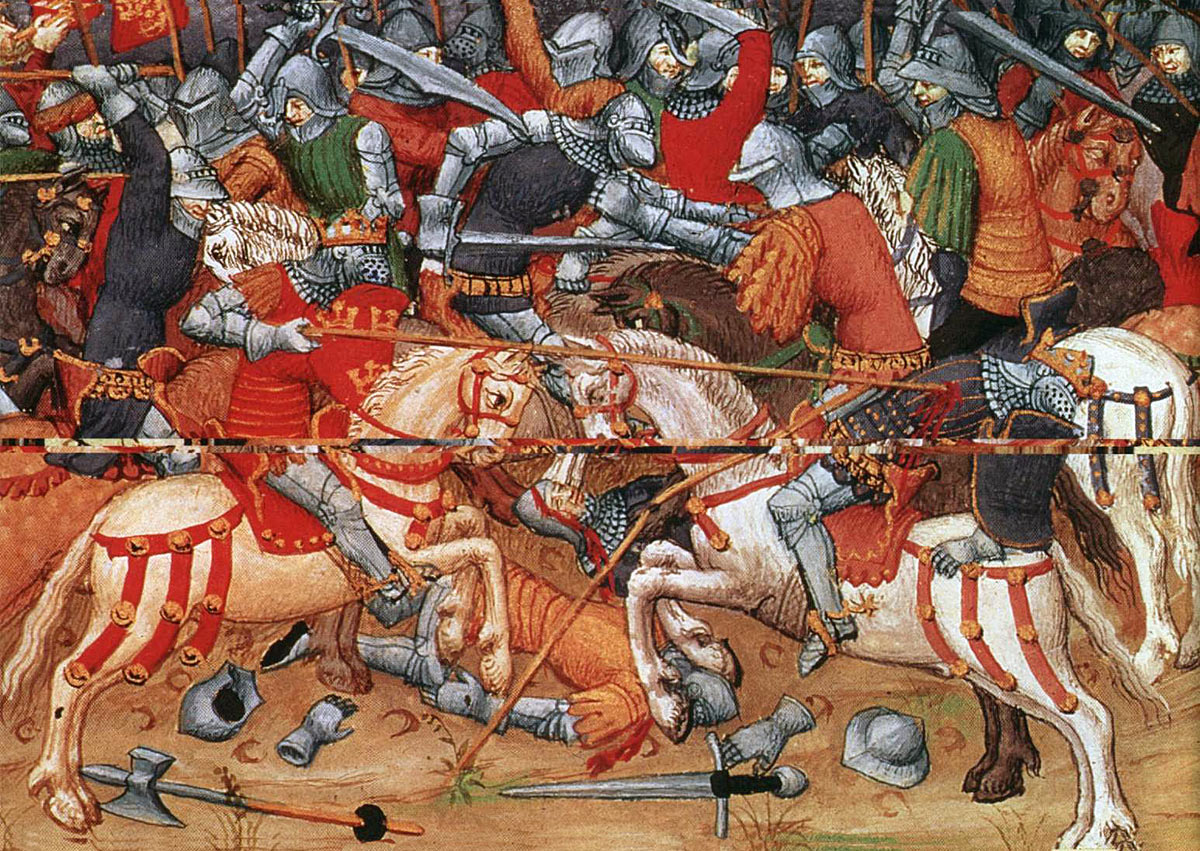
Edward IV’s crushing defeat of the Lancastrians on 29th March 1461, leading to his coronation as King of England
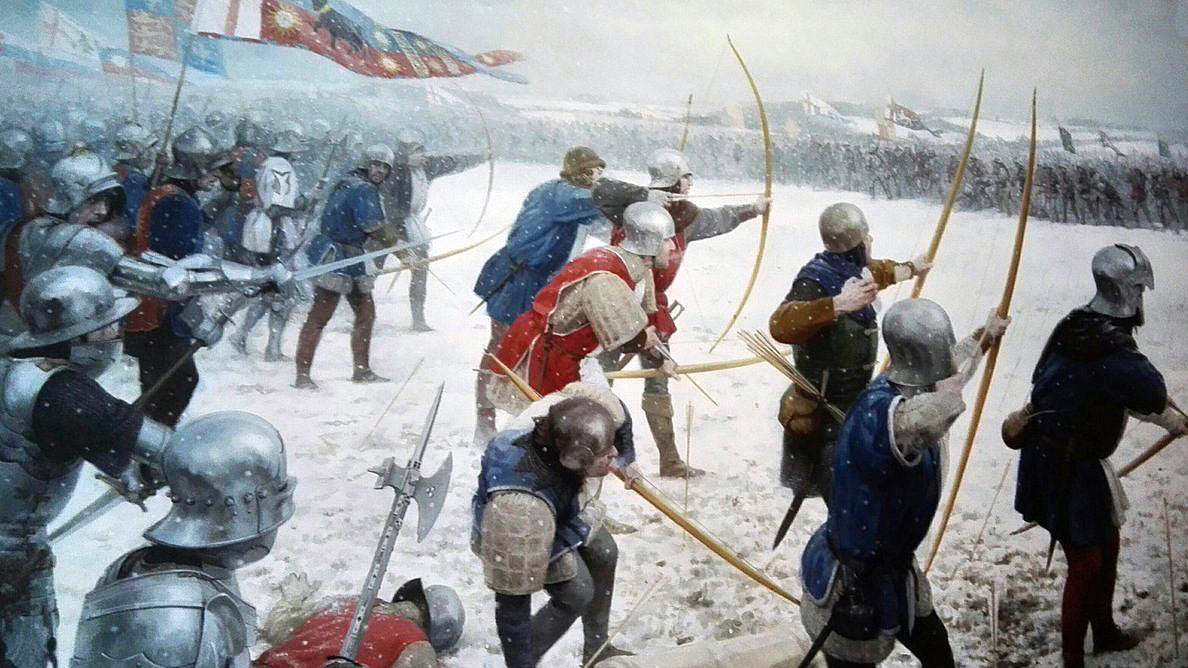

Fauconberg’s Archers loosing arrows on the Lancastrian line at the Battle of Towton fought on 29th March 1461 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Graham Turner
The previous battle in the British Battles series is the Second Battle of St Albans
The next battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Barnet
Battle: Towton
War: Wars of the Roses
Date of the Battle of Towton: 29th March 1461
Place of the Battle of Towton: To the south of Tadcaster in Yorkshire
Combatants at the Battle of Towton: Lancastrians against the Yorkists

Edward, Earl of March and Duke of York, later King Edward IV: Battle of Towton fought on 29th March 1461 in the Wars of the Roses
Commanders at the Battle of Towton: The Duke of Somerset commanded the Lancastrian army, with the Earl of Northumberland, Sir Andrew Trollope and Lord Dacre as his immediate subordinates.
Edward, Earl of March, son of the executed Richard, Duke of York and soon to be crowned King Edward IV, commanded the Yorkist army, with the Earl of Warwick, Lord Fauconberg and the Duke of Norfolk as his immediate subordinates.
Size of the armies at the Battle of Towton: The Lancastrian army probably comprised some 40,000 men, the Yorkist army some 35,000 men.
Winner of the Battle of Towton: The Yorkists, decisively.
Uniforms, arms and equipment at the Battle of Towton: The male commanders and their noble supporters and knights rode to battle on horseback, in armour, with sword, lance and shield.
Their immediate entourage comprised mounted men-at-arms, in armour and armed with sword, lance and shield, although often fighting on foot.
Both armies relied upon strong forces of longbowmen.
Handheld Firearms were beginning to appear on the battlefield but were still unreliable and dangerous to discharge.
Artillery, although widely used in warfare, was heavy, cumbersome and difficult to move and fire.
There is no indication that artillery was used at the Battle of Towton.
The end of the Hundred Years War caused numbers of English and Welsh men-at-arms and archers to return to their home countries from France. The wealthier English and Welsh nobles were able to recruit companies of disciplined armed retainers from these veterans, forming the backbone of their field armies.
Background to the Battle of Towton: Following the Battle of Wakefield, on 30th December 1460, King Henry VI refused to permit his Lancastrian army to enter London, fearing that its many freebooting reiver soldiers from the Scottish border country would loot the city.
The Yorkists, enjoying the support of much of the population of London, established themselves in the capital and Edward, Earl of March, was declared by Parliament the rightful King of England, in place of Henry VI, whom Parliament declared to be a usurper.
