at Barnet.
Lancastrian noblemen joined Queen Margaret’s army, with significant numbers of troops, as she marched north, to cross into Wales and join Jasper Tudor.
Intending to bring the Lancastrians to a last decisive battle, King Edward IV left London for Windsor, to await the arrival of re-inforcements for his Yorkist army and information on Queen Margaret’s intentions.
Edward left Windsor and began his march to the West Country on 24th April 1471.
The Lancastrian army, collecting supplies and additional men on its way, reached Bristol on 1st May 1471, the day Edward reached the Wiltshire town of Malmesbury.
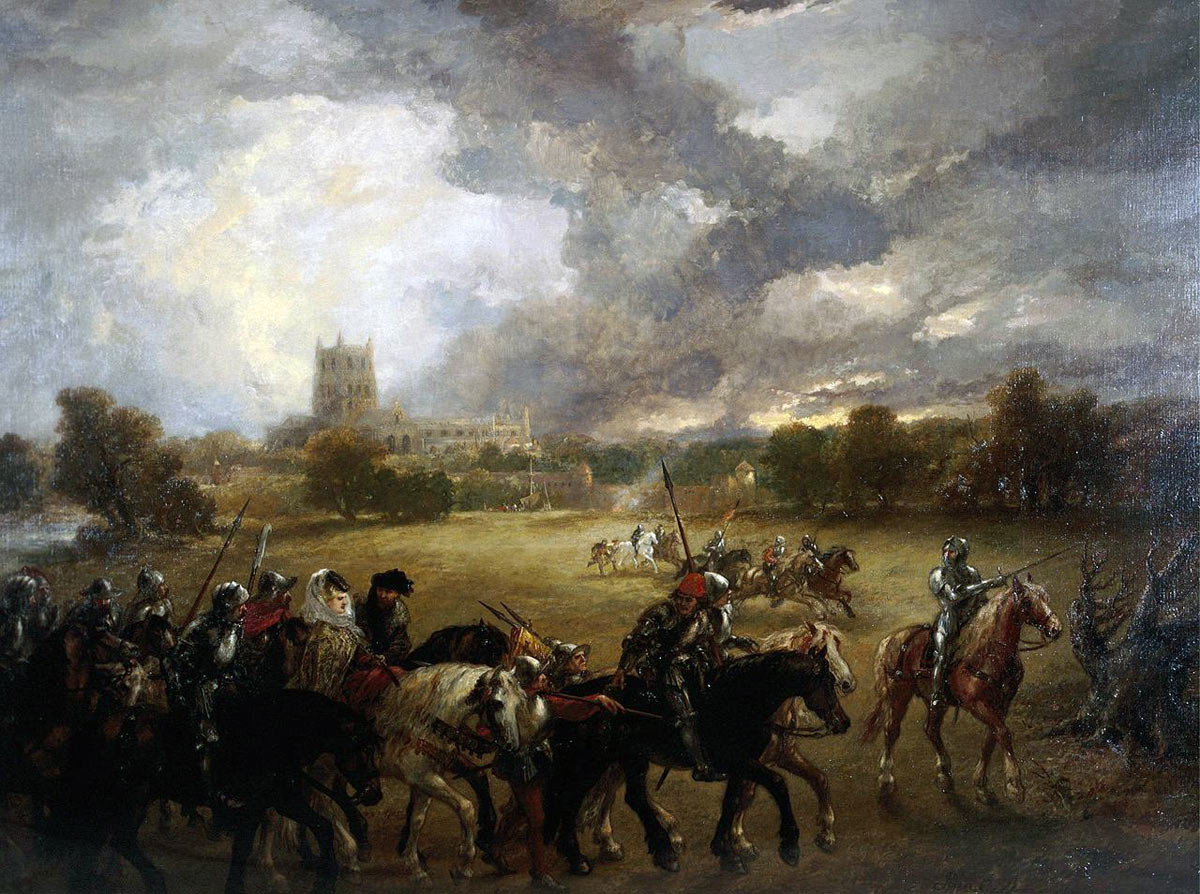

Capture of Queen Margaret of Anjou after the Battle of Tewkesbury on 4th May 1471 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by John Gilbert
Sensing the need for speed, Queen Margaret and Somerset spent only a day in Bristol, before marching for Gloucester, sending parties out to the east, to give Edward the impression that they might still be intending an advance on London.
