The surprise night attack on 20th/21st September 1777 by the British on the camp of General ‘Mad Anthony’ Wayne’s Pennsylvanians: also known as the ‘Paoli Massacre’
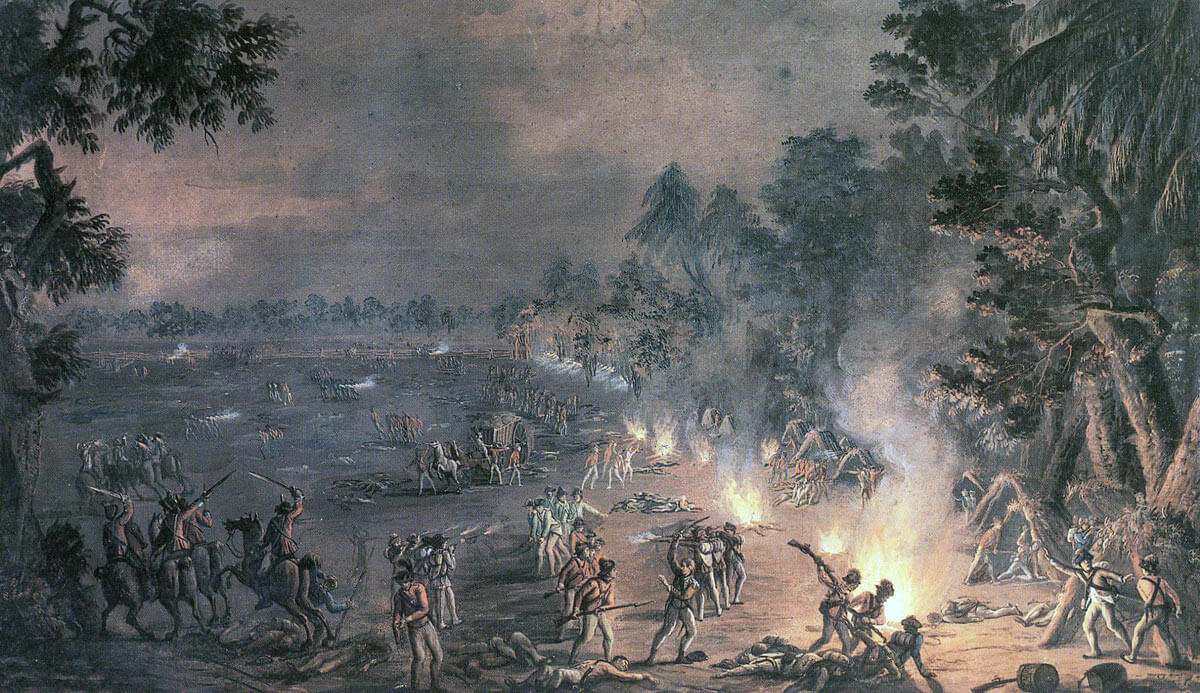
British Light Infantry and Light Dragoons attacking the Pennsylvania camp: Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary War: picture by Xavier della Gatta in 1782
The previous battle of the American Revolutionary War is the Battle of Freeman’s Farm
The next battle of the American Revolutionary War is the Battle of Germantown
To the American Revolutionary War index

General ‘Mad Anthony’ Wayne, American commander at the Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary War: picture by Alonzo Chapell
War: American Revolutionary War
Date of the Battle of Paoli: 20th/21st September 1777
Place of the Battle of Paoli: Pennsylvania in the United States of American
Combatants at the Battle of Paoli: Americans and the British
Generals at the Battle of Paoli: Major-General Anthony Wayne commanded the Americans. Major-General Charles Grey commanded the British troops.
Size of the forces at the Battle of Paoli:
The American force comprised around 1,500 men of Wayne’s Pennsylvania Continental Division and some 1,000 men of Smallwood’s Maryland Militia.
General Grey’s British brigade comprised some 1,200 men, with an additional 500-600 troops (the 40th and 55th Regiments) in support 2 miles away, not engaged in the battle.

Major-General Charles ‘No Flints’ Grey commanding the British troops at the Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary: picture by Joseph Collyer the younger
Uniforms, arms and equipment at the Battle of Paoli:
The British wore red coats, with bearskin caps for the grenadiers, tricorne hats for the battalion companies and caps for the light infantry. The Highland Scots troops wore the kilt and feather bonnet.
The two regiments of light dragoons serving in America, the 16th and 17th, wore red coats and crested leather helmets.
The Americans dressed as best they could. Increasingly, as the war progressed, infantry regiments of the Continental Army took to wearing uniform coats, blue for most regiments. The American militia continued in rough clothing.
Both sides were armed with muskets. The British and German infantry carried bayonets, which were in short supply among the American troops. The Highland Scots troops carried broadswords. Many men in the Pennsylvania and Virginian regiments carried rifled weapons, as did other backwoodsmen. Both sides were supported by artillery.