Henry VI, Margaret of Anjou and the Prince of Wales retreated with the Lancastrian army north to Yorkshire.
While Henry, Margaret and the Prince of Wales remained in York, the Lancastrian army assembled at Tadcaster, intending to defend the line of the River Aire.
At Tadcaster, Lancastrian noblemen, knights and soldiers joined the army’s ranks from across the north.
Edward, Earl of March, now proclaimed King Edward IV, with the Earl of Warwick, smarting from his defeat at the Second Battle of St Albans, advanced north in pursuit of the Lancastrian army.
———————————-
Account of the Battle of Towton:
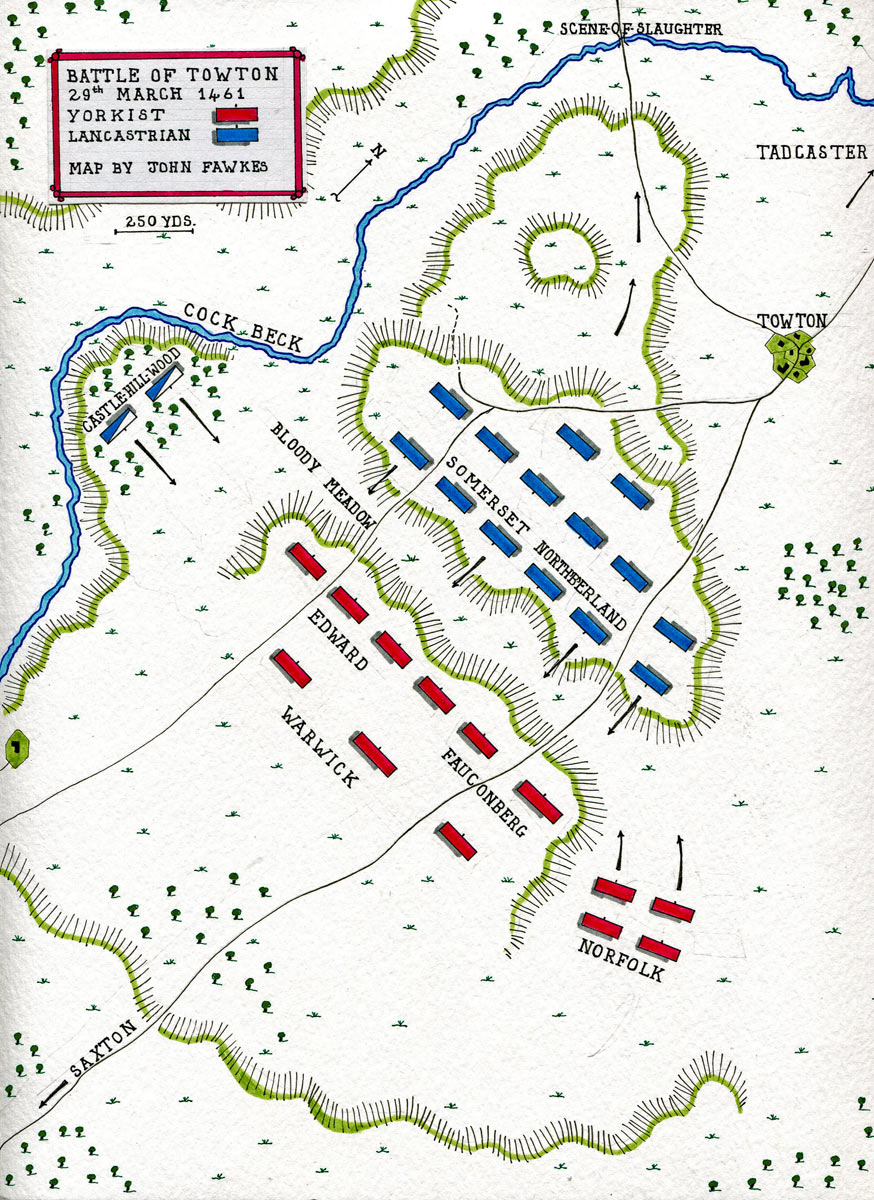
The Duke of Somerset, the Lancastrian commander, brought his substantial army south-west from Tadcaster to confront the Yorkist army of Edward, Earl of March. The Lancastrians took up a position to the south of the town of Towton.