Margaret and Somerset delayed the Yorkist army, by giving the impression they intended battle at Sodbury, before disengaging and heading with all speed towards Gloucester, where they intended to cross the River Severn.
The Lancastrian army reached Gloucester on the morning of Friday, 3rd May 1471, after marching through the night, to find the Yorkist garrison ready for them and the gates firmly shut.
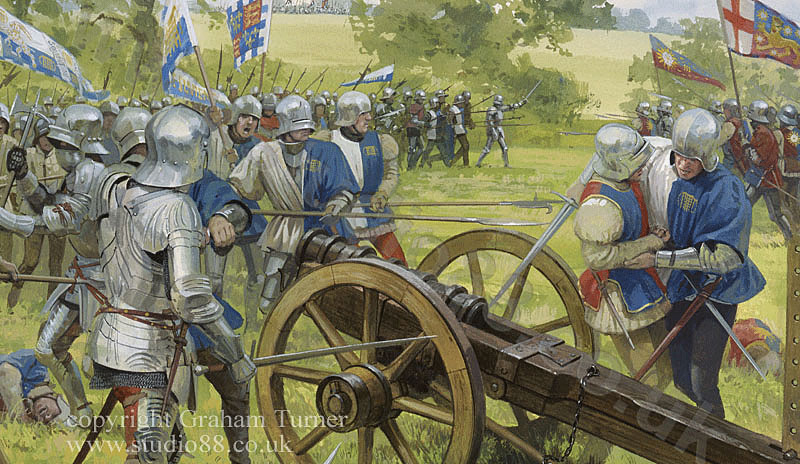

Battle of Tewkesbury on 4th May 1471 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Graham Turner
A siege was out of the question, with Edward’s army close behind them. Unable to cross the River Severn at Gloucester, the Lancastrians were forced to march a further ten miles to the north-east, to reach a crossing point over the river.
In the late afternoon of 3rd May 1471, Queen Margaret’s army reached Tewkesbury, where the River Severn could be crossed by the Lower Lode ford, a mile downstream of Tewkesbury Abbey, below its junction with the River Avon.
The Lancastrian army was too exhausted to continue and it could be disastrous for it to be caught by Edward’s men in the course of making the crossing.
Queen Margaret and the Duke of Somerset decided they would give battle to Edward’s Yorkist army when it came up the following day, Saturday, 4th May 1471.
———————————-
Account of the Battle of Tewkesbury:
King Edward IV’s army marched some 30 miles to reach Tewkesbury, late on 4th May 1471, hard on the heels of their Lancastrian opponents.
Edward’s troops had eaten or drunk little during the march.
Arriving within three miles of the Lancastrian positions, the Yorkist army pitched camp for the night, intending to attack the next day.
The following morning was spent in a careful reconnaissance of the Lancastrian army’s position to the south-west of the Abbey of Tewkesbury.
The Lancastrians were formed with the Duke of Somerset commanding the right division, Lord Wenlock commanding the centre and the Earl of Devonshire commanding the left division.
Edward, Prince of Wales, nominally through his rank the commander-in-chief, stood with the central division.
In the mid-morning of 5th May 1471, Edward formed his army with the van commanded by his brother, Richard, Duke of Gloucester, the centre by himself and the rear division commanded by Lord Hastings.
About 400 yards to the Yorkist left was the fenced parkland of Tewkesbury Park.
Edward ordered 200 mounted spearmen to take position inside the park perimeter, to provide him with a flank guard.
The Yorkists began the battle by advancing on the Lancastrian positions.
Hampered by the difficult country, intersected by ditches, hedges and ‘evil lanes’, Gloucester, at Edward’s direction, halted his advance and began a barrage of Somerset’s division by his cannon and archers.