British 16th Light Dragoons: Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary War
Winner of the Battle of Paoli: This was a decisive British success.
British Regiments at the Battle of Paoli:
16th Light Dragoons,
2nd Light Infantry Battalion (made up of the light companies from 13 regiments)
40th Foot, 42nd Foot (the Black Watch (the Royal Highland Regiment), 44th Foot and 55th Foot
American Regiments at the Battle of Paoli:
Wayne’s Pennsylvania Division: 1st Pennsylvania Regiment, 2nd Pennsylvania Regiment, 4th Pennsylvania Regiment, 5th Pennsylvania Regiment, 7th Pennsylvania Regiment, 8th Pennsylvania Regiment, 10th Pennsylvania Regiment, 11th Pennsylvania Regiment, Hartley’s Additional Continental Regiment, Company of Artillery, Dragoons from various regiments and Smallwood’s Maryland Militia

British Light Infantryman wearing the dyed red feathers: Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary War
Background to the Battle of Paoli:
Following the Battle of Brandywine Creek on 11th September 1777, General Washington’s army fell back towards Philadelphia. Lieutenant-General Howe remained on the Brandywine battlefield for five days. Howe is blamed for this dilatoriness and his failure to pursue Washington vigorously after he had driven him from his defensive position on the Brandywine Creek. It is said in Howe’s defence that he had to make arrangements for the wounded and bring up supplies, with limited transport available. Howe always moved with care and deliberation. Finally, the British advanced through Chester County towards the Schuylkill River, behind which lay Philadelphia, the largest city in the American colonies.
Washington crossed to the east bank of the Schuylkill River. leaving two forces to harass the rear of the British army, Smallwood’s Maryland Militia and Major General Anthony Wayne’s Division of Pennsylvania Continentals.