Lord March’s Yorkist army encamped at Pontefract and sent forward a detachment, commanded by Lord Fitzwalter, to seize the crossing over the River Aire at Ferrybridge.
Fitzwalter found the bridge demolished and set about restoring it, to provide a crossing point for the Yorkist army.
On 27th March 1461, Fitzwalter’s men completed the restoration of the bridge and spent the night in the town.
On Saturday 28th March 1461, the Lancastrian commander, Lord Clifford, with a force of mounted men, surprised Fitzwalter, killing him and driving his men off, before again demolishing the wooden bridge.
Legend, almost certainly apocryphal, has the Earl of Warwick with Fitzwalter and riding back to Pontefract after Clifford’s ambush. Warwick is there reputed to have killed his horse and uttered the oath ‘Let him fly who will, I will tarry with him that will tarry with me’.
On hearing of the fate of Fitzwalter’s men, Lord March dispatched the redoubtable Lord Fauconberg to deal with the Lancastrian raiders.
Fauconberg, with a powerful force of horsemen, crossed the River Aire four miles upstream from Ferrybridge at Castleford and, pursuing Clifford, caught his party and inflicted significant casualties, including the deaths of Lord Clifford and the Kentish Captain, Robert Horne.
In the meantime, the main Lancastrian army was taking up position on a shallow ridge south of the village of Towton, on the road from Tadcaster.
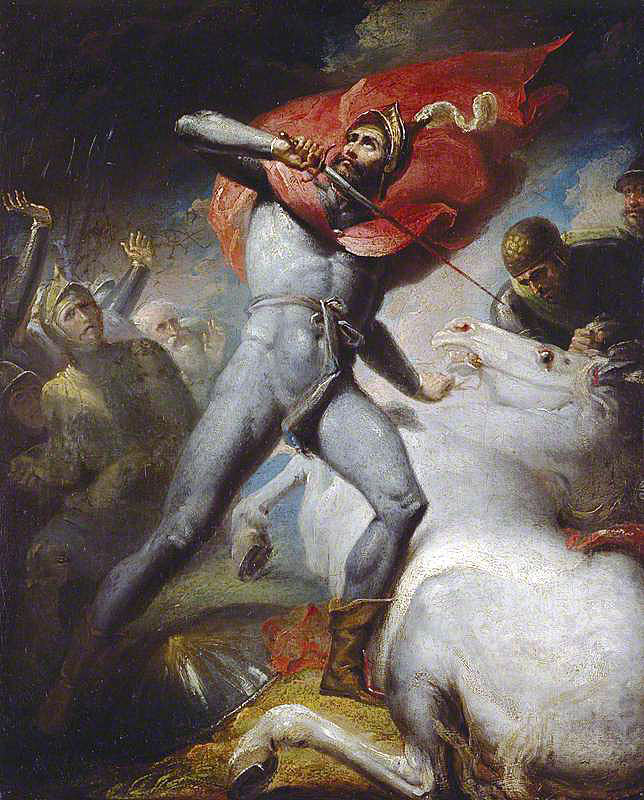

Allegorical picture of the Earl of Warwick slaying his horse before the Battle of Towton fought on 29th March 1461 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Henry Tresham
Flanked to the west by the Cock Beck, the short ridge did not give the Lancastrian army much room to deploy.
On its right lay Castle Hill Wood, where a force of Lancastrian mounted men was concealed in ambush.
In front of the Lancastrian line lay an open area, which came to be known as the ‘Bloody Field’, for the number of dead left there after the battle.
On 28th March 1461, the Yorkist army reached the village of Saxton, a mile or so south of the Lancastrian position.
Edward, Earl of March, resolved to wait until the next day, before advancing to the attack, to give the stragglers of his army time to come up and, in particular, to allow the Duke of Norfolk’s powerful contingent to reach the main army.
During the Yorkist advance, Norfolk was consistently a day’s march in the rear.
Palm Sunday, 29th March 1461, dawned cold and cloudy, with the wind blowing from the south.
As the Yorkists marched onto the field, it began to snow.
The Yorkist army advanced in three lines, the first led by Lord Fauconberg, the second by the Earl of March and the third by Sir John Wenlock and Sir John Dynham.
