A resounding defeat in the north of England for the Parliamentary Army of Sir Thomas Fairfax, fought on 30th March 1643
The previous battle in the English Civil War is the Battle of Edgehill
The next battle in the English Civil War is the Battle of Stratton
To the English Civil War index
Battle: Seacroft Moor
Battle: Seacroft Moor
War: English Civil War
Date of the Battle of Seacroft Moor: 30th March 1643
Place of the Battle of Seacroft Moor: to the north east of Leeds on the road from Tadcaster in Yorkshire. The name of the battle comes from Sir Thomas Fairfax’s report of his defeat to Parliament. Fairfax took the name from the village on the outskirts of Leeds where he was heading. The moor on which the battle took place was Whinmoor.

Lieutenant-General George Goring Royalist Commander at the Battle of Seacroft Moor 30th March 1643 in the English Civil War
Combatants at the Battle of Seacroft Moor:
The forces of King Charles I against the forces of Parliament.
Generals at the Battle of Seacroft Moor: General George Goring commanded the force of Royalist Horse that fought the battle.
Sir Thomas Fairfax commanded the body of Parliamentary Foot and small contingent of Horse.
Size of the armies at the Battle of Seacroft Moor:
The Royalist army comprised 20 troops of Horse and Dragoons, some 2,000 men.
Sir Thomas Fairfax’s force comprised some 4,000 Foot and a small force of probably 200 Horse and Dragoons.

Sir Thomas Fairfax Parliamentary Commander at the Battle of Seacroft Moor 30th March 1643 in the English Civil War
Winner of the Battle of Seacroft Moor: The Parliamentary force was heavily defeated by the Royalists.
Uniforms, arms and equipment at the Battle of Seacroft Moor:
See this section in the Battle of Edgehill.
Background to the Battle of Seacroft Moor:
The origins of the English Civil War are dealt with under this section in the Battle of Edgehill.
From the beginning of the English Civil War engagements between Royalists and Parliamentary supporters took place in every county of England and Wales. Only in certain areas did the fighting take on the dimensions of substantial field armies contesting full battles.
Yorkshire, Lancashire and the English Border counties were of importance to both sides. There was substantial wealth and population in these areas and the east coast ports provided a route for supplies of equipment and ammunition for the Royalists while the west coast ports gave the Royalists access to re-inforcements from Ireland. Holding the border counties enabled the Royalists to hinder Scots Covenanter forces entering England in support of Parliament.

Ferdinando Lord Fairfax Parliamentary Commander in the North of England: Battle of Seacroft Moor 30th March 1643 in the English Civil War
It was eventually the loss of the North of England following the Royalist defeat at the Battle of Marston Moor on 2nd July 1644 outside the City of York that began the final Royalist collapse in the North of England and disaster for King Charles I.
At the beginning of 1643 the Royalists held sway in the North of England.
Parliament led by Ferdinando Lord Fairfax held the West Yorkshire wool working towns of Leeds, Bradford and Halifax while supplies were brought in for the Parliamentary forces through the ports of East Yorkshire, particularly the Important Garrison Port of Hull.
Lord Fairfax’s field army lay at Selby to the south of York.
The Royalists occupied the City of York with the Earl of Newcastle’s field army at Clifford Moor to the north-west of York.
A series of events changed the strategic situation. On 22nd February 1643 Queen Henrietta Maria arrived at the Yorkshire port of Bridlington by sea with a substantial quantity of arms and a group of English officers recruited from European armies to fight for King Charles I. The Queen escorted by Dutch naval ships eluded a Parliamentary naval squadron and was met at Bridlington by the Earl of Newcastle.
The Queen waited in Bridlington until the time was right to convey her valuable cargo south to the King’s army in Oxford later in the year.
The arrival of the Queen in East Yorkshire had a significant impact on waverers. One of these was Sir Hugh Cholmondeley the Governor holding the important port of Scarborough. Cholmondeley committed himself to the King securing Scarborough for the Royalist side.
Sir John Hotham the Governor of the important port of Hull another waverer was influenced by the arrival of the Queen in East Yorkshire and the changing sides of his friend Sir Hugh Cholmondeley.