Light Company Officer of a Highland Regiment: Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary War
Howe’s army encamped at Tredyffrin, an area short of Swede’s Ford on the Schuylkill River. Wayne’s division moved close to the rear of the British and encamped at the road junction by the Admiral Warren Tavern, part way between the White Horse Tavern and the General Paoli, a tavern named after a Corsican bandit. Wayne’s orders to his men were to wait until the British moved forward to the Schuylkill and attack their baggage train.
There was a strong loyalist presence in Pennsylvania, which gave the British good intelligence during the campaign. In addition, 18th Century warfare was, in many respects, a casual business and it is possible that soldiers from both sides frequented the taverns, particularly the Paoli which lay part way between the camps. Howe was fully aware of Wayne’s presence and had precise knowledge of the strength of his force.
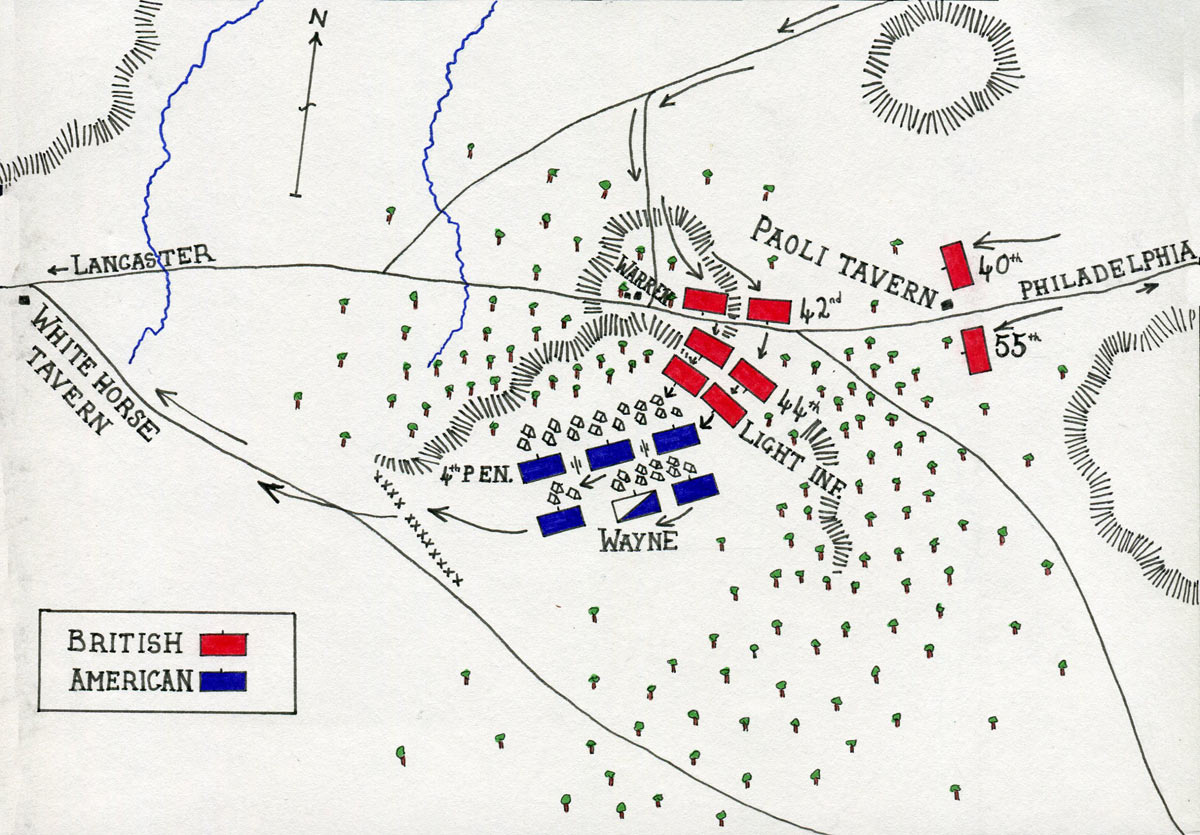
Map of the Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary War: map by John Fawkes
Account of the Battle of Paoli:
On the night of 20th September 1777, General Howe dispatched Major-General Grey to attack Wayne’s division. Grey left with his force at 10pm, and marched down the Moores Hall Road to the Admiral Warren cross-roads. As the leading British light infantry approached the junction, shots were fired by an American piquet. It is said that these shots alerted the Pennsylvanian camp, which lay behind woods to the South of the junction.
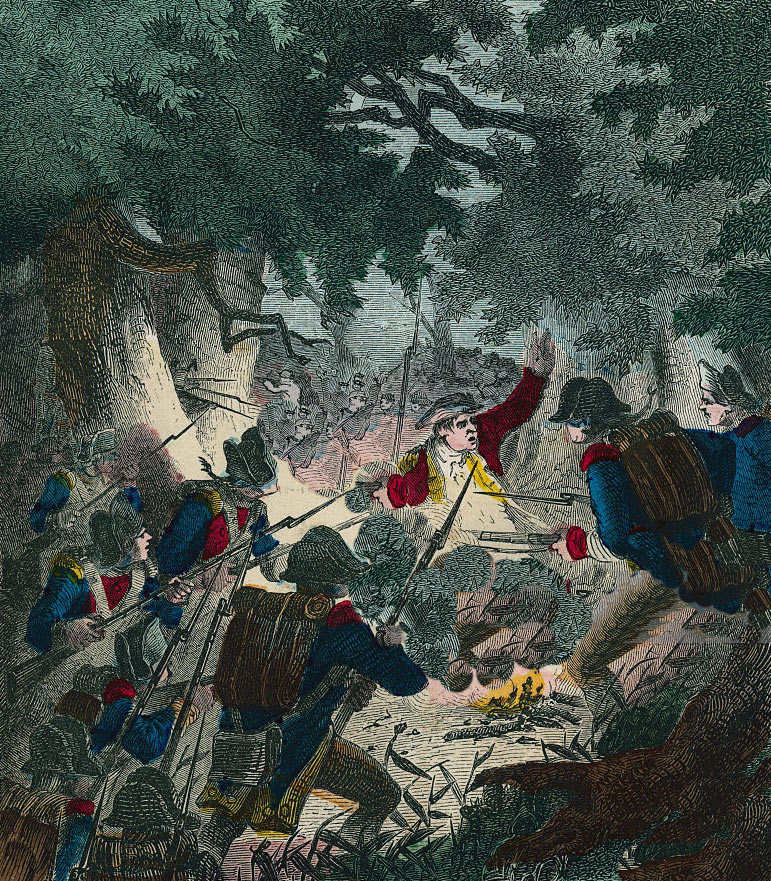

British Light Infantry attack the Pennsylvanian’s camp at the Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary War (the colourist has transposed the uniform colour so that the British troops appear in blue)
The British forced the blacksmith whose smithy lay by the Admiral Warren to act as guide. The first wave of British troops, comprising of the 2nd Light Infantry, a battalion formed from the light companies of thirteen battalions, rushed through the woods and attacked the American camp. The Light Infantry were followed by the 44th Foot and, in a third wave, by the 42nd Highlanders. A small group of 16th Light Dragoons accompanied the Light Infantry.