Before the battle began, the cavalry dismounted to fight on foot.
Lord Fauconberg, leading the Yorkist van, began the battle. At Fauconberg’s command, his archers advanced and discharged a single shower of arrows, before withdrawing out of range.
The Lancastrians, with the snow blowing full in their faces, were slow to respond.
Unable to see their enemy properly, the Lancastrian archers began a return barrage of arrows, all falling some ‘40 taylor’s yards’ short of the Yorkist line. The Lancastrians continued firing until much of their arrow supply was used.
Fauconberg’s Yorkist archers moved forward again and resumed their discharge, using the Lancastrian arrows as well as their own.

Allegory of the Horrors of Civil War: ‘Son kills father, father kills son’: Battle of Towton fought on 29th March 1461 in the Wars of the Roses
Many of the Lancastrian arrows remained embedded in the ground, to cause significant obstruction in the ensuing battle.
The Lancastrian army was the first to advance, descending the incline in front of its position and advancing towards the Yorkists.
The two sides clashed and a terrible struggle began.
Fighting in the snowy fields, the armies dissolved into struggling mobs, hacking at each other, as the corpses piled up in the snow.
The hard-fought battle lasted ten hours, from around 10am to 8pm, with neither side giving quarter.

Earl of Warwick and Edward, Earl of March, at the Battle of Towton fought on 29th March 1461 in the Wars of the Roses
The Lancastrian ambush party charged into the Yorkist left wing from Castle Hill Wood.
The pressure built on the Yorkist troops, with their fewer numbers and they were inexorably driven back.
The Earl of March moved from one part of the line to another, encouraging his soldiers and looking anxiously for the Duke of Norfolk and his much-needed Yorkist re-inforcements.
Towards dusk, the Duke of Norfolk’s men finally began to arrive on the battlefield, attacking around the Yorkist right wing into the Lancastrian flank.
Norfolk’s men were sufficient to turn the tide against the Lancastrians and they began to fall back.
The Lancastrians rallied several times, renewing the slaughter, but finally their troops began to break.
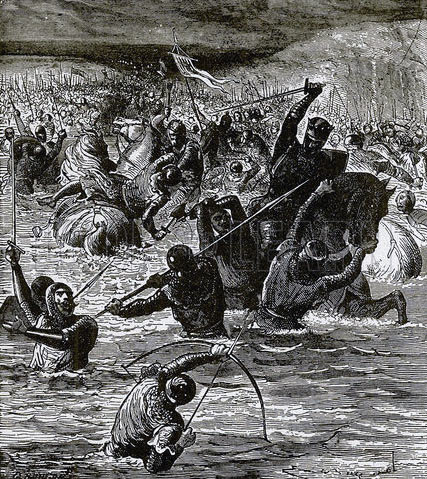
The Lancastrians made off towards Tadcaster, but were so closely pursued by the Yorkists, that many of them broke off to the west and tried to escape across the Cock Beck.
It is said that the Cock Beck was choked with dead Lancastrian soldiers, their blood flowing down into the River Wharfe.
The Lancastrian army, completely broken, was scattered across the county.
Casualties at the Battle of Towton:
Contemporary accounts of the Battle of Towton put the total casualties at between 20,000 and 40,000 dead of both sides.
Possibly 20,000 Lancastrians and 8,000 Yorkists died in the battle or the pursuit.
Towton is given as having the greatest number of dead of any battle fought in Great Britain.