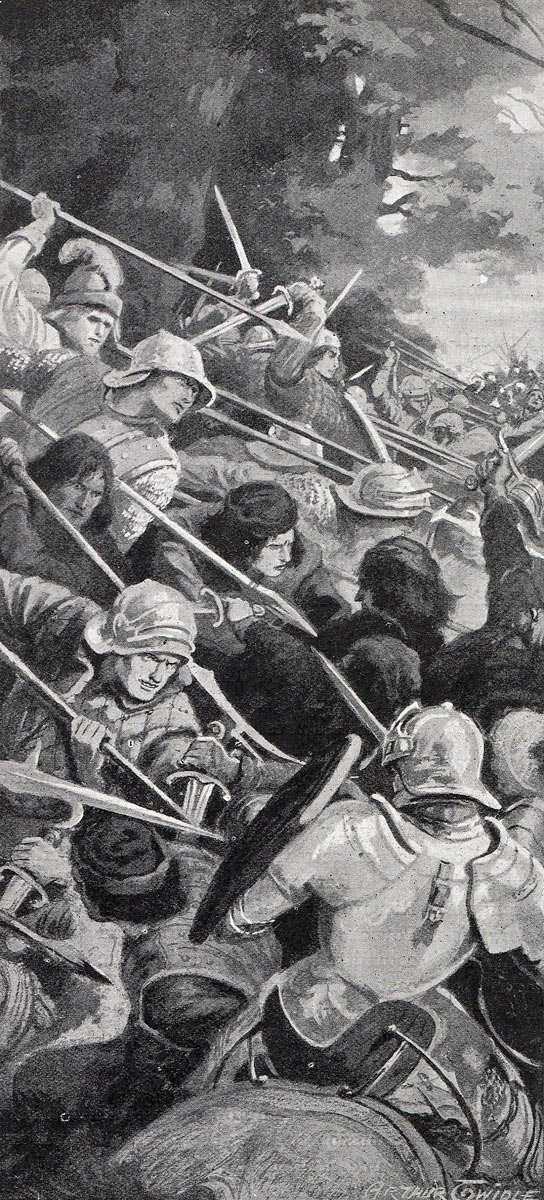

Attack of Gloucester’s Yorkist van at the Battle of Tewkesbury on 4th May 1471 in the Wars of the Roses
The Lancastrians attempted to return the fire, but their artillery was inferior to the Yorkists’ and cannon had been lost to a raiding party led by the Yorkist governor of the Gloucester garrison as the Lancastrian army straggled away from the city.
Somerset resolved to escape from the Yorkist barrage by launching a flank attack on Gloucester’s division.
Directing Wenlock to support him, Somerset advanced his men into the area between the Yorkist left flank and Tewkesbury Park, exactly the stratagem King Edward was guarding against, by positioning the 200 mounted spearmen in the park.
Gloucester wheeled his division and launched it in attack on Somerset’s men, while the 200 Yorkist mounted spearmen attacked Somerset in the right flank.
Wenlock failed to provide the support expected by Somerset, as the Lancastrian centre and left came under a sustained assault by the rest of the Yorkist army, led by King Edward IV.
Attacked in the front and flank and unsupported by Wenlock, Somerset’s division was repelled in confusion and the soldiers began to flee the battlefield.
It is said that Somerset encountered Lord Wenlock as he left the field, upbraided him for failing to support his attack on Gloucester’s division and split his head open with his battle mace.
The collapse of Somerset’s division was quickly followed by the disintegration of the other two Lancastrian divisions, under the vigorous attack of Edward’s and Lord Hasting’s troops.
As at Towton and Barnet, the Lancastrian defeat was followed by the killing of all those who did not drown in the rivers, the Spilgate stream or in a large mill-pond and were not swift enough to keep ahead of the victorious Yorkists in pursuit.
The area between the battlefield and Tewkesbury Abbey became known as ‘the Bloody Meadow’.
King Edward IV had won the battle that assured his grip on the English Throne.
Casualties at the Battle of Tewkesbury:
It seems likely that around 2,000 Lancastrians were killed in the battle and subsequent pursuit.