British Light Infantry attack the Pennsylvanian’s camp at the Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary War
At General Grey’s direction, the flints had been removed from the British soldiers’ muskets before they set out from camp, to ensure that no shots gave warning to the Americans.
In the face of the British charge, the Pennsylvania troops were dispersed and driven out of the camp to the West, many through a gap in a fence along the edge of the encampment. Groups of British soldiers mixed with the Americans and confused fighting continued as far as the White Horse Tavern.
General Smallwood’s Militia approached from the West, as the fight between the British and Pennsylvanians was coming to an end. Smallwood’s men came under attack as they passed the White Horse Tavern. The inexperienced and badly organised Maryland Militia dissolved in confusion.
Casualties at the Battle of Paoli: The American casualties seem to have been around 200 killed, wounded and prisoners, of whom around 55 were killed. It is said that many Americans deserted in the confusion. The British are reported to have had fewer than 20 casualties.
Follow-up to the Battle of Paoli: Paoli was a severe humiliation for the Pennsylvania Continental troops, but probably little more. The fight is referred to as the Paoli Massacre. It is difficult to see how that label can be justified, in the light of the small number of American fatalities. Claims are made that the British took no prisoners. This allegation appears frequently in the Revolutionary War and is made against both sides.
Wayne was heavily criticised for allowing his camp to be surprised. At Wayne’s demand, he was subject to a court martial, which exonerated him. Whether Wayne was taken unawares or not, the attack was well executed and highly successful, enabling General Howe to take Philadelphia within a few days, with little further resistance from the main American army under George Washington.

British Light Infantry Officer with his hat feathers dyed red: Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary War
Regimental anecdotes and traditions from the Battle of Paoli:
- Major General Charles Grey acquired the nickname of ‘No Flints’ Grey, as a result of his order that the British troops at the Battle of Paoli were to remove the flints from their muskets and rely solely on the bayonet, to avoid the Americans being warned of the attack by an ill-considered musket shot. Grey repeated this technique at the Battle of Tappan, known as the ‘Baylor’s massacre’ on 27th September 1778. Grey was promoted to lieutenant general and was due to take command of the British forces in America, but the Revolutionary War ended. Grey became the 1st Earl Grey. ‘Earl Grey Tea’ is named after his son, the 2nd Earl Grey.
- It is said that the British learnt from ‘Tory’ local farmers the American sign and countersign for the night, “here we are” and” there they go.” The British troops used this information to close on the American sentries and attack them with the bayonet.
- Following the battle, the Americans vowed to take vengeance on the British Light Infantry. The light companies are said to have dyed their hat feathers red, as a gesture of defiance, so that the Americans could identify them. Two British regiments continued to wear a small piece of red cloth behind the cap badge as a reminder of this gesture of defiance (the Royal Berkshire Regiment, of which the 49th became the 1st Battalion, and the Duke of Cornwall’s Light Infantry, of which the 46th Regiment became the 2nd Battalion).
- The Paoli Tavern was named for Pasquale Paoli, leader of resistance on the Mediterranean Island of Corsica against the French from 1768 to the end of the 18th Century. Paoli lived much of his life in exile in Britain, where he was considered a hero in the fight against the French.
- The Pennsylvanian encampment was nearer to the Admiral Warren Tavern than the Paoli Tavern. The Admiral Warren was named for Admiral Sir Peter Warren, the commander of the Royal Navy squadron at the capture of Louisburg in 1745, during King George’s War. In a deft piece of re-packaging, at the end of the Revolutionary War the loyalist publican was evicted and the tavern re-named the General Warren, for the American officer killed at the Battle of Bunker Hill. It still carries that name.

Sergeant of Grenadier Company in a Highland Regiment: Battle of Paoli on 20th/21st September 1777 in the American Revolutionary War: statuette by Pilkington Jackson
References for the Battle of Brandywine Creek:
Battle of Paoli by Thomas J. McGuire
History of the British Army by Sir John Fortescue
The War of the Revolution by Christopher Ward
The American Revolution by Brendan Morrissey
The Philadelphia Campaign Volume I Brandywine and the Fall of Philadelphia by Thomas J. McGuire
The previous battle of the American Revolutionary War is the Battle of Freeman’s Farm
The next battle of the American Revolutionary War is the Battle of Germantown
To the American Revolutionary War index