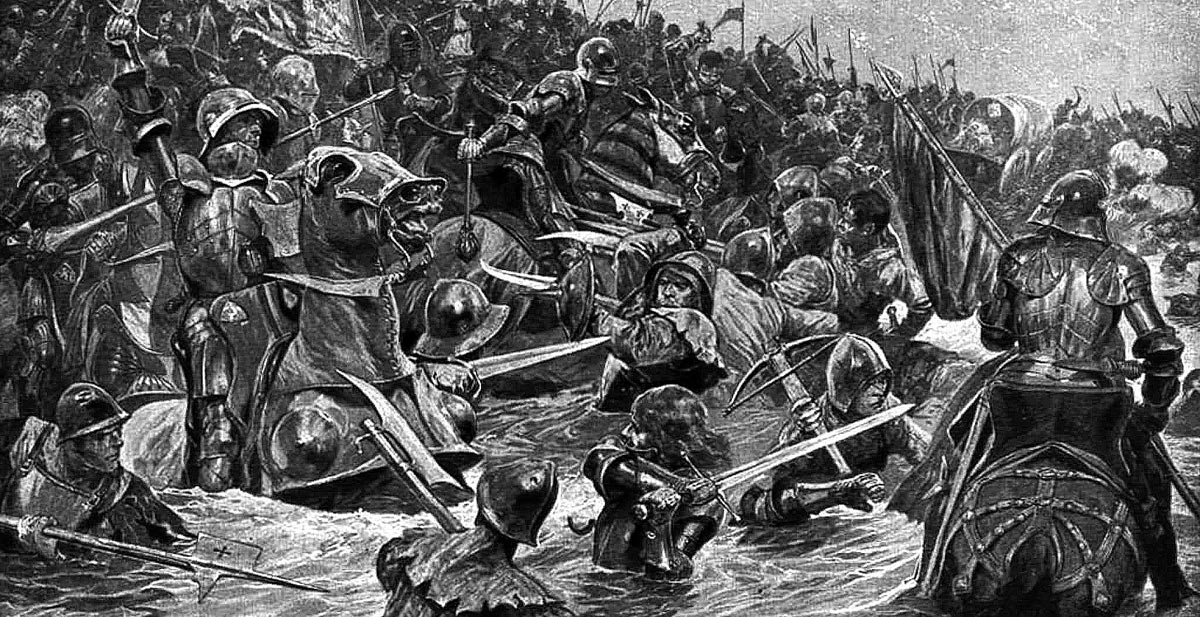

The struggle in the Cock Beck at the Battle of Towton fought on 29th March 1461 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Richard Caton Woodville
Among the Lancastrian nobility, the Earl of Northumberland died of his wounds; Lords Dacre, Westmoreland, Clifford, Neville, de Maulay and Welles were killed. Of the Lancastrian knighthood, Sir Andrew Trollope, Sir Henry Stafford, Sir John Heyton and Sir Richard Percy were killed, among many others.
The Lancastrian Earls of Devon and Wiltshire were taken. Both were executed and Devon’s head used to replace that of the Earl of March’s father, the Duke of York, on the Micklegate in York.
Of the senior Yorkists, Lord Fitzwalter, Sir Richard Jenney and Robert Horne were killed. Lord Scrope of Bolton was severely wounded.
Follow-up to the Battle of Towton: Queen Margaret and the Prince of Wales fled from York with a small party, riding to the border to seek sanctuary in Scotland.
The Earl of Warwick remained in the north of England, in case the Scots should take advantage of the slaughter of England’s fighting strength at the Battle of Towton.
Edward, Earl of March, travelled to London for his coronation as King Edward IV of England.
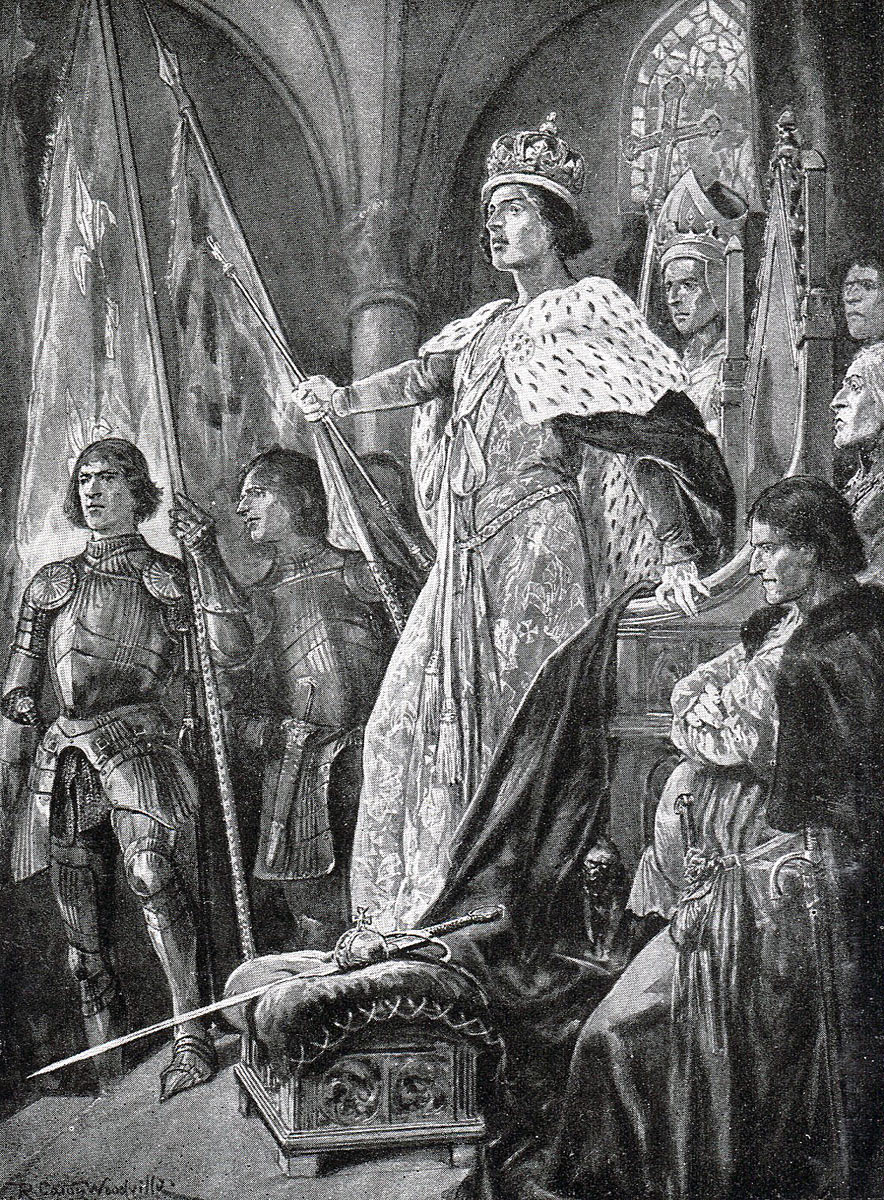

Coronation of King Edward IV on 29th June 1461 after the Battle of Towton fought on 29th March 1461 in the Wars of the Roses: picture by Richard Caton Woodville
Emblems of the Battle of Towton: The Earl of March’s housings in the battle were of crimson velvet, powdered with suns and white roses. On his helmet was the Lion of England.

Alabaster effigy of Sir Dafydd ap Mathew in Llandaff Cathedral; the knight who saved the life of King Edward IV at the Battle of Towton fought on 29th March 1461 in the Wars of the Roses