Hotham’s refusal to permit entry into Hull to King Charles I on 29th April 1642 before the English Civil War began, thereby denying access to the arsenal of weapons and ammunition stored for the Scots War which were then shipped to London, was a significant reverse for the King.
Lord Fairfax now took the view that the position of his Parliamentary field army at Selby was threatened and that he must move his army to Leeds in West Yorkshire.
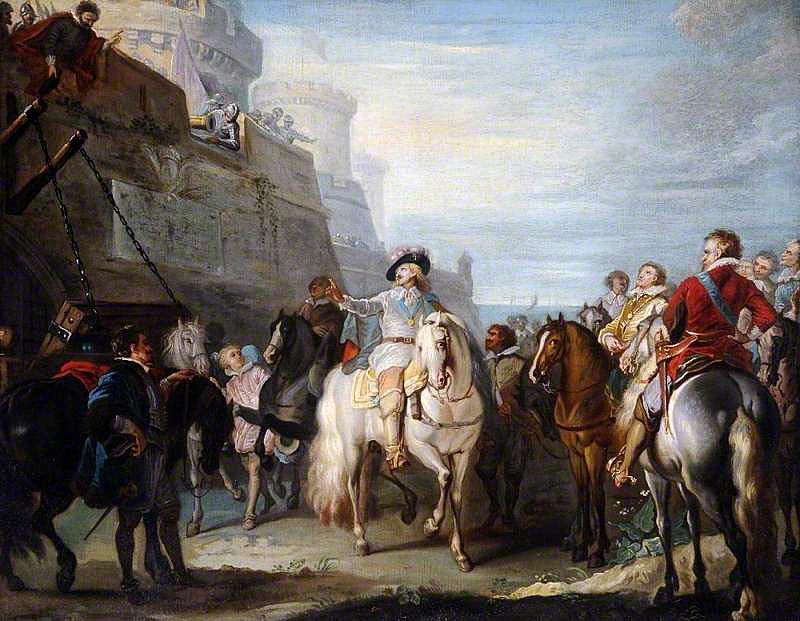

King Charles I refused entry to Beverley Gate Hull by Sir John Hotham on 29th April 1642 in the English Civil War
In order to distract the Earl of Newcastle while he marched with his cumbersome artillery train to Leeds Lord Fairfax dispatched his son Sir Thomas Fairfax with a significant force of Foot and a small body of cavalry to take Tadcaster, thereby appearing to threaten the important Royalist City of York.
Tadcaster was held by a force of some 300 Royalist Foot which on the approach of Sir Thomas Fairfax hastily withdrew to York.
While Newcastle with his Royalist Army on Clifford Moor was well positioned to move south and intercept Lord Fairfax’s slow march to Leeds he was, as Lord Fairfax intended, distracted by the move against Tadcaster fearing that the Parliamentary army intended an attack on the City of York.
Newcastle dispatched Lieutenant-General Goring, his general of Horse with a force of 20 troops of Horse, some 2,000 men, to clear the Parliamentary force out of Tadcaster. General King marched in support of Goring with a powerful force of Royalist Foot and some guns but took no part in the ensuing Battle of Seacroft Moor.
Sir Thomas Fairfax, with his instructions simply to distract the Royalists from the Parliamentary march to Leeds, spent some hours levelling the defences of Tadcaster before marching his men out of Tadcaster on the road to Leeds across Bramham Moor.