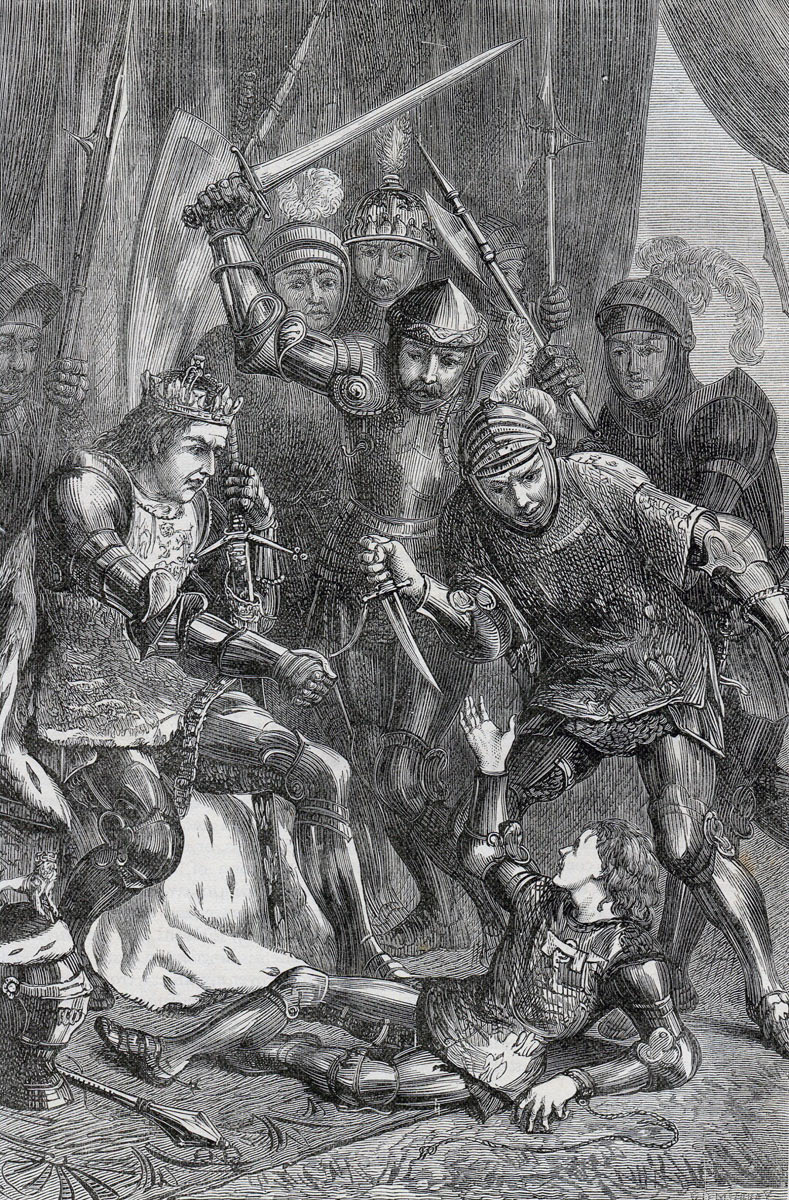

Murder of Edward, Prince of Wales, after the Battle of Tewkesbury on 4th May 1471 in the Wars of the Roses
Edward, Prince of Wales: The Lancastrian figurehead, Prince Edward, died in the Battle of Tewkesbury. Tradition, fostered by Shakespeare, has it that Prince Edward was captured and taken before King Edward IV. Edward, in a rage, struck the Prince, who was then stabbed to death by the other Yorkist leaders.
Other authorities say that Prince Edward died in the battle, at the hands of the Duke of Clarence’s men.
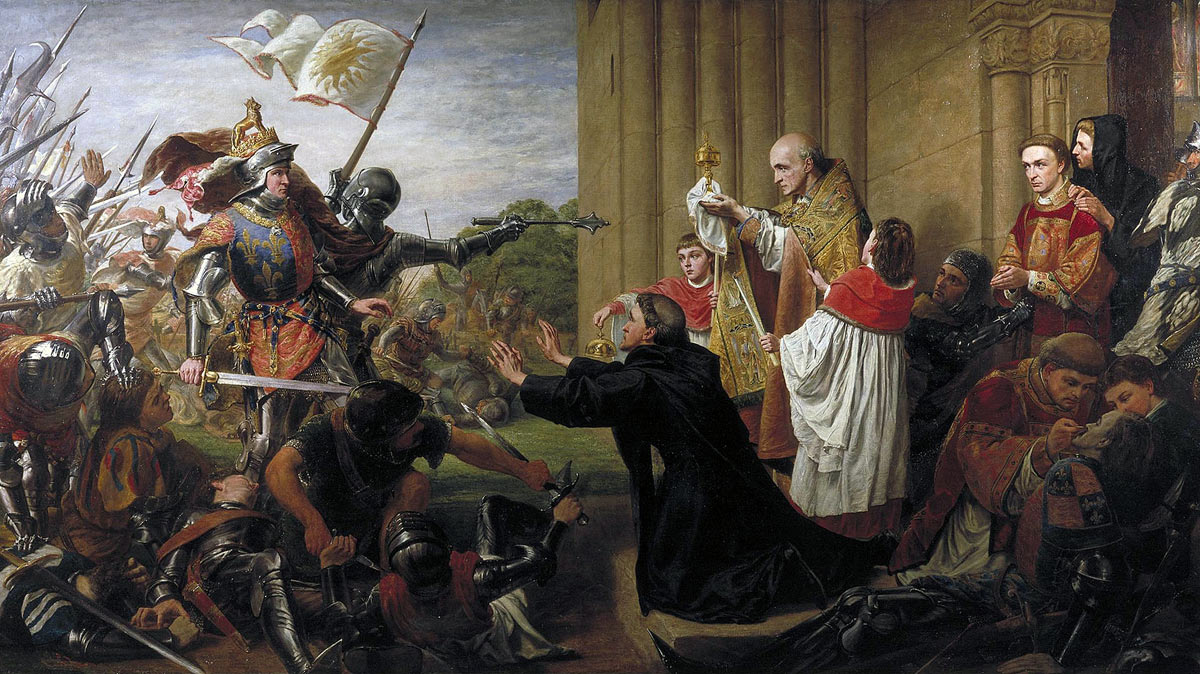

King Edward IV at the gates of Tewkesbury Abbey demanding the surrender of the Duke of Somerset from the Abbot after the Battle of Tewkesbury on 4th May 1471 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Richard Burchett
The Duke of Somerset, with 15 others, escaped to Tewkesbury Abbey, where they sought sanctuary. The abbot insisted that King Edward might not take them from the abbey’s sanctuary without guaranteeing their safety. It is said the Yorkists provided this guarantee, but the next day dragged Somerset and his companions from the abbey and, after summary trial, executed them.
Other senior Lancastrians to die in the battle were; the Earl of Devonshire, Lord Wenlock (reputed to have been killed by the Duke of Somerset), John Beaufort Marquis of Dorset, Lord John Somerset, Sir John and Sir Thomas Seymour, Sir John Delves, Sir Edward Hampden, Sir Robert Whittingham and Sir John Lewknor.

Execution of the Duke of Somerset after the Battle of Tewkesbury on 4th May 1471 in the Wars of the Roses
Most of the senior Lancastrians who died at or immediately after the Battle of Tewkesbury were buried in the churchyard of Tewkesbury Abbey.
Probably around 500 Yorkists were killed.
There does not appear to be a record of the casualties among the senior Yorkists.