Anecdotes and traditions from the Battle of Towton:
- Before the Battle of Towton, Edward, Earl of March, soon to be crowned King Edward IV, announced to his soldiers ‘that whoever had a mind to depart, might freely do so before the battle; but once it was begun, whoever fled shall die’.
- The usual Yorkist (and Lancastrian) practice of sparing the common soldiers and putting captured nobles to death was put in abeyance for the Battle of Towton. All captives were put to the sword.
- Spelman records that English archers used two forms of arrow in battle; the ‘sheaf’ arrow and the ‘flight’. The sheaf arrow was shorter and thicker, to be used at close range. The flight arrow was longer and thinner and fired with a high trajectory, for ranges up to 250 yards. Fauconberg’s initial discharge was of flight arrows, fired at a high trajectory. With their vision obscured by the driving snow, the Lancastrian archers responded with sheaf arrows, which fell short.
- The life of Edward IV is said to have been saved during the Battle of Towton by the Welsh knight, Sir Dafydd ap Mathew. Mathew was appointed Standard Bearer of England and permitted to have ‘Towton’ on the Mathew family crest.
- The Lancastrian, Lord Dacre, is said to have been shot with an arrow loosed by an archer hidden behind a ‘bur’ or elder tree. Dacre was buried in the grave yard of Saxton Church, with his horse.
References for the Battle of Towton:
Battles in Britain by William Seymour
Battlefield Walks in Yorkshire by David Clark
Wars of the Roses by Michael Hicks
Chronicles of the Wars of the Roses
British Battles by Grant
The previous battle in the British Battles series is the Second Battle of St Albans
The next battle in the Wars of the Roses is the Battle of Barnet