Account of the Battle of Seacroft Moor:
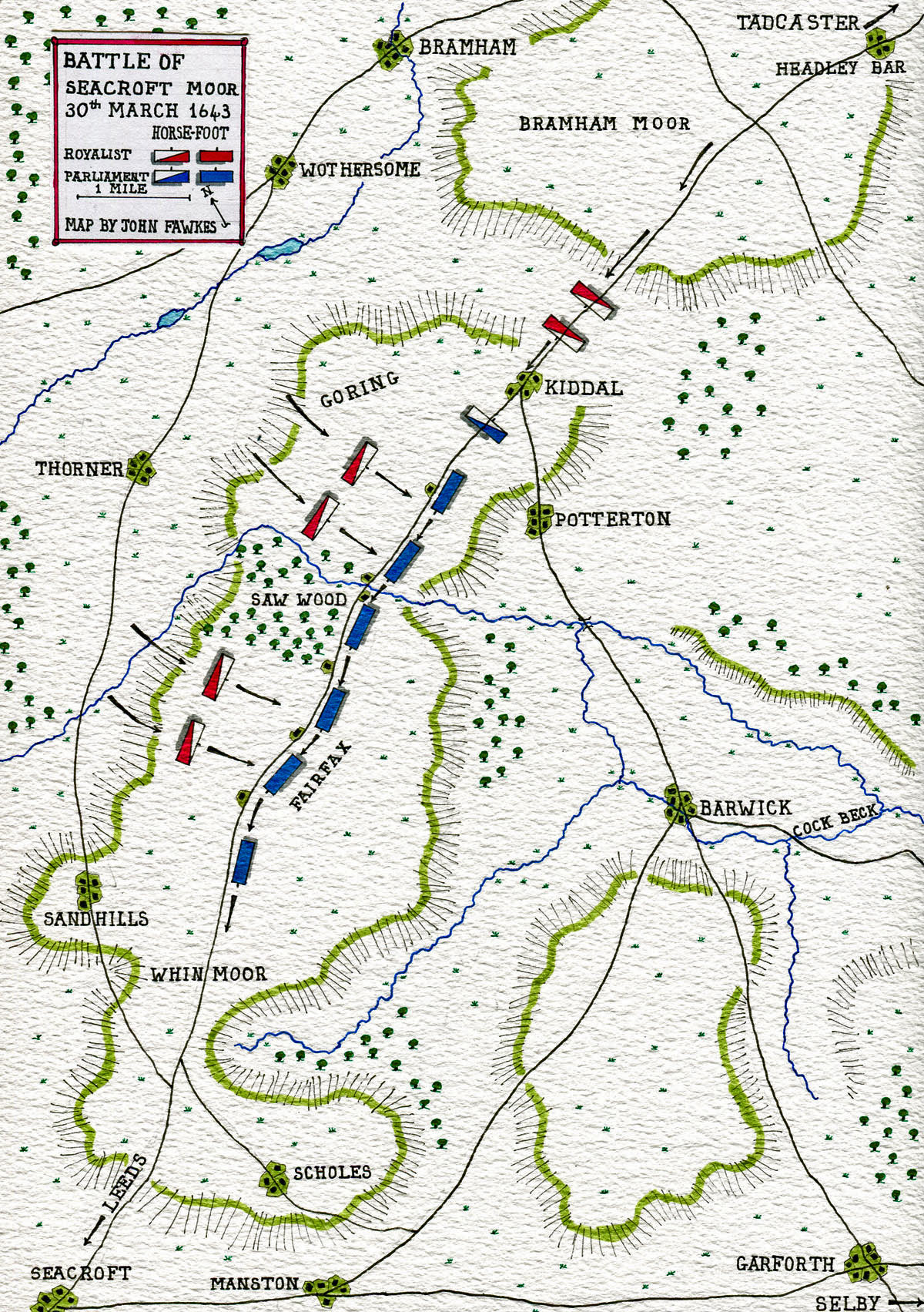
Lieutenant-General Goring on arrival on 30th March 1643 at Tadcaster took up the pursuit of Sir Thomas Fairfax’s men.
Sir Thomas Fairfax used his small party of some 200 Horse and Dragoons to block the narrow lanes leading up onto Bramham Moor on the road to Leeds.
After this initial operation Fairfax hurried to catch up the Parliamentary Foot.
To his irritation Fairfax found that the Foot were halted and dispersed among the village houses seeking refreshment in the unseasonable heat of the day.
In his account to Parliament of the battle Sir Thomas Fairfax stated that he split the Parliamentary Foot into two divisions and sent them on down the Leeds road while he continued to hold back the pursuing Royalist Horse.
Fairfax’s Foot marched across Bramham Moor and onto a second moor called Whinmoor (erroneously labelled Seacroft Moor by Fairfax in his report to Parliament) but again the soldiers dispersed into the surrounding houses in search of refreshment in the hamlet of Kidall where Fairfax again came up with them.