Follow-up to the Battle of Tewkesbury: Other than an unsuccessful attempt to take London in the period after the Battle of Tewkesbury, by a Lancastrian leader known as ‘the Bastard of Fauconberg’, the Lancastrian challenge to the reign of King Edward IV ended with their heavy defeat at the Battle of Tewkesbury, only to revive with the Tudor overthrow of Edward’s brother, the Duke of Gloucester as King Richard III, at the Battle of Bosworth in 1485.
Queen Margaret of Anjou was taken prisoner, after escaping across the River Severn, the day after the Battle of Tewkesbury. She joined her husband, King Henry VI, in the Tower of London, until she was ransomed by her cousin, King Louis XI of France, five years later.
Deprived of her estates, Margaret returned to France, where she lived until 1482.
Margaret of Anjou was a fiery and remarkable person in English History.
King Henry VI died in the Tower of London in mysterious circumstances, probably murdered, on King Edward IV’s return to London.
Anecdotes and traditions from the Battle of Tewkesbury:
- Grant describes how a knight put on his amour: ‘He put on first his sabatynes, or steel clogs; secondly, the greaves, or shin-pieces; thirdly, the cuisses, or thigh-pieces; fourthly, the breech of mail; fifthly, the tuillettes (hinged plates before the thigh); sixthly, the breastplate (front and back); seventhly, the vambraces or arm-covers; eigthly, the rere-braces, for covering the remaining part of the arm to the shoulder; ninthly, the gauntlets; tenthly, the dagger was hung; eleventhly, the short sword; twelfthly, the surcoat was put on; thirteenthly, the helmet; fourteenthly, the long sword was assumed; and, fifteenthly, the penoncel, which he carried in his left hand.’
References for the Battle of Tewkesbury:
Battles in Britain by William Seymour
Wars of the Roses by Michael Hicks
Chronicles of the Wars of the Roses
British Battles by Grant
The previous battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Barnet
The next battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Bosworth Field