By this time the Royalist Horse were no longer just behind the Parliamentary column. A section of Lieutenant-General Goring’s force took a side road to the north of the Leeds road and now came in on the Parliamentary flank while the pursuing Royalists charged up the road from behind them on the dispersed Parliamentary Foot.
The Parliamentary Foot, many of whom were inexperienced country folk from Bradford, were overwhelmed by the Royalist charge.
Fairfax’s men were not well equipped and there were few pikemen, the essential component for a force of Foot to hold off attacking cavalry while musketeers reload. Widely dispersed among the country dwellings the Parliamentary Foot could not be persuaded to adopt a proper formation as Goring’s horsemen rode them down.
The Royalist Horse charged through the whole Parliamentary force, cutting many Parliamentary soldiers down or taking them prisoner.
Sir Thomas Fairfax and some of his officers got away but the majority of his force was killed, captured or dispersed.
Casualties at the Battle of Seacroft Moor:
Sir Thomas Fairfax’s Parliamentary force lost 100 men killed and 1,000 taken prisoner by the Royalist Horse commanded by General George Goring. Probably the majority of the remainder deserted to their homes.
Royalist casualties were small, the number unrecorded.
Follow-up to the Battle of Seacroft Moor:
Sir Thomas Fairfax reached Leeds two hours after his father arrived with the main Parliamentary army from Selby.
Sir Thomas Fairfax stated of the Battle of Seacroft Moor: ‘This was one of the Greatest losses we ever received ….”
Fairfax was faced with an outraged clamour from the wives and families of the Parliamentary soldiers lost at the Battle of Seacroft Moor. Such was the outcry that Fairfax launched an attack on Wakefield where the Royalists were thought to be holding the prisoners from the Battle of Seacroft Moor.
Anecdotes and traditions from the Battle of Seacroft Moor:
- General George Goring became Lord George Goring in November 1644 on the elevation of his father as 1st Earl of Norwich. Before the English Civil War Goring served in the Dutch Army and was severely wounded at the Siege of Breda in 1637. On his return to England Goring was appointed Governor of Portsmouth. In 1641 Goring was part of the Royalist ‘Army Plot’ intended to overawe Parliament into complying with the King’s will. Goring appears to have betrayed the plot to a Parliamentary sympathizer. With the outbreak of the English Civil War Goring was besieged in Portsmouth which he was compelled to surrender in September 1642. After a brief period abroad with Queen Henrietta Maria Goring was appointed lieutenant-general of the Earl of Newcastle’s Horse in the Royalist Army of the North of England leading to the Battle of Seacroft Moor. Clarendon describes Goring as having ‘wit, and courage, and understanding and ambition, uncontrolled by any fear of God or man’ but lacking industry. Clarendon declared ‘of all his qualifications dissimulation was his masterpiece’. Goring took a prominent role in the Royalist Army at the Battle of Marston Moor. Goring’s failure to bring his army and particularly his cavalry to join the King’s Army before the Battle of Naseby is considered a significant contributor to the Royalist defeat at that battle.
- Sir Thomas Fairfax the Parliamentary commander at the Battle of Seacroft Moor was prominent in the English Civil War in the North of England under the command of his father Ferdinando Lord Fairfax. Sir Thomas Fairfax’s part in the Parliamentary conduct of the Battle of Marston Moor on 2nd July 1644 was decisive. When the New Model Army was formed at the end of 1644 Parliament gave Sir Thomas Fairfax the command.
- Leeds parish register records the burial on 1 April 1643 of “Captaine Boswell, slayne at Seacroft battell”.
References for the Battle of Seacroft Moor:
The Battle of Seacroft Moor 1643 from ‘The Barwicker No. 85’
The King’s War by C.V. Wedgwood
The English Civil War by Peter Young and Richard Holmes
History of the Great Rebellion by Clarendon
Cromwell’s Army by CH Firth
British Battles by Grant Volume I
The previous battle in the English Civil War is the Battle of Edgehill
The next battle in the English Civil War is the Battle of Stratton
To the English Civil War index